Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms
advertisement

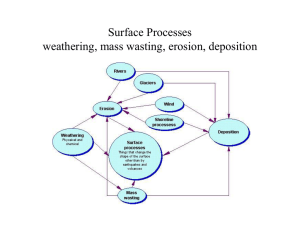
Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Glaciation • Earth once covered with glaciers • Last glaciation ended around 10,000 years ago Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Glaciers • Rivers of ice that move slowly • Move downslope under the influence of gravity and the pressure of own weight • Form where rate of accumulation of snow and ice is greater than rate of melting • Largest reservoir of fresh water on Earth Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Types of glaciers 1. Valley glaciers: form in mountainous locations and move down valleys 2. Continental ice sheets/glaciers: enormous areas of glacial ice and snow Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Causes of an ice age • Change in the Earth’s orbit around the sun • Change in the angle of the Earth’s axis Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Processes of glacial erosion Glaciers erode the landscape they travel over in two ways: 1.Plucking 2.Abrasion Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms 1. Plucking • Bottom of glaciers scrape along valley floors – creates friction causing melting around the base of the glacier • Meltwater refreezes • Freezes around the rocks on the valley floor and these become part of the glacier • Glacier moves • Newly trapped rock is plucked out of the valley floor • New material is then used in process of abrasion Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms 2. Abrasion • bedrock beneath the glacier is eroded by the debris/material embedded in the sides and bottom of the glacier • ‘Sandpaper effect’ – scrapes the rock over which it is travelling and leaves scratches or grooves in the rock • Striations – show the direction of the ice flow Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Factors affecting the rate of glacial erosion • Thickness of ice • Topography • Geology • Gradient • Accumulation and ablation Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Landforms of glacial erosion (Features of erosion) 1. Cirque • Birthplace of a glacier • Three steep sides • Also called a corrie or coom 2. Arête • Narrow ridge • Formed when two cirques formed side-byside or back-to-back Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Landforms of glacial erosion (continued) 3. Pyramidal peak • Peak at top of mountain • three or more cirques are eroded backto-back around the sides of a mountain…leaving a peak Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Landforms of glacial erosion (continued) 4. U-shaped valley • Glacier moves through this valley, changing the shape from a V-shape to a U-shape • Valleys have steep sides and flat floors • Glacier cuts off interlocking spurs of the Vshaped valley leaving truncated spurs Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Landforms of glacial erosion (continued) 5. Ribbon lakes • Long, narrow lakes found in glaciated Ushaped valleys • meltwater and rainwater accumulates forming a ribbon lake 6. Fjords • Drowned U-shaped valleys • Result of melting glaciers Ribbon lake Cirque/lake U-shaped valley Hanging valley Pyramidal peak Arete Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Glacial deposition • Dropping or laying down of sediment that was once transported by a glacier • Occurs in lowland areas • Deposited material is called glacial drift • Material deposited directly by ice is called till or boulder clay • Material deposited by glacial meltwater is known as fluvio-glacial deposits Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Examples of landforms of glacial deposition • Moraines • Drumlins • Erratics Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Examples of landforms of fluvio-glacial deposition • Eskers • Outwash plains • Kames and kettleholes Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Landforms of glacial deposition 1. Moraine • Deposited debris • Various sizes ranging from large boulders to fine rock flour • Material may be angular or rounded in shape Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Five types of moraine I. Lateral moraine II. Medial moraine III. End/terminal moraine IV. Ground moraine V. Englacial moraine Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Landforms of glacial deposition 2. Drumlins • Oval-shaped hills consisting of boulder clay • Show direction of glacier movement • Occur in swarms or cluster • ‘Basket of eggs’ topography • ‘Drowned drumlins’ – as the ice melted sea levels rose and the drumlins appear as islands in the sea Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Landforms of glacial deposition 3. Erratics • Material transported by the glacier and are said to be ‘out of place’ when deposited • Esker – long winding ridges of stratified sand and gravel that wind its way across lowland areas Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Landforms of glacial deposition 4. Outwash plains • Glaciers melt • Release vast amounts of water • Spreads outwards beyond the end/terminal moraine • Carries large volumes of rock and gravels and sands Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Landforms of glacial deposition 5. Kames • Piles of sediment consisting of gravels and sand • Deposited along the front of a retreating glacier Chapter 13: Glacial Processes, Patterns and Associated Landforms Landforms of glacial deposition 6. Kettle holes • Blocks of ice separate from the main glacier • Buried partly in meltwater sediments • Blocks of ice melt leaving depressions or holes • Fill with water – form kettle hole lakes