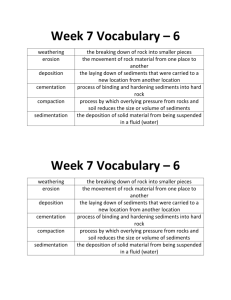
erosion-deposition
advertisement
Erosion and Deposition Erosion- process that moves weathered sediments from one place to another Deposition- the dropping of sediments that have been eroded Erosion and deposition are two parts of the same process. Erosion only occurs when there is enough energy to carry the sediments. Deposition occurs when the energy decreases. There are four main forces that cause erosion and deposition: 1. Gravity 2. Running Water 3. Glaciers 4. Wind Clip I. Gravity “mass movement” A. slump - on steep slopes; material weakens Underneath; ex.- a pile of sediments at the bottom of a hill, with an indentation in the hill B. creep - sediments move s-l-o-w-l-y downhill; caused by repeated freezing and thawing; ex. - a slanted fence C. Rockslides - rocks break loose and tumble to the bottom of the hill; ex.- piles of rocks D. Mudflows - happens in relatively dry areas when a thick layer of sediments mixes with water, becomes heavy and pasty, slides downhill II. Running Water A. Rill/Gully Erosion - “scar” left after water has run downhill; rills are small, gullies larger and more Permanent B. Sheet Erosion - happens in a flat area after it rains C. In Streams - moving water constantly picks up and carries sediments as it moves; deposition at mouth of river Alluvial fan - triangular area of deposition in a river or stream (much like a sandbar) Delta - an alluvial fan that occurs at the mouth of a river or stream III. Glaciers - masses of moving ice and snow A. Valley glaciers - smaller; more common B. Continental glaciers - huge; in polar regions Glacial Erosion - glaciers act like bulldozers; carry away a lot of material and wear down rocks; Striations - scrapes left on rock from a glacier; Rocks stuck in ice abrade rock beneath it *** Glacial valleys are U-shaped, as opposed to V-shaped valleys formed by streams. Glacial Deposition - occurs when ice begins to melt; Sediments deposited Till - glacial deposit made up of a jumble of different Sized rocks Outwash - and and gravel that is released in the meltwater IV. Wind Deflation - small sediment such as sand are picked Up and carried away Abrasion - wind carried sediments act like sandpaper Deposition occurs near supportive backgrounds Loess - thick deposits of fine wind-eroded materials