File

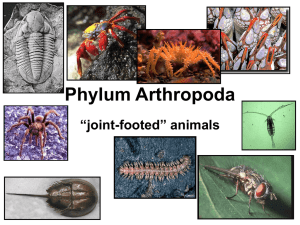
Phylum Arthropoda
It doesn’t get any bigger than this!
Major Features
• An exoskeleton (external skeleton) made out of chitin.
• Must molt (shed their skeleton) in order to grow.
• Have jointed appendages
– Serve a variety of roles (walking, swimming, repro, eating, sensing)
• Three body regions – head, thorax, abdomen.
Features cont’d
• Well-developed nervous system
– Includes a brain and a ventral nerve cord
– Includes sense organs (antennae, compound eyes)
Diversity
Classification
• Broken into subphyla.
– Subphylum Crustacea
– Subphylum Uniramia
– Subphylum Chelicerata
Subphylum Crustacea
• “Crustaceans” – barnacles, shrimp, lobster, crab, crayfish… marine
arthropods.
• The sow bug is a terrestrial example.
Crustacea cont’d
(We’ll use crayfish as our representative)
External structure:
• Cephalothorax – skeleton over head and thorax are fused.
• Head has compound eyes, antennae, and pairs of mouth appendages.
• Thorax has 5 pairs of limbs (4 pairs of walking legs, 1 pair of pincers [chelipeds]).
• Abdomen has swimmerets, uropods and telson.
Crustacea cont’d
Crustacea cont’d
Internal structure:
• Digestive system – 2-chambered stomach, digestive glands, intestine. Green glands for excretion.
• Cardiovascular system – heart pumps blood into the space surrounding the internal organs
(the “hemocoel”).
– Blood contains a blue pigment (hemocyanin).
Crustacean circulation
Crustacea cont’d
Internal structure cont’d:
• Nervous system – brain, ventral nerve cord, and ganglia in several segments.
– Receptors line antennae – include chemical receptors and force receptors.
• Reproduction – separate genders.
– Sperm transferred by 1 st pair of swimmerets.
– Females carry fertilized eggs on their swimmerets.
Crustacea cont’d
Subphylum Uniramia
• “Insects” – most diverse group on
Earth.
General structure:
• Head has compound or simple eyes, antennae, and mouth appendages.
• Thorax has 3 pairs of legs
– Sometimes includes wings.
• Abdomen stores the internal organs.
Insects cont’d
We will use grasshoppers as our representative.
External structure:
• 3 rd pair of legs adapted for jumping.
• Has two pairs of wings.
• Females – have a posterior structure called an
ovipositor for digging holes to lay eggs in.
• Has tympanum – a thin membrane – on abdomen for hearing.
Grasshopper Exterior
Insects cont’d
Internal Structure:
• Digestive system – complete, with mouth, stomach, intestine, and anus.
• Excretion – uses structures called Malpighian
tubules that release uric acid into intestines for disposal.
• Respiration – uses openings in the exoskeleton called spiracles that that lead into a trachea.
– Air is pumped by the contraction and relaxation of the body wall.
Spiracles and Malpighian Tubules
Insects cont’d
• Circulation – a heart pumps hemolymph into the aorta, which empties into a hemocoel
(open space around organs).
– Hemolymph in insects is NOT used to carry O
2
, so it has no pigment.
• Reproduction – Fertilization is internal.
Genders are separate.
– Fertilized eggs are ejected into the ground.
Circulation and Reproduction
Insects cont’d
• Metamorphosis: a change in physiology and anatomy that occurs as an insect matures from a larva to an adult.
– (Many insect larvae, including grasshoppers, are called nymphs).
Subphylum Chelicerata
Arachnids (spiders, ticks, scorpions, mites).
General Features:
• Cephalothorax
– Has 6 pairs of appendages attached to it
• 4 pairs are walking legs
• 1 pair are pedipalps – these sense and hold prey
• 1 pair are fangs (chelicerae)
• Abdomen – stores internal organs
Arachnid structure
More arachnids!
Arachnids cont’d
(Representative organism = spiders)
• Capable of delivering venom to prey through fangs.
• Digestion: prey is injected with digestive juices. Juices gradually digest prey.
– Spider will “suck up” liquefied prey to complete digestion.
Arachnids cont’d
• Respiration: Uses “book lungs” – folds of tissue inside the body wall.
– The folded surface provides plenty of room for gas exchange.