Meteoroids-Asteroids-Comets

Meteoroids! Asteroids!
Comets!
Oh, my!
What makes up our Solar System?
• The sun
• Planets
• Moons
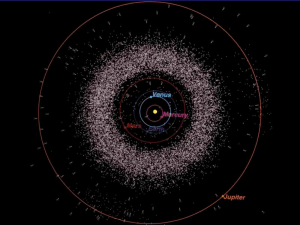
• Asteroid belt (between Mars and Jupiter)
• Lots of space
• All sorts of bits and pieces of rock
Meteorite, Meteoroid, Meteor?
What’s the difference?
Meteorite vs. Meteoroid
• Meteoroid = while in space a meteorite is called a meteoroid
• Meteorite = a small rock or rocky grain that strikes Earth’s surface
• So the difference is just based on where the rock is when you are describing it
Meteor
• Sometimes called a
“Shooting Star”
• When a meteorite enters Earth’s atmosphere, friction causes them to burn up, producing a streak of light
Where do they come from?
How big are they?
• Pieces of rock that broke off other objects
• Sizes range from as small as a pebble or as big as a huge boulder
Are they dangerous?
• Most meteoroids disintegrate before reaching the earth by burning up in Earth’s atmosphere
• Some leave a trail that lasts several minutes
• Meteoroids that reach the earth are called meteorites. Large ones can cause damage
Flagstaff, Arizona
• 49,000 years ago
• Meteorite about 150 feet in diameter
• Weighed 650 pounds
• Energy = 2.5 million tons of dynamite
• 4000 feet wide, 650 feet deep
• Still visible today
Barringer Meteorite Crater
What’s a “Meteor Shower”?
• Usual rate = six meteors per hour
• During a Meteor Shower = rate may be as high as 60 meteors per hour
• Occur when Earth passes through the tail or debris of a comet
• Presides (mid-August)
• Leonids (mid-November)
Comets
• Bodies in space made up of ice, dust, small gritty particles
• Sometimes called “dirty snowballs”
• When close to the sun, ice vaporizes, producing a spectacular streak of gas, referred to as a “tail”
• Many in a regular orbit around the sun
Comets
Where do comets come from?
• Many ordinate in a region called the Oort cloud which is located beyond the orbit of the dwarf planet Pluto
• Others originate in the Kuiper Belt beyond the orbit of Neptune
• This region is filled with billions of comets
Famous Comets
• Comet Hale-Bopp
• Halley’s Comet
• Comet Kohoutek
A Comet’s Tail
Asteroids
• An irregularly shaped rocky object in space
(like a space potato)
• May be the shattered remains of objects left over from the time when the planets were formed
How big are asteroids?
• Larger than meteoroids
• (In fact, the main difference between meteoroids and asteroids is their size.)
• Size ranges from 10 feet across to bigger than a mountain
Asteroids
• Approx. 150,000 asteroids in the Solar
System
• Most are in a band that orbit the sun between Mars and Jupiter (Asteroid Belt)
• Why are there all of those asteroids between Mars and Jupiter and not another planet?
Near-Earth Asteroids (NEAs)
• At least 1000 asteroids orbit outside of the
Asteroid Belt – these could be a danger to
Earth
• Asteroids that cross Earth’s orbit are called Near-Earth Asteroids or NEAs
• NEA / Earth collision not likely
• But if it did, the affect of the impact would depend on the size of the asteroid
Large Asteroid hits Earth
65 Million Years Ago
• Catastrophic Collision
• Asteroid 6 to 12 miles in diameter
• Near the Yucatan
Peninsula in the Gulf of Mexico
Large Asteroid hits Earth
65 Million Years Ago
• Collision produced an explosion =
100 trillion tons of dynamite
• Gouged out a crater about 60 miles in diameter
• How would an event like this affect Earth?
What do Scientists Think
Happened?
• Forests were wiped clean for a distance of
300 to 600 miles in all directions
• 300 foot wave struck the coast of Texas
• Powerful Earthquakes
• Landslides destroyed long stretches of coastline
What do Scientists Think
Happened
• Explosion threw huge amounts of debris into the air, covering large parts of North
America
• Poisonous gases and dust soared high into the atmosphere, spread over most of the Earth, and then fell back onto the
Earth’s surface
What do Scientists Think
Happened
• Sunlight was blocked from reaching the
Earth’s surface for many months
• Temperatures plummeted to the freezing point in normally warm areas
• Not enough sunlight for photosynthesis
• Plants died . . . Animals died
• Many animals became extinct (including many types of dinosaurs)
The Rise and Fall of Life on Earth
• See the dip around 65 Million years ago?
• This represents the extinction of about 75% of all the species alive at that time.
Is the Earth in danger of a large asteroid impact?
• Not that we know of!
• None of the asteroids or comets discovered so far is on a collision course with Earth.
• However, we can't speak for those that are not yet discovered. In principle, one of those could hit any time, but statistically the chances are very small.
Torino Scale
• A system used to rate the hazard level of an object moving toward Earth
Review
• Q: What is the difference between a meteoroid, meteororite, and a meteor?
• Meteoroid = while in space a meteorite is called a meteoroid
• Meteorite = a small rock or rocky grain that strikes Earth’s surface
• Meteor = “Shooting Star”
Review
• Q: What is the difference between an asteroid and a meteoroid?
• The main difference is the size of the object.
• Q: Which is larger, asteroid or meteoroid?
• Asteroids are larger than meteoroids.
Review
• Q: Why is it important to study smaller bodies in our Solar System such as comets or asteroids?
• They help us learn about the history of our
Solar System.
Review
• Q: Why do planets and moons with atmospheres have less impact craters than those without atmospheres?
• The atmosphere slows and burns smaller objects like meteorites, thus many do not reach the surface to create an impact.
Review
• Bright streaks of light that result when rocky bodies burn up in the atmosphere are called ___________.
• Frozen bodies made of ice, rock, and dust, sometimes called “dirty snowballs” are called _____________.
• Small, rocky bodies that revolve around the sun are called ______________.
Review
• Bright streaks of light that result when rocky bodies burn up in the atmosphere are called meteors .
• Frozen bodies made of ice, rock, and dust, sometimes called “dirty snowballs” are called comets .
• Small, rocky bodies that revolve around the sun are called asteroids .
Review
• Q: Discus what could happen if the Earth experienced another large asteroid impact.
How would it affect life on Earth?
• Forests flattened for many miles
• If asteroid landed in water, it would cause giant waves and landslides
• Powerful Earthquakes
The devastation continues…
• Poisonous gases and dust fills the atmosphere, blocks out the sun
• Temperatures drop drastically
• No photosynthesis = plants die = animals die
• Some animals become extinct
Review
• Q: Where is the Asteroid Belt?
• Asteroid Belt is between Mars and Jupiter
• Q: What is the Torino Scale?
• A system used to rate the hazard level of an object moving toward Earth