Internal Gear/Lobe Pump
advertisement

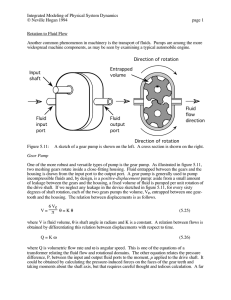
Introduction • Topic: Internal Gear/Lobe Pump • Name: Matthew Stoangi • Objective: To provide a clear understanding of the mechanics involved within an internal gear pump. As well as to acknowledge it’s function as a widely used oil pump design. Internal Gear/Lobe Pump 4 Lobe in 5 Lobe Oil Pump Internal View External View Internal Gear/Lobe Pump: Defined •Uses the meshing of gears to pump fluid by displacement in hydraulic applications. •Gear pumps are fixed displacement devices where a fixed amount of fluid is pumped per single revolution •Gear pumps are designed to operate in both forward and reverse directions •Can function as either a pump or a motor 3. Fluid Fills Void 2. Diverging Gears Create Suction 1. Fluid Enters Through Intake Port & Moves Towards Discharge Port 4.Converging Gears Expel Fluid 5. Fluid Exits Through Discharge Port Gears In Constant Mesh – No Fluid Travel At This Point Image: <http://en.wikipedia.org> Operation Summary • Gears separate on intake side of pump • Suction pulls the fluid from intake port to fill the void • Fluid is carried through the housing by the gears to the discharge port • Fluid is expelled out the discharge port by the mesh of the gears • Tight mechanical tolerances combined with constant rotation create the effective seal necessary to prevent reverse leakage and to promote overall efficiency Advantages Of Design: • Total of two moving parts • Non-pulsating constant and even discharge • Ideal for high-viscosity liquids • Operates well in either direction • Single adjustable gear clearance • Relatively compact and efficient design Disadvantages Of Design: • Requires moderate speeds to be efficient • Pressure limitations • Single bearing accepts entire load • Effective with high viscosity fluids only Applications • Lubrication: – Internal Combustion Engines • Industrial: – Moving/Transferring Fluids • Circulation: – High viscosity fluids Intake Port Discharge Port Photo Taken With Outer Gear Removed To Expose Ports Conclusion In conclusion, upon dissection it has been discovered that the suction forces created by the meshing gears are responsible for the flow of the fluid through the pump. This flow of fluid creates a positive and non-pulsating displacement which makes this pump ideal for use in lubrication applications. References • "Gear Pump." Wikipedia Encyclopedia. Updated: September 7 2005 Accessed: October 3 2005 <http://en.wikipedia.org> • "Internal Gear Pumps." Pump School. Created: 1998 Accessed: October 3 2005 <http://www.pumpschool.com/> • "Centered Internal Gear Pump." Integrated Publishing. Accessed: October 3 2005 <http://www.tpub.com/>