Water in the Air Chapter 16 section 1
advertisement

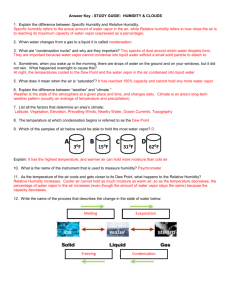
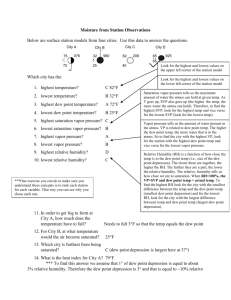
Water in the Air Chapter 16 section 1 S6E3.b. – Relate various atmospheric conditions to stages of the water cycle. Water in the Air I. Water Cycle A. the continuous movement of water from Earth’s oceans and rivers into the atmosphere, into the ground, and back into the oceans and rivers. II. Humidity A. Humidity info 1. air’s ability to hold water vapor changes as air temperature changes. B. Relative Humidity 1. given as a percentage 2. when air holds all the water it can - saturated 3. relative humidity 100% - fully saturated 4. actual water vapor content X 100 = relative humidity (%) saturation water vapor content C. Factors affecting Relative Humidity 1. two factors, water vapor and temperature a. relative humidity decreases as the temp. rises and increases as the temp. drops D. Measuring Relative Humidity 1. instrument used - psychrometer a. two thermometers, wet-bulb (covered with a cloth) and dry-bulb b. difference in temp readings between the thermometers indicates the amount of water vapor in the air, larger difference, less water vapor, lower humidity. III. Condensation A. Condensation info 1. before condensation can occur the air must be saturated, relative humidity of 100%. B. Dew Point 1. the temp at which a gas condenses into a liquid 2. air is saturated 3. must have a surface to condense on. V. Precipitation A. Rain 1. water drops in the cloud become a certain size they will fall. B. Sleet and Snow 1. sleet forms when rain falls through a layer of freezing air. 2. snow forms when temp are so cold that water vapor changes directly to a solid. C. Hail 1. balls or lumps of ice 2. forms in cumulonimbus clouds 3. updrafts of air carry raindrops high in the clouds, raindrops freezes, as it falls it is uplifted again high in the clouds (can happen many times), when the hail is too heavy it falls to the ground. Review 1. If an air mass is cooled and the amount of humidity in the air mass stays the same, does the relative humidity of the air mass increase or decrease? Answer: it increases 2. What causes dew? Answer: at night and in the early morning, the air cools and can hold less moisture. Dew is the water that condenses from the air in the early morning. 3. How does hail form? Answer: when raindrops are carried to the tops of clouds by updrafts. The raindrops freeze and become hail. The hail grows larger as it is repeatedly covered with layers of freezing water from updrafts. 4. What does a relative humidity of 75% mean? Answer: the air contains 75% of the maximum amount of water that the air can hold at a given temperature. 5. What happens to relative humidity as the air temperature drops below the dew point? Answer: as the air temperature drops below the dew point, relative humidity increases to the saturation point and condensation occurs. 6. Which cloud is most likely to produce light to heavy, continuous rain? Answer: nimbostratus cloud 7. What is the relative humidity of air at its dew point? Answer: 100 % 8. Which of the following is NOT a type of condensation? a. fog b. cloud c. snow d. dew