Middle East Vocab - Literacy Strategies 1
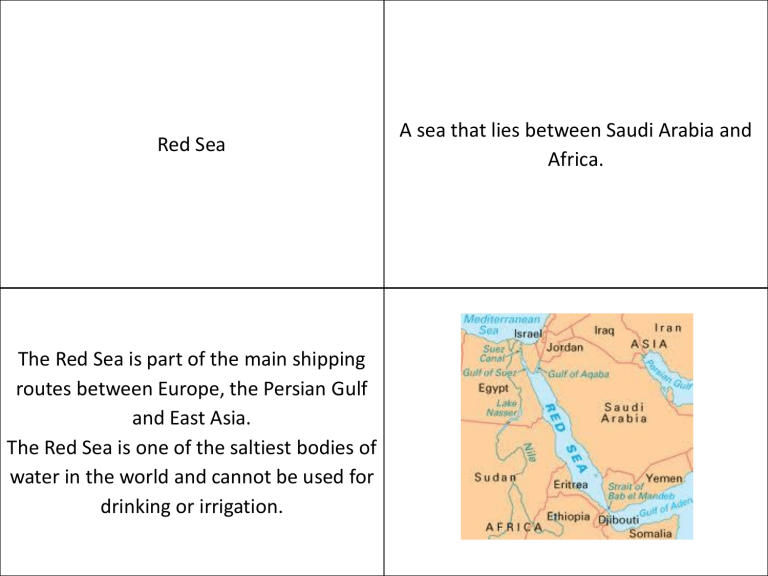
Red Sea
A sea that lies between Saudi Arabia and
Africa.
The Red Sea is part of the main shipping routes between Europe, the Persian Gulf and East Asia.
The Red Sea is one of the saltiest bodies of water in the world and cannot be used for drinking or irrigation.
Persian Gulf
A large body of water that lies between
Iran and Saudi Arabia.
The Persian Gulf area is the world's largest single source of crude oil, and related industries.
Tigris and Euphrates Rivers
Two large rivers in Iraq that are used as a source for much of the area’s water needs.
The area where these rivers run is the cultural hearth, or where religion began in the the Middle East.
Arabian Peninsula
The countries of Saudi Arabia, Kuwait,
Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates
(UAE), Oman and Yemen. This group of countries is surrounded on three sides by water.
This area is the world’s largest peninsula.
It is considered a geopolitical power because of its huge reserves of oil and natural gas.
Suez Canal
A waterway that connects the
Mediterranean Ocean with the Red Sea, dramatically reducing transit time for trade worldwide.
The canal supports 8% of the world's shipping traffic.
Because of its narrow width, it is considered a chokepoint because it can easily be blocked to interrupt this flow of trade.
Israel
ISRAEL
Government: Democracy
Economy: Market
GDP Rank 40
Religion: 75% Jewish, 17% Muslim, and
2% Christian
HDI: 17 of 187
A Middle East country on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea
Iraq
Iraq
Government: Democracy??
Economy: Mixed
75% GDP from Oil
Religion: 97% Muslim, 3% Christian, or other
HDI: 132 of 187
A country in Western Asia with two major rivers, the Tigris and the Euphrates.
Iran
IRAN
Government: Theocracy (Authoritarian)
Economy: Command
75% GDP from Oil
Religion: 98% Muslim, 2% other
HDI: 89 of 187
Also called Persia, this country is in
Western Asia.
Afghanistan
A landlocked country forming part of South
Asia, Central Asia, and to some extent
Western Asia.
The United States is currently winding down a war against the Taliban in
Afghanistan, that was started after 9-11.
Saudi Arabia
The largest Arab state in Western Asia by land area, making up most of the Arabian
Peninsula
SAUDI ARABIA
Government: Monarchy (Authoritarian)
Economy: Command
45% GDP from Oil
Religion: 100% Muslim
HDI: 56 of 187
Arid
Much of the Middle East does not have enough water to support animal life or agriculture.
Very dry or desert-like.
Semi-Arid
Areas of low annual rainfall and having sparse plant life with short coarse grasses.
Syria and Northern Iraq have a semi-arid climate.
Desert
A dry, hot, sandy, usually barren and uninhabited area
The Arabian Peninsula has one of the worlds largest deserts.
Renewable and Non-renewable Natural
Resources
Natural resources are materials found in a natural environment that can be used in some way.
Renewable resources can be replaced in a relatively short time span, while nonrenewable resources require many hundreds of years to regenerate.
Natural resources give a country geopolitical power.
Scarcity Not enough of something.
The Middle East has a scarcity of water to use for drinking and growing plants.
Palestine
The United Nations voted to recognize a
Palestinian state in November 2012, but the Palestinians still face enormous limitations: They don't control their borders, airspace or trade, they have separate and competing governments in
Gaza and the West Bank, and they have no unified army or police.
A historical region that covered parts of modern Israel, Jordan and Egypt.
The British ordered that the land in a large part of this region would be used to create the State of Israel.
Terrorism
The use of violence and threats to frighten or bully, especially for political reasons.
Terrorist acts by Israel and Palestine are a threat to peace between the two countries.
Diaspora
The scattering of people from their homeland or
A community formed by people who have left or been removed from their homeland
An example of a diaspora is a community of Jewish people settling together after they were dispersed from another land.
Zionism
A form of nationalism of Jews and Jewish culture that supports a Jewish nation state in Israel
Zionism supports Jews keeping their
Jewish identity, and has supported the return of Jews to Israel as a means for Jews to be a majority in their own nation, freed from anti-semitic discrimination
Theocracy A government run by a religious leader.
Iran is an example of a theocracy.
Islam
A monotheistic religion practiced by many people, particularly in the Middle East and
Africa. Its holy book is the Quran (also spelled Koran)and Muhammad is its main prophet.
A follower of Islam is called a Muslim.
Muslims believe in the Five Pillars.
Sunni
Muslims who believe that religious leaders
(Imams) are chosen.
About 90% of Muslims are Sunni.
Shite
Muslims who believe that religious leaders
(Imams) descended from the prophet,
Mohammed. They believe that only
Imams can interpret the Quran (Koran.)
Shite (Shia) are found in Iran, Iraq and
Lebanon. They represent only about 10% of Muslims.
Monarchy
A type of government ruled by a single person.
Saudi Arabia is an example of a monarchy in the Middle East
Geopolitical Power
The combination of geographic and political factors that influence or define a country or region.
The richness of natural resources in the
Middle East give the region great geopolitical power.
Arab Spring
A revolutionary wave of demonstrations, protests, and wars in the Arab world that began in December 2010.
To date, rulers have been forced from power in Tunisia, Egypt, Libya, and Yemen.
Major uprisings and protests have broken out in Bahrain, Syria, Algeria, Iraq, Jordan,
Kuwait, Morocco, and Sudan.
Corruption
Evil, decay and dishonesty, particularly in government.
Instability, a lack of transparency
(disclosure of information), and oil wealth have helped promote corruption in parts of the Middle East.
Authoritarian
A government where decisions are made by one person or a very small group of people.
The revolutions of the Arab Spring were prompted by reaction to extreme authoritarian governments.
Some examples of authoritarian governments in the Middle East include:
Iran (a theocracy)
Syria (a presidential republic)
Yemen (a republic)
Chemical Weapons
A device that uses chemicals specifically made to cause death or harm to human beings.
Iraq was the first country to use modern chemical warfare in its 1984 war with Iran.
Today, the instability of the Syrian government poses a chemical weapons threat to the entire Middle East region.
Civil Unrest
Conflict caused by a group of people, including demonstrations, riots, sabotage or other forms of crime. It is meant to be a demonstration to the public and the government, but can worsen and become general chaos.
The Arab Spring was a period of civil unrest over many Middle Eastern countries as citizens protested governments.
OPEC
An international organization of oil exporting countries. Member nations include: Algeria, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq,
Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia,
United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela
Controls 41% of the world’s crude oil and
15% of its natural gas
Cartel
A formal agreement among competing firms to control industry output, market shares, price or other issues. The purpose is to increase individual members’ profits by reducing competition.
OPEC is an example of a cartel, formed to control profits on oil and natural gas.
Choke Point
A chokepoint is a strategic passage or canal which could be closed or blocked to stop sea traffic.
Oil tankers face a number of risks at chokepoints, ranging from heavy traffic to piracy.
Any disruption can lead to instability in oil prices.
Cultural Hearth The birthplace of a culture.
The area around the Tigris and Euphrates rivers forms the cultural hearth of the
Middle East. This region is known as
Mesopotamia.
Judaism
A religion whose followers are waiting for the Messiah (savior of the people) to come.
Judaism was founded by Abraham.
The Torah is its holy book.
Israel was founded as a Jewish state or homeland for Jews.
Christianity
A monotheistic religion whose followers believe in the Holy Trinity. They believe that Jesus was the son of God, born without sin, was crucified, died and resurrected (came back to life.)
The holy book for Christianity is the Bible.
Prophets include Abraham, the Jewish prophets and the Apostles (followers of
Jesus who spread his message.)
Monotheism
A religion whose followers believe in a single god.
Examples of monotheistic religions include
Judaism, Christianity and Islam.
Secular Something that is not related to religion.
Secularism in Islam means favoring a modern nonspiritual democracy with separation of mosque and state, as opposed to Islam as a political movement.