File
advertisement

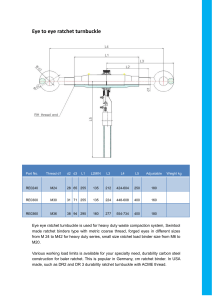
Mechanisms & Devices Question 8 Devices Flow Control Valve – To control the operating speed in a pneumatic circuit. ThermocoupleTo detect changes in temperature electronically. TurbineTo transform the kinetic energy of water into electrical energy. Shock AbsorberTo slow down the action of a suspension spring. TransformerTo change the voltage of AC without changing it’s frequency. The energy conversation that occurs in a car battery: Chemical energy to electrical energy. Ratchet and pawl mechanism A ratchet and pawl is used to allow a shaft, axle or pin to rotate in one direction only. The teeth on the ratchet wheel are so shaped that the pawl slides over them in one direction and engages with them so as to restrict movement in the other direction. A ratchet and pawl can be used in ratchet spanners, fishing reels, ratchet screwdrivers, micrometers and winding machines etc. Idler gear An additional gear that is inserted between two other gears with the purpose of changing the direction of gear rotation. Idler gears do not have an influence on the gear ratio of the system. They allow the input gear and output gear shafts to rotate in the same direction. Heat sink A heat sink is used in electronics to conduct away heat generated by a component. These heat sinks are normally corrugated or finned to dissipate heat to the surrounding air and protect components such as transistors. The benefits of using solar panels Solar panels are used to harness the free energy from the sun and use it to generate electrical energy or to provide hot water and heating for buildings. The advantages of using vee pulley belts over flat belts: Gives a greater area of contact with the pulley wheel. Provides a stronger grip. Reduces slip. Can drive larger forces. Chain and sprocket: A chain is used to transmit motion from one toothed wheel to another. This eliminates slip and is in common use on bicycles and motor cycles. A chain and sprocket gives a strong drive. Toggle mechanism: This linkage is widely used as a clamping mechanism, it is used in a ‘vice grips’ as it holds very firmly and is quick to use. Light dependent resistor (LDR): An electronic sensing component that can be set up to sense the presence or absence of light. The functions of the electronic transistor: Can be used as an electronic switch or an amplifier. Devices Mechanical ClutchTo make and break the drive between two shafts. RectifierTo conver AC to DC (incl. A diagram) Universal JointTo allow motion to be transmitted between two shafts which are not in line. Electrical RelayAllows a small current and voltage to turn on a circuit which operates at a higher voltage and current. Devices Heat PipeTransfers heat from one place to another. Bimetallic Contact Breaker. A bimetallic strip acting as a switch. (different metals expand at different rates when heated) Light Dependant Resistor -LDRResistance changes with light intensity. Flow RegulatorTo control air flow in a pneumatic circuit. Devices SensorDetects changes in the environment (LDR). MotorChanges electrical energy into mechanical energy. ThermistorResistance cahnges with changes in temperature. Bevel GearsTo connect shafts which move at right angles. Solar CellConverts light energy into electrical energy. Devices Differential GearsAllows wheels on the same axel to rotate at different speeds. ThermostatMeasures temperature Strain GaugeTo measure the distance between points on a component. Non-Return ValveAllows air/fuel to flow in one direction only. Intregated Circuit (IC)An electronic circuit containing components produced intregrally in a small piece of semiconducting material. (chip) Devices Heat PumpUsed to extract heat from a body at one temperature and transfer it to a body at a higher temperature. Used in heating systems and air conditioning. FlywheelAbsorbs all the up and down forces of the pistons and by means of a crankshaft smoothens out the forces into a smooth balanced rotary motion.