FMP`s for Structural - Montana Pesticide Safety Education Program
advertisement

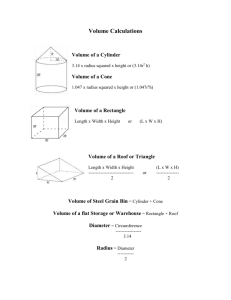
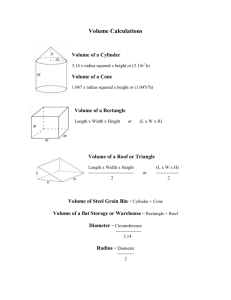
Using FMP’s for a Structural Fumigation Cecil Tharp MSU Pesticide Education Specialist FMP’s must be written prior to fumigations Pre-Inspection Inspect the structure and/or area to determine suitability for fumigation. Leaks Hazards: Proximity to other individuals / structures / or animals Urban Residence or Rural Residence? Storage Sealing Materials Seal Aeration Fan Motors Seal Aeration Fan Inlets Seal Steel Bin Roof Eaves Seal Steel Bin Door Create a diagram or sketch of the fumigation site: identify hazards Create a Monitoring Plan: Keep a log or manual of monitoring records for each fumigation site. What will you do if you have leaks? How do you monitor; placement? What do you do when you have leaks >.3 ppm (Emergency Contact; PPE) > 15 ppm (Emergency Contact; PPE) Multiple and single gas detectors Several Manufacturers Lumidor Dräger Analytical Tech., Inc. MSA Toxirae Others FMP -- Continued Placard all entrances to site Give owner and other workers a copy: FMP MSDS The number and identification of persons who routinely enter the area to be fumigated and the proximity of other persons and animals. Current emergency telephone numbers of local Health, Fire, Police, Hospital and Physician *Determining Product Rates Step #1: Determining Volume π = 3.14 r = Radius = ½ Diameter D = Diameter C = Circumference = πD Determine volume: Cylinder Formula: volume = 3.14 x r2 x H r = ½D 3.14′ x (13.5′ x 13.5′) x 16′ = 9,156 Ft3 Volume: Cylinder when only circumference is known Circumference = 84.78’ Diameter = Circumference ------------------3.14 Diameter = 84.78 / 3.14 Diameter = 27 Radius = 13.5 feet Formula: volume = 3.14 x r2 x H 3.14′ x (13.5′ x 13.5′) x 16′ volume = 9,156 cubic feet Volume of ½ cylinder Volume = (3.14 x r2 x H) / 2 Calculating Volume: Cone 1.047 x radius2 x height 1.047 x 182.25 x 16 Volume = 3,053 cubic ft Calculating Volume of Rectangle or Triangles Rectangle volume = L x W x H Triangle (Loft) Formula = (L x W x H) ÷ 2 Base Volume: 80′ x 20′ x 20′ = 32,000 cubic ft Loft Volume: (80′ x 20′ x 10′) = 16,000 ÷ 2 = 8,000 cubic ft Total Volume: 32,000 + 8,000 = 40,000 Ft3 Step #2: Determine amount of fumigant to add to your application site Refer to product label recommendations Tablets or Pellets Per 1,000 square feet Tablets or Pellets per 1,000 bushels Usually expressed as range You must determine what part of range is best Leaks Moisture Tarped Story Problem. An inspector was called out to help an applicator figure out how many phostoxin pellets to place in a grain silo. The silo has an 80’ circumference, 25’ height from eaves to ground, and 5’ high cone. Temperature is 80 degrees F. This silo also contains 500 bushels of grain. Story Problem: Answers 1. Total Volume of Silo? Diameter = 80 / 3.14 Diameter = 25.47 Radius = 25.47 / 2 Radius = 12.73 Cylinder = 3.14 x 12.732 x 25 Cylinder = 3.14 x 162.05 x 25 Cylinder = 12,721 ft3 Cone = 1.047 x 162.05 x 5 Cone = 848.33 cubic ft. Total Volume = 848.33 + 12,721 13,569.33 cubic ft 2. How many pellets need to be used? 450 – 900 pellets / 1,000 bu withtarp500 bushel 225 – 450 pellets 350 – 725 pellets / 1,000 ft3 no tarp 4,749 – 9,837.33 pellets * Ranges with severity of infestation, leaks, tarp etc… 3. How long before aeration? 48 hours Take 20 minutes: Do story problem titled ‘Jordon’s Feed Mill story problem’ (Work in groups using Product Label) Jordon’s Feed Mill Story Problem Jordon’s Feed Mill has a grain silo that is 75’ in circumference and a vertical distance from the eaves to the bottom of the bin of 15’. The cone top is 3’ high. Larry’s Pest Control has been contracted to fumigate one of the silos for the lesser grain borer. The silo is filled with approximately 500 bushels of spring wheat. Larry can either fumigate on Tuesday July 21st in the evening, or Thursday July 23rd in the evening. The weather for Tuesday is forecast to be partly cloudy with a 70% chance of rain and a high of 95 degrees F. Thursday is forecast to be sunny with a temperature of 101 degrees F. The peak grain temperature ranges from 70 – 80 degrees F. There are horses 50 yards from grain silo. Detail your fumigation management plan strategy to include at least the following details. ‘Jordon’s Feed Mill story problem’ 1. What is the volume of this grain bin? Diameter = 75 / 3.14 Diameter = 23.88 Radius = diameter / 2 Radius = 11.94 – cyl = 3.14 x 11.942 x 15 volume = 3.14 x 142.45 x 15 volume = 6,714.74 cubic ft – cone = 1.047 x 11.942 x 3 cone = 447.43 cubic ft – Volume = 447.43 + 6,714.74 Volume = 7,162.17 cubic ft 2. How many pellets will you need to use when fumigating? -450 – 900 pellets / 1,000 bu with tarp 500 bushel 225 – 450 pellets -350 – 725 pellets / 1,000 ft3 no tarp 2,506 – 5,192.45 pellets * Ranges with severity of infestation, leaks, etc… 3. Calculate the required fumigation period based on fumigant grain temperature? -48 hr 60 – 80 degrees F grain temperature if sealed properly Review Fumigant Management Plans 4. Which day would be the best one to start the fumigation? -Tuesday July 21st because of moisture that afternoon. Moisture will helps convert aluminum or magnesium phosphide into phosphine gas. 5. When should ventilation begin? -Thursday evening or Friday morning, < 0.3 ppmillion 6. What personal protective equipment should you wear and how does this relate phosphine gas concentrations? -wear dry cotton gloves, wash after, respiratory equipment (NIOSH / phosphine gas approved)-up to 15 ppm Questions? MSU Pesticide Education: www.pesticides.montana.edu Degesch America: www.degeschamerica.com Detector Tubes ADVANTAGES Initial low cost Variety of tubes Variety of ranges Easy to use No calibration DISADVANTAGES Point in Time reading Must know gas $4 to $9/reading Expiration Date Disposal High Std. Deviation Glass tubes Pumps can malfunction Operator error Color can fade after reading