The Ecosystem - washburnsciencelies
advertisement

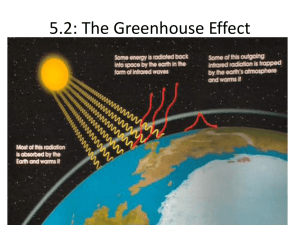
THE ISSUE OF GLOBAL WARMING 6.1 The greenhouse effect Assessment Statements 6.1.1 Describe the role of greenhouse gases in maintaining the mean global temperature. 6.1.2 Describe how human activities add to greenhouse gases. 6.1.3 Discuss qualitatively the potential effects of increased mean global temperature. 6.1.4 Discuss feedback mechanisms that would be associated with an increase in mean global temperature. Assessment Statements 6.1.5 Describe and evaluate pollution management strategies to address the issue of global warming. 6.1.6 Outline the arguments surrounding global warming 6.1.7 Evaluate contrasting human perceptions of the issue of global warming. 6.1.1 Describe the role of greenhouse gases in maintaining the mean global temperature. The chemical reactions that support life-processes work at optimal temperatures of around 15oC. This temperature is maintained by certain greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trapping radiation that heats the surface. Short-wave ultraviolet light from the sun is reflected from the surface as infrared light. Atmospheric gases are transparent to the shorter ultraviolet light, but either trap or reflect back the longer infrared light. This works just like glass in a greenhouse. 6.1.2 Describe how human activities add to greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases consist of water vapor (which makes up 95% of it), carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. Humans add up to 2.7 gigatons of carbon dioxide every year. This is primarily caused by deforestation and the onset of global industrialization and the subsequent production of pollution derived from fossil fuels. There are natural sources for CO2 as well, but scientists assume most comes from humans. 6.1.2 Describe how human activities add to greenhouse gases. Main human activities releasing greenhouse gases are as follows: Burning fossil fuels and releasing carbon dioxide Deforestation creating carbon dioxide Increased cattle ranching leading to increased methane levels Rice farming in padi fields leads to methane release Fertilizers in agricultural systems has led to higher nitrous oxide concentrations. 6.1.3 Discuss qualitatively the potential effects of increased mean global temperature. Increasing mean global temperature will have the following effects: Retreat of polar ice caps and glaciers Increase in sea level causing coastal flooding and relocation Increased flooding Change in biome distribution and species composition Severe water shortages and possibly wars over supply Agriculture may shift towards poles Increased diseases 6.1.3 Discuss qualitatively the potential effects of increased mean global temperature. An increase in storm activity such as more frequent and intense hurricanes (more atmospheric energy) Up to 4 billion people affected by water shortages, including reduced rainfall over the USA, and much of Europe. 200 to 550 million more people going hungry 60 million more Africans exposed to malaria Extinction of up to 40 percent of wildlife 6.1.4 Discuss feedback mechanisms that would be associated with an increase in mean global temperature. Here are some of the positive feedback loops: Albedo – Amount of incoming solar energy reflected back into the atmosphere by the Earth’s surface. As the mean global temperature increases, more ice will melt each year. Less ice will mean less albedo, which will lead to an increase in temperature. Increased carbon dioxide released from biomass decomposition, especially in forest regions leads to further increase in temperature. 6.1.4 Discuss feedback mechanisms that would be associated with an increase in mean global temperature. Rotting vegetation trapped under permafrost releases methane that is unable to escape due to the ice covering it. As the ice melts, it releases the methane, which increases greenhouse gases. Increased forest cover in high latitudes decreases albedo and increases temperature. Warming increases the decomposition of gas hydrates leading to a release of methane and an increase in temperature. 6.1.4 Discuss feedback mechanisms that would be associated with an increase in mean global temperature. Large sea ice slows heat loss from the relatively warm ocean to the cold atmosphere, as sea ice masses melt and no longer moderates the energy balance, warming escalates. Here are some of the negative feedback loops: Increased evaporation in tropical latitudes due to higher levels of precipitation will lead to increased snowfall on the polar ice caps, reducing the mean global temperature. 6.1.4 Discuss feedback mechanisms that would be associated with an increase in mean global temperature. Deforestation leads to increased aerosols and thus reduced solar radiation at the surface causing cooling. Increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere leads to increased plant growth by allowing increased levels of photosynthesis (Carbon dioxide fertilization effect). Increased plant biomass and productivity would reduce atmospheric concentrations of CO2. Increased evaporation increases cooling. 6.1.5 Describe and evaluate pollution management strategies to address the issue of global warming. National and International methods to prevent further increases in mean global temperature: Controlling and reducing the amount of atmospheric pollution Stopping forest clearance and increasing forest cover Developing alternative renewable energy sources Improving public transportation Setting national limits on carbon emissions Developing carbon dioxide capture methods 6.1.5 Describe and evaluate pollution management strategies to address the issue of global warming. Carbon taxes (environmental taxes for burning fossil fuels) Carbon trading (allows companies to trade permits for producing emssions) Carbon offset schemes (Investing in projects that cut emissions elsewhere) One of the most successful international agreements is the Kyoto protocol for reducing carbon dioxide emissions The success of international solutions to climate change depend on the following: 6.1.5 Describe and evaluate pollution management strategies to address the issue of global warming. The extent to which governments wish to sign up to the international agreement Whether governments are preventative (before it gets out of hand) or reactive (respond once it is obvious) Ways individuals can reduce greenhouse gas emissions: Grow your own food or eat locally produced or organic food Reduce your heating – weather-proof your home Use energy-efficient products 6.1.5 Describe and evaluate pollution management strategies to address the issue of global warming. Unplug appliances and turn off lights when not in use Reduce the use of refrigerants and air conditioning Use a manual lawnmower instead of electric or gas Turn off taps and take showers instead of baths Walk, ride a bike, and use public transportation more often Use biofuels Eat lower down the food chain (vegetables rather than meat) Get involved in local political action 6.1.6 Outline the arguments surrounding global warming Non-human factors affecting global climate include: Greenhouse gases produced by natural sources (volcanoes, sunspots, animals and peat moss) Volcanic ash and dust blocking out solar radiation Earth’s tilt and variation in orbit causing regional and seasonal temp changes Reduced albedo due to position and extent of ice sheets Changes in albedo due to cloud cover 6.1.6 Outline the arguments surrounding global warming Ocean currents can lead to warming or cooling Natural fluctuations in atmospheric circulation (El Nino and La Nina) Bush fires can release carbon into the atmosphere In addition, climate change is a complex issue for a number of reasons: It is an issue on a huge scale (all parts of the planet) The interaction between the parts of the planet are many and varied 6.1.6 Outline the arguments surrounding global warming Includes natural and anthropogenic forces Not all the feedback mechanisms are fully understood Many of the processes are long term and the impacts of changes may not have occurred yet It also includes a lot of uncertainty which comes down to two questions: How much is the planet warming? Where will the impacts of global warming be greatest?