Mayan Civilization 1

Mayas
Mesoamerican
Setting
•
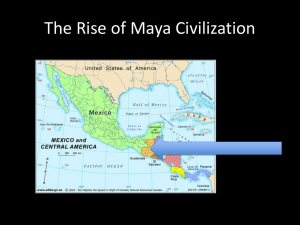
Central Mexico to northern Central
America
•
Maya Homeland
•
Highlands to south
•
Some by active volcanoes – ash made rich fertile soil
•
Cool with wet and dry seasons
•
Lowlands to north
•
Yucatan Peninsula
•
North = flat and hot
•
South = wetter & greener
Mesoamerican
Setting
•
Rainforest Agriculture
•
Lowland rainforest
•
Soil fragile & thing
•
Hot and steamy
•
80 inches of rain/year
•
Slash-and-burn
•
Cut down trees/brush & burn
•
Use for a few years and move on
•
Years later return
•
Need 70 acres for 5 people
Maya Civilization
•
Lost Cities
•
John Stephens – American Explorer
•
Frederick Catherwood – British Artist
Maya Civilization
Pre-Classic Mayas
•
1800 BC to AD 250
•
Developed Skills
Maya Civilization
Classic Mayas
•
AD 250 to 900
•
Cities: Tikal, Palenque, Copan
•
Tikal had about 2700 buildings
•
Had few thousand inhabitants in actual city – most lived on farms within 3-5 miles
Maya Civilization
Post Classic Mayas
•
AD 900 to 1520
•
Ended after Spanish conquered
Mexico
•
Chichen-itza built
•
Between 800 and 900 began to collapse
•
Warfare
•
Food shortage
•
Natural disaster
•
Drought
Quiz
1.
Where was the Mayan civilization located?
1.
What were the three main time periods?
2.
How would they farm in the rainforests?
3.
Where did most of the people live (city)?
4.
Why did the civilization collapse?
Maya Society
Life Among the Mayas
•
Social Structure
•
King/Ruler
•
Considered a god-king
•
Had advisors
•
Nobles, Priests, Warriors
•
Nobles
•
•
•
Read and write
Led armies during war
Collected taxes
•
Supervised construction
•
Priests maintained favor with the gods
•
Led rituals, sacrifices, consulted
Maya Society
Life Among the Mayas
•
Social Structure
•
Merchants, Artisans
•
•
•
•
•
Trade and crafts also a part of economy
Travel by sea, river, roads to other city-states
Painted murals of Mayan life and battles
Sculptures for temples
Weavers and potters
•
Peasants
•
•
Backbone of society
Grew maize, squash, beans and other crops
•
•
•
When not farming, working on temples
Soldiers during war
Women prepared food, wove
•
Slaves
•
•
•
•
•
•
Manual labor for owners
Sometimes parents sold children
War prisoner
Criminals
Sometimes better life than peasants
Sometimes sacrificed when master died
Maya Society
Life Among the Mayas
•
Daily Life
•
Men on farm, hunt, maintained buildings
•
Women raise children, tend to flocks, garden
•
Basic social unit
– extended family
•
Several related families lived together – cluster of simple houses
•
Day of ceremonies – go to city
•
May trade
•
May attend ballgame
Maya Society
Gods and Rulers
•
Maya Rule
•
Each city had own king
•
Usually passed from father to son
•
Worked with nobles and priests
•
Gained prestige by winning wars
•
Had a sphere of influence
•
Area dominated by particular ruler
•
Created alliances
Maya Society
Gods and Rulers
•
Maya religion
•
Most gods represented natural phenomena like rain, lightning
•
Believe king descended from gods
•
Communicate to gods through sacred rituals
•
King carried on sacred rituals like the ballgame
•
Some rituals required spilled blood – kings pierce self to get blood for ritual
•
Human sacrifice – often removing heart
•
•
Prisoners
Slaves
•
Children
•
Festivals
•
Costumes, music, dancing
Quiz #2
1.
What role did nobles play?
2.
Who was the backbone of society?
Why?
3.
How did slaves live better than peasants?
4.
What was the kings job?
5.
How did the people view him?
6.
What is a sphere of influence?
7.
What is the ballgame?
8.
What do you know about how they would sacrifice humans?
9.
What were festivals like?
Maya
Achievements
Writing
•
Based on hieroglyphs
History Carved in Stone
•
Carved in stone
•
Painted on walls, pottery, books
•
Records kept in codex
Astronomy
•
Predict solar and lunar eclipse
Math
•
Understood concept of “0”
Architecture
•
Pyramid with temple at top
•
Move stone with out wheel