6 MSDs - Ergo
advertisement

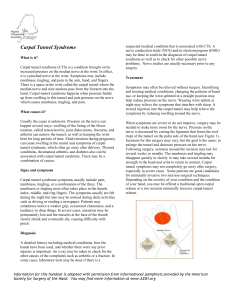
Target the Problem, Not the Symptom Musculoskeletal Disorders Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs) Too Much Wear and Tear and Not Enough Recovery Time Perspectives On MSDs • MSDs are common • Most of us have experience • Home & work • Usually mild & temporary • Can be disabling Every Human Activity Work Home Recreation Upper Extremity Musculoskeletal Disorders • • • • • • • Tendonitis Epicondylitis Rotator cuff syndrome De Quervain’s disease Trigger finger Ulnar nerve compression Carpal tunnel syndrome Ganglion Cyst Ganglion Cyst Upper Extremity Musculoskeletal Disorders Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Development Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Tendon Sheath Inflamed Tendons Irritated Nerves Nerves Nerve •Electric current travels up the nerve •Fat does not conduct electricity •Message moves quickly when the nerve is healthy. •Message is inhibited when nerve is damaged. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Upper Extremity Musculoskeletal Disorders Intersection Syndrome Intersection Syndrome Intersection Syndrome Intersection Syndrome Intersection Syndrome Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Trigger Finger DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) Medial Epicondylitis (Golfers Elbow) Shoulder Rotator Cuff Rotator Cuff Attachment Biceps Tendonitis Biceps Tendonitis Biceps Tendonitis Radial Nerve Rotator Cuff Muscles Plantar Fasciitis Conditions Associated with the Spine Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease Lumbar Vertebrae Spinal Disc Disc Bulge Disc Herniation Pressure on Low Back in Various Postures Pressure on Low Back in Various Postures Reclined Position Reclined sitting posture. The user's torso and neck are straight and recline between 105 and 120 degrees from the thighs. The knees should be slightly below the hips. Sitting Upright Upright sitting posture. The user's torso and neck are approximately vertical and inline, the knees should be equal to or lower than the hips. Low Back Extension Proper Lifting Techniques The Power Lift •Get close to the object and move over the load as much as possible. •Place your feet on each side of the object. •Lift with your legs keeping your back straight, your buttocks out and your head up. •Lift smoothly and breath. Proper Lifting Techniques The Golfers’ Lift •Place one hand down on fixed surface to support upper body. •Keep back straight and raise one leg out behind you as you lean down to pick up the object. •To lift look up, push down on the fixed surface and you lower your leg. •Lift smoothly and breath. Early Intervention • • • • • Ice Packs (20 minutes) Ice Massage (10 minutes) Ibuprofen/Naproxen/Aspirin (follow directions) Recovery time Waiting results in a longer recovery time and possibly surgery. Rest and Recovery • Give your body the time it needs to rest and recover from physical exertion and injury. • Proper nutrition is essential for healing as well