A seed plant is anchored in the ground by its
advertisement
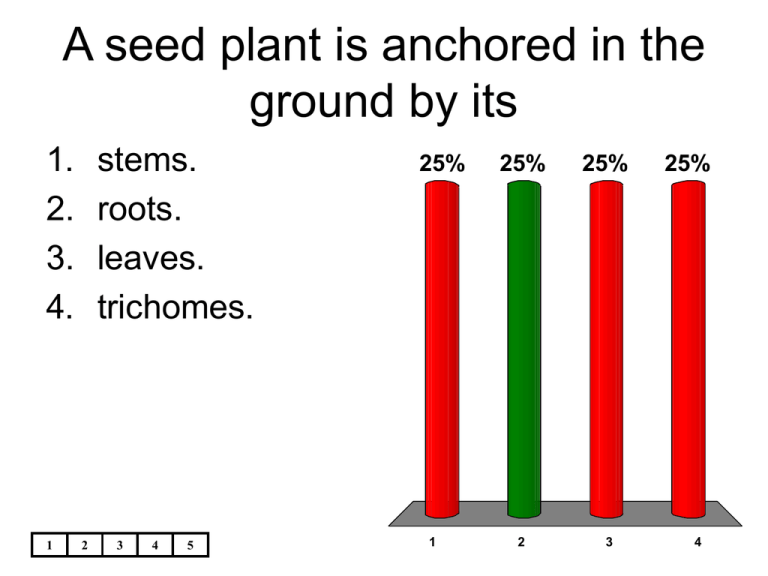
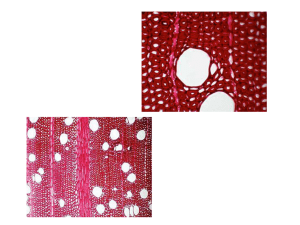
A seed plant is anchored in the ground by its 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 stems. roots. leaves. trichomes. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Ground tissue is found in a plant’s 1. stems only. 2. stems and leaves only. 3. roots and stems only. 4. roots, stems, and leaves. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 What type of tissue is the first tissue in a plant seedling? 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 ground vascular meristematic dermal 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 In angiosperms, xylem consists of tracheids and 1. sieve tube elements. 2. companion cells. 3. vessel elements. 4. parenchyma cells. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 If some of the xylem of a young oak tree were destroyed, it would most likely interfere with the tree’s ability to 25% 25% 25% 25% 1. conduct sugars to the roots. 2. absorb sunlight. 3. absorb water from the soil. 4. conduct water to the leaves. 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 Unlike tracheids, vessel elements 1. die before they conduct water. 2. form a continuous tube. 3. are found in angiosperms. 4. are found in phloem. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Vascular tissue in plants consists of 1. meristem. 2. xylem and phloem. 3. parenchyma and collenchyma cells. 4. epidermal cells. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The outer covering of a plant consists of 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 ground tissue. vascular tissue. dermal tissue. meristematic tissue. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which of the following is the only tissue that produces new plant cells? 1. meristematic tissue 2. phloem 3. ground tissue 4. xylem 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which of the following should a student examine under a compound microscope to observe cell reproduction? 1. epidermis of a leaf 25% 25% 25% 25% 2. tip of a shoot 3. xylem from a tree trunk 4. phloem from the leaf of a plant 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 A carrot is a(an) 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 taproot. fibrous root. monocot. extensive root system. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which of the following are found mainly in monocots? 1. taproots 2. long, thick primary roots 3. extensive root systems 4. small secondary roots 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which of the following is most likely to be used as a food source? 1. root of a monocot 2. root of a dicot 3. root with many root hairs 4. fibrous root 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The layer of cells that encloses the vascular tissue in the central region of a root is the 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 endodermis. cortex. xylem. phloem. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The vascular cylinder of a root consists of 1. xylem only. 2. phloem only. 3. phloem and xylem. 4. phloem, xylem, and ground tissue. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Starting from the root cap, which of the following is the correct sequence of cell activity in a root? elongation division differentiation division elongation differentiation differentiation elongation division division differentiation elongation 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Minerals from the soil move into roots by 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 diffusion. transpiration. active transport. root pressure. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 There is a one-way movement of water and minerals from the cortex into the vascular cylinder of a root because 1. water molecules are in high concentration in the cortex. nutrients are in low concentration in the cortex. the root pressure is low. the Casparian strip is waterproof. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The soil around a lilac bush was watered with a solution containing radioactive phosphorus. Several hours later, radiation was detected in its stems. Through which cells did the radioactive phosphorus travel to the stems? 1. sieve tube elements 2. companion cells 3. tracheids and vessel elements 4. cells of the cortex 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 2 25% 3 25% 4 Root pressure causes a plant’s roots to absorb water. forces water in xylem downward. is produced within the cortex of the root. is produced in the vascular cylinder by active transport. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 2 25% 3 25% 4 One of the main functions of stems is to 1. carry out photosynthesis. 2. transport substances between roots and leaves. 3. store carbohydrates. 4. store water. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The vascular tissue in a plant’s stem 1. has buds. 2. is continuous from the roots to the leaves. 3. carries nutrients up the stem but not down. 4. consists of nodes. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Unlike roots, stems 1. transport water. 2. have ground tissue. 3. are protected by epidermal cells. 4. may carry out photosynthesis. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Figure 23–1 shows cross sections of monocot and dicot 1. 2. 3. 4. 25% 25% 25% 25% 1 2 3 4 roots. leaf veins. root hairs. stems. 5 Vascular bundles are 1. surrounded by pith in monocot stems. found in only dicot roots. scattered throughout dicot stems. surrounded by parenchyma in both monocot and dicot stems. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which one of the following statements is true? 1. The tissues in a monocot stem are different from those in a dicot stem. Xylem and phloem cells of monocots are arranged in a cylinder. The vascular bundles of monocot and dicot stems are continuous from the root’s vascular cylinder. The pith and cortex of dicot stems consist of meristematic cells. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 2 25% 3 25% 4 The primary growth of a stem 1. is produced by cell division in the cambium. is produced by cell division in the xylem and phloem. increases the length of the stem. increases the width of the stem. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 In dicot plants, secondary growth 1. changes primary xylem and phloem to secondary xylem and phloem. 2. makes the roots longer. 3. results from an increase in the primary xylem and phloem. 4. produces bark and wood. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 2 25% 3 25% 4 What might a thin tree ring indicate? 1. increased production of xylem 2. xylem production in winter 3. decreased production of phloem 4. a year of drought 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which of the following describes the heartwood of a tree? 1. active xylem that transports water and minerals 2. old, nonfunctioning xylem 3. old, nonfunctioning phloem 4. produces protective layers of cork 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 2 25% 3 25% 4 Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse in and out of a leaf through the 1. palisade mesophyll. 2. guard cells. 3. phloem. 4. stomata. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Most of the photosynthetic activity in plants takes place in the 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 mesophyll. guard cells. stomata. xylem. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which of the following does NOT directly enable photosynthesis to take place in a leaf? 25% 25% 25% 25% 1. guard cells 2. stoma 3. phloem 4. xylem 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 In Figure 23–2, the X points to a 1. 2. 3. 4. 25% 25% 25% 25% 1 2 3 4 guard cell. mesophyll cell. vein. stoma. 5 In Figure 23–2, the water pressure in the 1. stoma is low. 2. stoma is high. 3. guard cells is high. 4. guard cells is low. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The stomata of leaves are usually open in 1. light if a plant has enough water. 2. light if a plant has too little water. 3. darkness if a plant has enough water. 4. darkness if a plant has too little water. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which of the following terms is LEAST related to the other terms? 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 oxygen stomata carbon dioxide transpiration 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which of the following statements is NOT true? 1. The opening of stomata increases transpiration. The stomata of a wilted plant are open. Plants may release carbon dioxide through the stomata. Stomata may be closed during the day. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The attraction of water molecules to other molecules is called 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 adhesion. cohesion. capillary action. transpiration pull. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Through which plant cells does water move by capillary action? 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 phloem cells guard cells mesophyll cells xylem cells 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Water will move higher in a narrow glass tube than in a wide glass tube because of 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 adhesion only. capillary action. pressure. cohesion only. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The closing of a plant’s stomata will 1. increase capillary action in the plant’s stem. increase transpiration pull. cause wilting. cause less water to be pulled up from the plant’s roots. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The movement of sugars in a plant can be explained by 1. capillary action. 2. transpiration pull. 3. the pressure-flow hypothesis. 4. root pressure. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 When a plant moves sugars from its leaves to its roots, the sink is the 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 leaves. roots. stems. same as the source. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 According to the pressure-flow hypothesis, which of the following statements is NOT true? 1. Water moves from the xylem to the phloem of a plant. Water is necessary for sugars to move through phloem. Phloem is able to move sugars in either direction to meet the nutritional needs of the plant. The movement of water into a nutrientrich region of the phloem decreases the pressure in that region. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The principal organs in which plants carry out photosynthesis are leaves. _________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 Phloem consists of vessel elements and companion cells. _________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 Meristematic tissue produces new cells by mitosis. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 The high concentration of mineral ions in the plant cells causes water molecules to move into the plant by diffusion. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 A decrease in the active transport of minerals into a root would not cause the root to release water into the soil. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 A bud consists of ground tissue. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 The vascular bundles in a dicot stem are arranged randomly. _________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 The secondary growth of a dicot stem results from cell divisions in the stem’s vascular cambium and xylem. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 In a tree, the heartwood increases in width over time. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 The thin, flat part of a leaf is called the petiole. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 Transpiration is the loss of oxygen through a plant’s leaves. _________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 When the guard cells of a leaf lose water, the stomata open. _________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 In plants, the opening and closing of stomata balance water loss with the need for carbon dioxide. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 Water rises to the top of a giant redwood tree by transpiration pull. _________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 When plants pump nutrients from their roots to their branches, the roots are the sink. _________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 Participant Scores 0 0 Participant 1 Participant 2 0 0 0 Participant 3 Participant 4 Participant 5 The three main organs of seed plants are roots, leaves, and ____________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 The sugary sap of maple trees is tapped as it moves through the _________________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 When water moves up through xylem cells called ____________________, it passes through openings between the cells. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 The roots of grasses are a type of root called a(an) ____________________ root. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Figure 23–3 Figure 23–3 shows a cross section of a(an) ____________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Root hairs take in water from the soil through the process of ____________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 As the relative concentration of mineral ions in a root’s epidermal cells increases, the relative concentration of water molecules ____________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 The ____________________ on a stem contain undeveloped tissue that can produce new stems and leaves. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Figure 23–1 In Figure 23–1, B is pointing to _________________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 ____________________ consists of the outer layers of secondary xylem in dicot stems. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 If a cross section of a tree has 12 tree rings, it is most likely ____________________ years old. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 The layer of growing tissue that surrounds the expanding phloem tissue in trees is the _________________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Stomata open into the _________________________ layer of a leaf. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 ____________________ cells control the opening and closing of stomata. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 In angiosperms, capillary action raises water to a higher level in ____________________ tissue. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 How is the function of a tree trunk related to photosynthesis? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Contrast the flow of materials in xylem and phloem. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Where are the youngest cells in a plant found? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 What three kinds of tissues does meristematic tissue develop into? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Contrast the growth of fibrous roots and taproots in soil. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Which roots are more effective in reducing erosion, fibrous roots or taproots? Explain your answer 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Figure 23–3 In Figure 23–3, what is structure C, and what tissues is it made up of? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 What types of tissues are found in a root’s zone of maturation? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 What do roots absorb from the soil? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 How is the function of a stem similar to that of a root? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Contrast the arrangement of vascular bundles in monocot stems and dicot stems. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 By what three processes does water rise from the roots to the top of a tree? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Root pressure causes guttation, the exuding of water droplets seen in the morning on blades of grass and on the leaf edges of some monocots. Why does guttation not occur in the leaves of trees? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 According to the pressure-flow hypothesis, how does water from xylem cause sugars to flow through phloem? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 In the pressure-flow hypothesis, what does the term sink refer to? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 In what ways do the leaves of a plant depend on the plant’s roots and stem? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 A nail that has been hammered into the trunk of a tree is found at the same height year after year, even as the tree grows taller. Explain why. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 How do the functions of the three kinds of cells that form ground tissue differ? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Describe the three main functions of stems. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Explain the role of active transport in the movement of water and dissolved nutrients from the soil to the root of a plant. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Explain how the ringlike arrangement of vascular bundles in a dicot stem results in two rings of vascular tissue in the stem. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Explain how the structure of the mesophyll of a plant is adapted to carry out photosynthesis. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Explain why the stomata of a plant open after the plant has been watered. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Under what conditions of rainfall, temperature, and light would a plant’s stomata be closed? Explain your answer 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 According to the pressure-flow hypothesis, under what conditions might root tissue be the source and leaf tissue the sink? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5