PowerPoint Presentation - Ductile Deformation Processes
advertisement

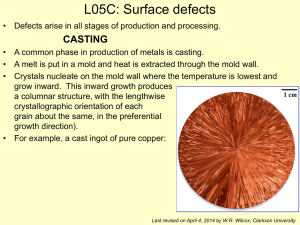
Ductile Deformation Processes Chapter 9 in Van der Pluijm and Marshak How can solid rock flow like taffy? Swiss Alps Ice is a solid phase that flows when conditions are appropriate and there are forces acting on the material. “g” Ductile deformation is permanent Accomplished by these 3 mechanisms: • Cataclastic flow • Diffusional mass transfer • Crystal plasticity Mechanism is determined by: • • • • • • Temperature Stress Strain rate Grain size Composition Fluid content Effect of Composition Plag. Quartz Olivine Pyroxene Calcite Halite Gypsum Slow 1) Cataclastic flow: small pieces sliding past each other Cataclastic flow: Is it brittle or ductile? Ductile on large scale but brittle on small scale 2) Crystal Plasticity: The crystal changes shape by movement of lattice defects Point Defects are vacancies or impurities Dislocations form in 2 ways: • During crystal growth • During deformation By moving the dislocations, the crystal changes shape Migrating defects change the lattice shape. Occurs under stress Line defects in olivine Twinning also changes the crystal shape 3) Diffusional Mass Transfer has three mechanisms: • Grain boundary diffusion • Volume diffusion • Pressure solution High T Low T Grain boundary diffusion Atoms will diffuse along the edges of the grain to create shape changes (strain). Volume diffusion Atoms will diffuse through the center of the grain to create shape changes (strain). Pressure solution: Material is dissolved under stress Dissolved rock goes into veins Deformed Marble Mylonite