Kitchen Management
advertisement
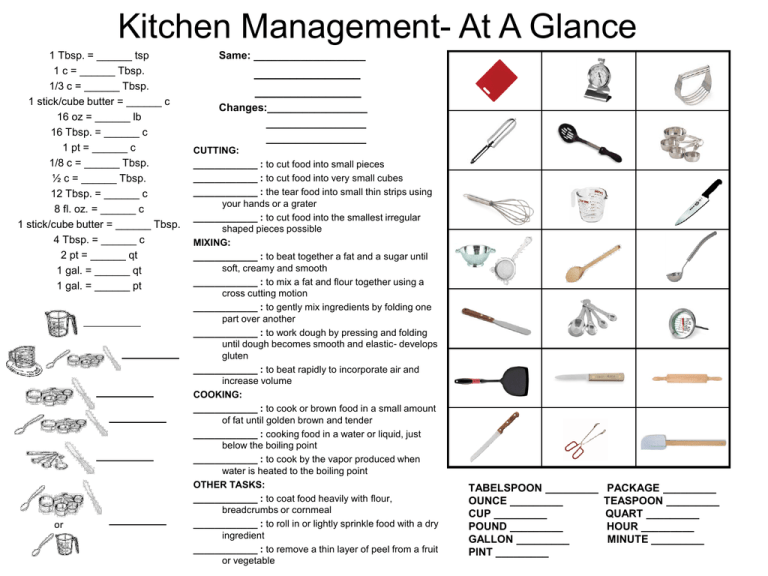
Kitchen Management- At A Glance 1 Tbsp. = ______ tsp 1 c = ______ Tbsp. 1/3 c = ______ Tbsp. 1 stick/cube butter = ______ c 16 oz = ______ lb 16 Tbsp. = ______ c 1 pt = ______ c 1/8 c = ______ Tbsp. ½ c = ______ Tbsp. 12 Tbsp. = ______ c 8 fl. oz. = ______ c 1 stick/cube butter = ______ Tbsp. 4 Tbsp. = ______ c 2 pt = ______ qt 1 gal. = ______ qt 1 gal. = ______ pt or Same: ___________________ _______________ _______________ Changes:_________________ _________________ _________________ CUTTING: ____________ : to cut food into small pieces ____________ : to cut food into very small cubes ____________ : the tear food into small thin strips using your hands or a grater ____________ : to cut food into the smallest irregular shaped pieces possible MIXING: ____________ : to beat together a fat and a sugar until soft, creamy and smooth ____________ : to mix a fat and flour together using a cross cutting motion ____________ : to gently mix ingredients by folding one part over another ____________ : to work dough by pressing and folding until dough becomes smooth and elastic- develops gluten ____________ : to beat rapidly to incorporate air and increase volume COOKING: ____________ : to cook or brown food in a small amount of fat until golden brown and tender ____________ : cooking food in a water or liquid, just below the boiling point ____________ : to cook by the vapor produced when water is heated to the boiling point OTHER TASKS: ____________ : to coat food heavily with flour, breadcrumbs or cornmeal ____________ : to roll in or lightly sprinkle food with a dry ingredient ____________ : to remove a thin layer of peel from a fruit or vegetable TABELSPOON _________ OUNCE _________ CUP _________ POUND _________ GALLON _________ PINT _________ PACKAGE _________ TEASPOON _________ QUART _________ HOUR _________ MINUTE _________ Kitchen Management- At A Glance KEY 1 Tbsp. = 3 tsp 1 c = 16 Tbsp. 1/3 c = 5 1/3 Tbsp. 1 stick/cube butter = 1/2 c 16 oz = 1 lb 16 Tbsp. = 1 c 1 pt = 2 c 1/8 c = 2 Tbsp. ½ c = 8 Tbsp. 12 Tbsp. = 3/4 c 8 fl. oz. = 1 c 1 stick/cube butter = 8 Tbsp. 4 Tbsp. = ¼ c 2 pt = 1 qt 1 gal. = 4 qt 1 gal. = 8 pt Liquids Flour Sugar Brown Sugar Salt or Shortening Same: Temperature, Directions, Cooking Temp Changes: Amount of ingredients, Cooking time, Size of pan CUTTING: Chop: to cut food into small pieces Dice: to cut food into very small cubes Grate/shred: the tear food into small thin strips using your hands or a grater Mince: to cut food into the smallest irregular shaped pieces possible MIXING: Cream: to beat together a fat and a sugar until soft, creamy and smooth Cut-In: to mix a fat and flour together using a cross cutting motion Fold-In: to gently mix ingredients by folding one part over another Knead: to work dough by pressing and folding until dough becomes smooth and elastic- develops gluten Whip: to beat rapidly to incorporate air and increase volume COOKING: Sauté: to cook or brown food in a small amount of fat until golden brown and tender Simmer: cooking food in a water or liquid, just below the boiling point Steam: to cook by the vapor produced when water is heated to the boiling point OTHER TASKS: Dredge: to coat food heavily with flour, breadcrumbs or cornmeal Flour: to roll in or lightly sprinkle food with a dry ingredient Peel/pare: to remove a thin layer of peel from a fruit or vegetable Cutting Board Oven Thermometer Pastry Blender Peeler Slotted Spoon Dry Measure Cups Wire Wisk/Whip Liquid Measure Cup Chef’s Knife Colander/Strainer Wooden Spoon Ladle Straight Edge Spatula Measure Spoons Meat Thermometer Turner Paring Knife Rolling Pin Bread Knife Tongs Rubber Scraper TABELSPOON = T, Tb, Tbsp OUNCE = oz CUP = C, c POUND = #, lb GALLON = gal PINT = pt PACKAGE = pkg TEASPOON = t, tsp QUART = qt HOUR = hr MINUTE = min Kitchen Safety and Sanitation- At A Glance = ______ seconds Ammonia + Bleach = _________________ = _____ °F and ______°F 1. ___________ 2. ___________ 3. ___________ 4. ___________ 1. __________________ 2. __________________ 3. __________________ __________ Microwaves cause food molecules to ___________________ __________ Microwave Safe Materials 1. ___________ 2. ___________ 3. ___________ __________ Standing Time Is: __________ __________ It’s Important Because: CAUTION! Use these when taking foods out of the microwave: = ____________ (#1!) = ____________ = ____________ Which Cooking Container Is Best When Microwaving? (CROSS OUT the wrong answers) Kitchen Safety and Sanitation- At A Glance KEY Fat = ______ 20 seconds Water Ammonia + Bleach = Deadly, Toxic Gas _________________ = _____ 41 °F and ______°F 135 Sugar Warmth 1. ___________ Moisture 2. ___________ Food 3. ___________ Time 4. ___________ Salmonella __________ E. Coli- 160 degrees __________ Botulism __________ Staphylococci __________ Hepatitis __________ Microwaves cause food molecules to Vibrate ___________________ Microwave Safe Materials 1. ___________ Paper Plastic 2. ___________ Glass 3. ___________ Standing Time Is: The amount of time food is allowed to sit AFTER microwave cooking It’s Important Because: It allows the food to finish the cooking process CAUTION! Use these when taking foods out of the microwave: Hot Pads 1. ___________ Cover with a Lid 2. ___________ Cover Baking Soda 3. ___________ Fire Extinguisher In the refrigerator for 2-3 days (#1!) = ____________ Under cold, RUNNING Water = ____________ In the microwave, if used immediately = ____________ Which Cooking Container Is Best When Microwaving? (CROSS OUT the wrong answers) Carbohydrates- At A Glance Muffin: Cooked Rice Pasta Biscuit: Sugar Other Name = = Food Source Purposes of Ingredients Flour Eggs Salt Sugar Liquid Fat Leavening C = __ grams Carbohydrates- At A Glance KEY Bran Muffin: Cauliflower top few tunnels Provides Energy Cooked Rice Pasta Biscuit: Flaky layers Straight sides Simple Sugars = C = _4_ grams = Roughage Complex Starches Fiber Cellulose 20-35 g Sugar Sucrose Fructose Glucose Maltose Lactose Other Name Food Source Must have WATER Table Sugar Simple Sugars Fruit Sugar Blood Sugar Malt Sugar Milk Sugar Aids in Digestion Cholesterol Insoluble Soluble Purposes of Ingredients Flour Structure and body Eggs Color, texture, nutrients Salt Flavor, controls yeast Sugar Aids browning, feeds yeast Liquid Moisture, activates yeast Fat Leavening Flavor, tenderness Airy, volume, light, porous (yeast, baking powder/soda) Fats and Oils- At A Glance Fat = ___/gram Functions of Fat Cholesterol is never found in: CHOLESTEROL: Low-Fat Cooking Methods ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ L H Fatty Acids: Appear to: Appear to: Appear to: Fats and Oils- At A Glance KEY 9 Insulation KADE Flavor Oils Fat = 9/gram Energy Functions of Fat Feel Full Longer Solids Reserve Energy Cholesterol is never found in: PLANTS Healthy Skin Cell Growth CHOLESTEROL: Fat-like substance L H DL Low-Fat Cooking Methods Grilling Broiling Poaching Roasting Yogurt for Mayo Oils for Solid Fats osers DL eros Fatty Acids: Saturated Polyunsaturated Monounsaturated Appear to: Appear to: Appear to: LDL HDL LDL HDL LDL HDL Meat Milk Products Butter Lard Shortening Tropical Oils Vegetable Oils -Corn oil -Safflower oil Olives Olive Oil Avocado Peanuts Peanut Oil Proteins- At A Glance Amino Acids How many? What are they? Proteins = ___/gram Complete vs Incomplete Functions of Eggs Milk Proteins- At A Glance KEY Amino Acids How many? 9 What are they? Building blocks of protein 4 Proteins = ___/gram Builds and Repairs Body Tissue Complete vs Incomplete Complete Milk Cheese Meat Fish Eggs Incomplete Nuts Beans Rice Legumes Cereals/Grains Functions of Eggs Binder Meatloaf Thickener Pudding Milk Homogenization Fat Particles Stir & Low heat Pasteurization Kill Bacteria 3 Cups Fortified A&D Coating Breaded Chicken Leavening Angel Food Emulsifier Mayo Vitamins, Minerals & Water- At A Glance 1. Deficiency: _______________________________________ 2. Toxicity: __________________________________________ 3. Water Soluble: _____________________________________ 4. Fat soluble: _______________________________________ 5. Macro: ___________________________________________ 6. Micro or Trace: _____________________________________ 7: Electrolyte: ________________________________________ Functions of Water How do you prevent this… Conservation cooking methods include: Veggies with the most vitamins and minerals? Sampling Vitamin C What destroys the nutrients in… Folate Iron Sodium Function Food Source Deficiencies Toxicities Vitamins, Minerals & Water- At A Glance KEY 1. Deficiency: Not enough of something (shortage) 2. Toxicity: Too much of something (toxic/poisonous) 3. Water Soluble: Dissolves in water 4. Fat soluble: Dissolves in fat 5. Macro: Large/big amount 6. Micro or Trace: Small/tiny amount 7: Electrolyte: Minerals that help maintain fluid balance in the body How do you prevent this… Conservation cooking methods include: Microwave Bake Steam Stir Fry Simmer Sauté Soak/cover with ascorbic acid/fruit juice. Veggies with the most vitamins and minerals? Function Vitamin C -Maintains connective tissues -Protects body against infection -Citrus fruits -Orange juice -Strawberries -Scurvy -Breakdown of collagen -Kidney stones -Interferes with actions of Vitamin E -Makes new cells -Green leafy vegetables -Legumes -Seeds -Neural tube defects -Anemia -Heartburn -Diarrhea -Masks B12 deficiency -Helps carry oxygen to the blood -Helps cells use oxygen -Red meat -Dark green leafy vegetables -Anemia -Makes red blood cells -Paleness -Weakness -Heart disease -Elevated LDLs -Maintains fluid balance -Salt -Packaged foods -Muscle cramps -High blood pressure What destroys the nutrients in… Heat Air Water A. Carries water soluble vitamins B. Regulates body temperature C. Carries waste products out D. Prevents dehydration Sampling Folate Iron Sodium Food Source Functions of Water Deficiencies Toxicities Dietary Guidelines MyPlate- At A Glance 1. Eat ____________ foods. 2. Balance______________ to manage weight. 3. _____________sodium, fats and added sugars, refined grains and alcohol. 4. _____________vegetables, fruits, whole grains, milk seafood and use oils in place of solid fats. 5. Build healthy ______________that meet nutritional needs over time at an appropriate calorie level. 6. Include ______________________ as part of healthy eating patterns. Cross out the bad food choice Healthy Eating Patterns 1. Balance calories: -Enjoy your food, but eat _________. -Avoid _______________ portions. 2. Foods to increase: -Make half your plate ___________________. -Switch to fat-free or low-fat _________. -Make at least half your grains _______________. 3. Foods to reduce: -Compare _______________ in foods Caloric needs and choose foods with arethe based on __________ Choose oils that provide numbers. _____________ fats. -Drink ___________ instead of Label, color, and identify key consumer message Dietary Guidelines MyPlate- At A Glance KEY 1. Eat nutrient dense foods. 2. Balance calories to manage weight. 3. Reduce sodium, fats and added sugars, refined grains and alcohol. 4. Increase vegetables, fruits, whole grains, milk seafood and use oils in place of solid fats. 5. Build healthy eating patterns that meet nutritional needs over time at an appropriate calorie level. 6. Include physical exercise as part of healthy eating patterns. 8 oz of seafood/week 60 minutes physical exercise Cross out the bad food choice X Healthy Eating Patterns 1. Balance calories: -Enjoy your food, but eat less. -Avoid oversized portions. 2. Foods to increase: -Make half your plate fruits and vegetables. -Switch to fat-free or low-fat milk. -Make at least half your grains whole grains. 3. Foods to reduce: -Compare sodium in foods and choose foods with the lower numbers. -Drink water instead of sugary drinks. Caloric needs are based on Choose oils that provide healthy fats. Age Gender Physical Activity Label, color, and identify key consumer message Fruits Grains Make half your plate fruits and vegetables. Make half your grains whole grains. Vegetables Make half your plate fruits and vegetables. Eat red, orange and dark green vegetables. Protein Keep meat and poultry portions small and lean. Dairy Switch to low-fat or fat-free milk. Get your calcium rich foods.