UNIT 5 THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND NAPOLEON (1789
advertisement

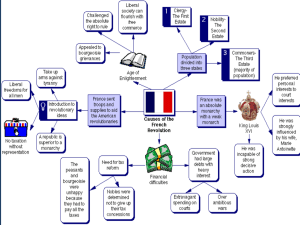
UNIT 5 THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND NAPOLEON (1789-1815) CHAPTER 23 PART 1 – REGENTS NOTES CAUSES OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION • Under the Old Regime in France, the burden of taxation fell mostly on the commoners making it highly unequal • Before the Revolution, the people of France were divided into Three Estates based on social class • Many people felt the monarchy and government were denying basic human rights and failed to meet the needs of the people • The French Revolution challenged the power of the monarch • The bourgeoisie (educated middle class) resented their lack of political power under the Old Regime; hey made up a large part of the Third Estate OLD REGIME EFFECTS OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION • It was a turning point in global history because it inspired other nations to seek democracy and independence • Power shifted to the bourgeoisie, so the middle class gained influence • After Napoleon’s downfall in 1815, nationalistic feelings were stimulated in Europe and Latin America • The Revolution allowed radical political groups like the Jacobins to come to power REIGN OF TERROR • French dictator Robespierre took power after Louis XVI was abdicated (taken out of power) • He ushered in the Reign of Terror • Anyone perceived to be an enemy would be executed by the guillotine • He executed members of every class in France NAPOLEON BONAPARTE • One major effect of his rule was that he restored political stability • The French people supported him because they hoped he would provide stability for the nation • He failed to expand his empire into Russia because of the country’s size and climate (cold, harsh weather) CONGRESS OF VIENNA • In 1815, this organization of European nations wanted to restore old monarchies and regimes to power • The Congress established a balance of power in Europe after the defeat of Napoleon PART 2 – CHAPTER 23 NOTES THE OLD ORDER • Old Regime—social and political system in France during the 1770s • Estates—three social classes of France’s Old Regime • First Estate - Catholic clergy—own 10 percent land, pay few taxes • Second Estate - rich nobles—2 percent population, own 20 percent land • The Third Estate - 97 percent of people are peasants, urban workers, middle class, have few privileges, pay almost all of the taxes, want change FRENCH NUNS (CATHOLIC CHURCH) FRENCH PEASANTS THE FORCES OF CHANGE • Bourgeoisie – middle class group who embraced Enlightenment idea • High taxes and rising costs damage economy by 1780s • King Louis XVI and his wife Marie Antoinette known for extravagance; Louis doubles nation’s debt • He calls Estates-General on May 5, 1789 - meeting of representatives from all three estates to approve a new tax he wanted to impose on the Second Estate • First time Estates-General met in 175 years ESTATES-GENERAL BOURGEOISIE (MIDDLE CLASS) NATIONAL ASSEMBLY • June 17, 1789 • Delegates, who represented the Third Estate, proclaimed the end of absolute monarchy and the beginning of a representative government • Tennis Court Oath—delegates decide to write new constitution for France BASTILLE DAY • July 14, 1789 • Rumors spread in Paris that Louis was going to use military force to suppress the National Assembly • Mob attacks and seizes the Bastille (French prison); they killed guards in an effort to steal gunpowder to defend Paris • Event known as “Storming the Bastille” • Symbolic act of the revolution; national holiday STORMING THE BASTILLE GREAT FEAR • • • • • Rumors and panic spread throughout France Attacks by peasants taking place across France Peasants destroy legal papers binding them to feudal system In October 1789, Parisian women revolt over rising price of bread They demand action, forcing Louis to return from Versailles to Paris DECLARATION OF THE RIGHTS OF MAN • National Assembly adopts Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen • Revolutionary leaders use the slogan, “Liberty, Equality, Fraternity” • The document stated that “men are born and remain free and equal in rights” • Document guaranteed freedom of speech and religion DECLARATION OF THE RIGHTS OF MAN CHANGES IN THE CHURCH • National Assembly seizes church lands and turns clergy into public officials • This caused the new government to lose the support of peasants NEW GOVERNMENT • • • • In September 1791, Assembly finishes new constitution Legislative Assembly—new body created to pass laws Major problems, including debt, food shortages remain Assembly split into Radicals, Moderates, Conservatives JACOBINS • Jacobins - radical political organization behind 1792 governmental changes • Louis XVI is found guilty of treason and beheaded • Guillotine—machine designed during the Revolution to behead people LOUIS XVI IS EXECUTED ROBESPIERRE • Maximilien Robespierre—Jacobin leader rules France for a year in 1793 • Becomes leader of the Committee for Public Safety and a dictator • The Committee for Public Safety imposed his “Reign of Terror” REIGN OF TERROR • Robespierre’s rule, which includes killing many opponents • Thousands die during the Terror, including former allies and Marie Antoinette • 85 percent of those who die during the Terror are middle or lower class but no one was safe from the guillotine • In July 1794, Robespierre arrested, executed by his fellow revolutionaries • Two-house legislature and five-man Directory restore order and lead the new government NAPOLEON BONAPARTE • He was a military genius who seizes power in France and made himself emperor • In 1795, Napoleon defeats royalist rebels attacking National Convention and was declared a military hero • Napoleon wins stunning victories in Italy, gaining popularity • In November 1799, he carries out a coup d’état (seizure of power) and overthrows the Directory NAPOLEON BONAPARTE NAPOLEON RULES FRANCE • In 1800, a new constitution is approved through a plebiscite (vote of the people) • To fix economy, he sets up national banking system, efficient tax collection, and a fairer tax code • Establishes government-run public schools to train officials • Signs concordat—agreement—with pope restoring Catholicism in France • Creates Napoleonic Code—uniform system of laws • Napoleon did not expand freedom of speech for the French • In December 1804, Napoleon crowns himself emperor of France NAPOLEONIC CODE NAPOLEON CREATES AN EMPIRE • Sells the Louisiana Territory to United States for $15 million in 1803 to raise money, cut his losses in America, and to increase America’s power as a British rival • Britain, Russia, Austria, Sweden join forces against Napoleon • Napoleon conquers a large portion of Europe by crushing enemy forces in several brilliant battles • Napoleon forces Austria, Russia, Sweden to sign peace treaties NAPOLEON’S EMPIRE (1810) NAPOLEON’S EMPIRE (1812) THE BATTLE OF TRAFALGAR • In 1805, British win Battle of Trafalgar which ensures British naval superiority • Using a brilliant and bold maneuver, British Admiral Horatio Nelson split up the French fleet into smaller groups and then attacked them • This defeat forces Napoleon to give up his plan to invade Britain NAPOLEON RIDES INTO BATTLE THE CONTINENTAL SYSTEM • Napoleon strikes Britain through blockade (forced closing of ports) • Continental System - economic plan to strengthen Europe, weaken Britain • Smugglers and uncooperative allies make France’s blockade fail • Britain responds with blockade of its own, led by its stronger navy THE PENINSULAR WAR • In 1808, Napoleon sends troops across Spain to attack Portugal in an effort to enforce his Continental System • Napoleon makes his brother king of Spain, making things worse • Spanish fight as guerrillas (small groups that attacked and then fled into hiding) • British aid Spanish guerrillas • Napoleon loses 300,000 soldiers during this war • Nationalist rebels fight the French in other conquered territories THE PENINSULAR WAR THE INVASION OF RUSSIA • Relations with Russia break down so Napoleon decides to invade • In June 1812, Napoleon’s Grand Army marches into Russia with 420,000 men • Czar Alexander I used a scorched-earth policy (destroying crops and livestock) so French would starve • Russians retreat from Moscow after being defeated at Battle of Borodino • Napoleon’s forces move on to Moscow; Alexander burned the city rather than surrender it to the French • Napoleon eventually retreated after losing thousands of soldiers to Russian raiders, starvation, and cold weather NAPOLEON RETREATS FROM MOSCOW, RUSSIA CZAR ALEXANDER I NAPOLEON’S DOWNFALL • Britain, Prussia, Sweden, Russia, Austria join forces against Napoleon • Napoleon raises another army, but meets quick defeat by allied powers • April 1814 - Napoleon finally surrenders and is exiled to island of Elba THE HUNDRED DAYS • Louis XVIII, new king, is soon overthrown and Napoleon returns from exile • Battle of Waterloo - British and Prussian forces led by the Duke of Wellington defeat Napoleon’s army in June 1815 • This defeat ends the Hundred Days which was Napoleon’s last attempt at power • British send Napoleon to the island of St. Helena where he eventually died in 1821 • Freed European countries began to establish a new order BATTLE OF WATERLOO BATTLE OF WATERLOO DUKE OF WELLINGTON NAPOLEON IS EXILED CONGRESS OF VIENNA • Series of meetings that reshape Europe during the winter of 18141815 • Klemens von Metternich - foreign minister of Austria who was an influential leader at Congress • He wanted to restore a balance of power so that no one country would be a threat to others • Main goal = establish security and stability for the nations of Europe • Important effect = nationalistic feelings grew in countries that were placed under foreign rule (ex: Latin American countries) CONGRESS OF VIENNA