Westward Expansion
advertisement
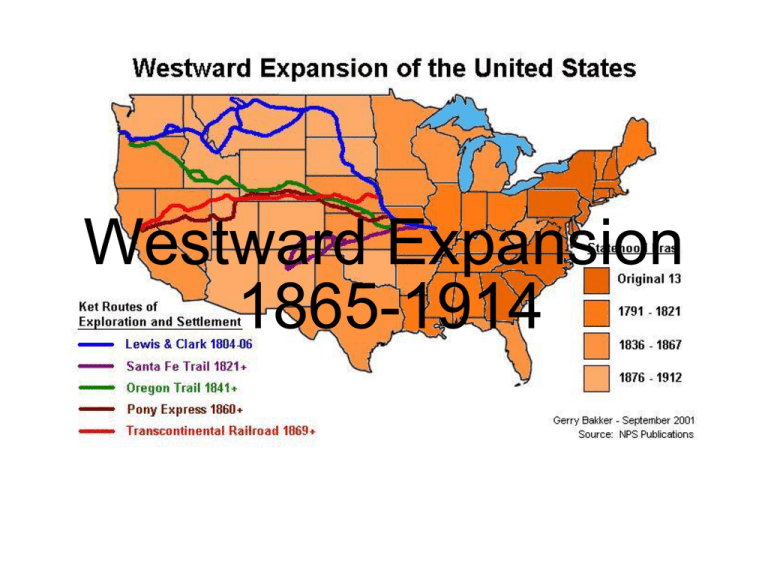
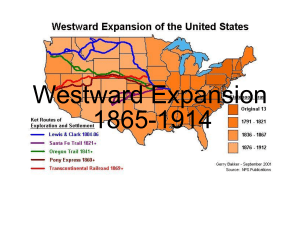
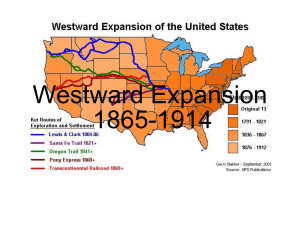
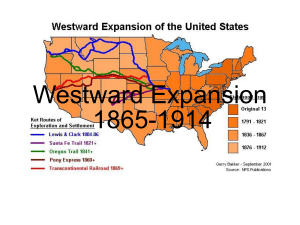
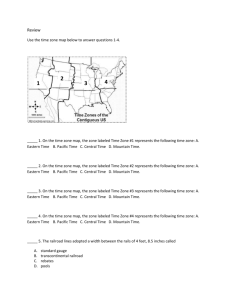
Westward Expansion 1865-1914 U.S. Land Acquired in the 1800s Manifest Destiny • Americans believed they should own all the land from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean; coast to coast. COSTS OF EXPANSION • NEAR EXTINCTION OF BUFFALO. • DAMAGE TO ENVIRONMENT • DISPLACEMENT OF NATIVE AMERICANS • TREATMENT OF IMMIGRANTS THE PLAYERS • • • • • • • • MINERS FARMERS AND SETTLERS EXODUSTERS CATTLEMEN AND COWBOYS RAILROAD WORKERS RAILROAD OWNERS NATIVE AMERICANS POPULISTS MINERS • SERIES OF GOLD STRIKES – COLORADO PIKES PEAK 1859 – NEVADA COMSTOCK LODE 1859 – IDAHO – MONTANA – ARIZONA – SOUTH DAKOTA – CALIFORNIA 1849 Gold Rush-1849 - 1870 • Gold was discovered in California in 1849. • The Comstock Lode, a Bonanza, was later discovered. • People who moved west to mine are called miners. • Immigrants, such as Mexicans, Chinese and the Irish, went to work in the mines. • Immigrants were treated poorly with long hours, low pay and very dangerous work. People moved West to find gold. Boom towns and Ghost towns. Gold or Silver strike 1. Miners arrive and build a small town. 2. More people come to sell supplies. 3. Real houses get built. Boom Town 1. Gold or silver production falls – decreases. 2. Miners move on. 3. The town is abandoned. Ghost Town. One man panning for gold. I hope I find gold and become rich! FOREIGN BORN MINERS. • BY 1860 1/3 WESTERN MINERS WERE CHINESE • HOSTILITY TOWARDS MINERS 1. MINERS TAX 2. CHINESE EXCLUSION ACT 1882 Working on the mine. FARMERS/SETTLERS • • • • • EXODUSTERS SODBUSTERS OR SODDIES DRY FARMING HOMESTEADERS BOOMERS/SOONERS African Americans Moved West. African Americans were called Exodusters. • Many African Americans moved to the West from the 1840s to late 1890s. • They were escaping the difficult life in the South where Whites practiced Jim Crow Laws and denied African Americans their new Constitutional Rights. • The Promised Land • Opportunity to fail or succeed on their own terms Why were African Americans called Exodusters? • African Americans were called Exodusters after the book from the Bible called the Exodus. • This book described how the Jews escaped from slavery in Egypt. • The African Americans were escaping slavery in the South, just as Jews escaped slavery from Egypt. That is why they were called Exodusters. Exodusters moving West. I hope there’s no KKK. I hope there’s no slavery in the West. Maybe we can vote in the West. PUSH FACTORS • PUSH FACTORS – DISPLACED FARMERS, FORMER SLAVES, WORKERS – COST OF EASTERN FARMLAND TOO COSTLY – ETHNIC AND RELIGIOUS REPRESSION – FRESH, NEW START PULL FACTOR • PULL FACTOR – PRIVATE PROPERTY – LEGALLY ENFORCEABLE, TRANSFERABLE PROPERTY RIGHTS – LIMIT SETTLERS’ RISK – LAND REGISTERED, MEASURED,AND DEEDED – BRANDING (CATTLE) – WATER RIGHTS ESTABLISHED PULL FACTOR - GOVERNMENT ENCOURAGEMENT OF SETTLEMENT • PACIFIC RAILWAY ACTS 1862 & 1864 – Large land grants to Railroads – Total lands about 175 million acres • MORRILL LAND-GRANT ACT 1862 – State governments given land to sell to raise money – Sold to bankers and land speculators • HOMESTEAD ACT 1862 – 160 acres, 5 years The Homestead Act of 1862. An application for land. • People staked their claim by finding a section of land that was marked. (160 acres) • Then they registered the piece of land with the government. • After cultivating the land for five years, it was theirs for free. Homesteaders. • People moved West to stake their claim. People traveled West on wagon roads, and on the railroad and by steamship. Plowfarms, plows and families in front of their sodhouses. (soddies and sodbusters) A difficult life for the farmers. • Farmers had to cut through thick, hard earth called sod. • Winters were harsh; cold, windy with a lot of snowstorms called blizzards. • Summers were hot and had little rain. • Farmers had to use a technique called dryfarming (growing crops that needed little water.) • Sometimes grasshoppers would eat all the crops. Farmers in crisis. • Farmers could not repay their debts. • The Populist party tried to help farmers. They wanted government to reduce railroad rates and to help with (falling) decreasing prices for grain. • Populists wanted all the silver mined in the West to be turned into coinage (money). • Free silver would make it easier for farmers to repay their debts. • The United States did not turn silver into money. The Cattle Kingdom. DEMAND SPURS GROWTH • PRIOR TO CIVIL WAR – PORK PREFERRED • SNUBBING OF PORK –UNWHOLESOME • NATIONAL BEEF BINGE!!! • GROWTH OF CATTLE RANCHES Cowboys and Vaqueros. Ranchers and Cowhands drove the cattle to the Transcontinental Railroad. Why did the Cattle Kingdom fail? • • • • • • • MID 1880’S OVER EXPANSION PRICE DECLINES WEATHER – COLD AND HOT CATTLE FEVER BARBWIRE SHEEP Why did the Cattle Kingdom fail? The Transcontinental Railroad finished in 1869. Many Immigrants, such as Irish, Mexicans and Chinese were building the Railroad. The Union Pacific meets the Central Pacific in Utah in 1869. Impact of the Railroads. • Railroads brought growth and new settlement all across the West. • The railroads enabled people, supplies, and mail to move quickly and cheaply and safer across the plains and the mountains. • The largest cities and towns developed where major railroad lines met. • Because of their rapid growth, western territories began to apply for statehood. Nevada, Colorado, North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana and Washington all became states from 1864 – 1890. The Railroad spurs the growth of other industries. • The lumber industry grows, because wood is needed to build the train tracks. • The steel industry grows because steel is needed to build the tracks. • The coal industry grows because coal is needed to fuel the train. • The growth of these industries opens thousands of new jobs for workers. The Great Plains Blue skies and open prairies. Nature on the Great Plains. The location of the Great Plains. States on the Plains. • Homesteaders came to the Plains to farm the land. • Miners searched for gold. • Railroad companies built the train. • Exodusters came to Kansas to start a new life and later became miners and Homesteaders and worked on the railroad. • Immigrants worked on railroads and in mines and became Homesteaders. Native American Land • Native Americans lived here first. • Native Americans and Whites came into bloody conflicts over the land. • They tried to protect their lands, but finally, the United States government forced them onto reservations. Buffalo roamed the Plains. Plains Indians hunt the buffalo. The buffalo is used for tepees, clothes, tools, food and more. The buffalo hide business becomes popular and settlers kill millions of buffalo. BROKEN PROMISES! • The United States government made many treaties with the Native Americans not to fight and not to touch certain areas of their land. • For example, The Fort Laramie Treaty was a treaty made with the Cheyenne tribe, where Americans said an area of land belonged to the Cheyenne forever! • However, when gold was discovered there, the Americans forced them to sign a new treaty giving up the land. • The United States government broke many treaties with the Native Americans. Many Wars. Many Heroes. Many Wars • Sioux War of 1876 Many Heroes • Sitting Bull and Crazy Horse • The Apache Wars • Battle of Little Bighorn Geronimo • Nez Perces Chief Joseph Lakotas & Cheyenne Indians defend their lands, but are defeated in the end. Native Americans are forced onto reservations. The Dawes Act divided Indian land and gave some to the Indians in hopes they would become farmers. But they sold it to Whites for low prices. Deerskin, bird feathers and cloth were also used in Native American culture. Native Americans prayed for a new world without Whites in the Ghost Dance Religion. Painting of the Ghost Dance. Laws today protect Native American Reservations. Native Americans Today • Today, many Native Americans are a part of our society. • However, many still live on reservations and try to maintain their cultures. • New laws returned some Native American lands back to the rightful owners. • How would you feel about your history if you were a Native American? Native Americans today.