Hurricane Powerpoint
advertisement

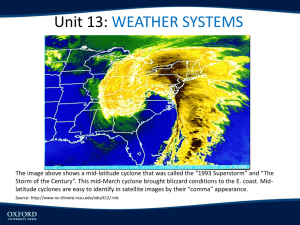
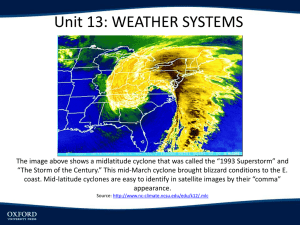
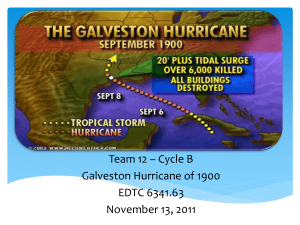
Natural Disasters in the South: Hurricanes and Flooding Asheville Middle School Thursday, December 8, 2011 You and Hurricanes • If your home was to be destroyed and you could only take three things with you, what you take? Words • • • • • • Hurricanes Flooding Equator Atmosphere Troposphere Dangerous • Coriolis Effect • Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale • Categories • Wind shear • Moisture Today’s Objective • • • • Where do hurricanes form? What conditions do hurricanes need to form? How are hurricanes classified? What are the damages associated with each category of hurricanes? • How does geography affect natural disasters? The Southern United States Population = 313,232,044 Square Miles = 3,718,691 Atlantic Beach, Florida The Atlantic Ocean Precipitation Flooding http://www.tamilnet.com/art.html?catid=13&arti d=27795 Hurricanes Winslow Homer Conditions to Form a Hurricane • Warm ocean water (at least 80˚F/ 27˚C) through a depth of about 150 feet • An atmosphere that cools fast • Moist air near mid-level troposphere • A minimum distance from the equator of about 300 miles (but not within 5˚ latitude) • A disturbance near the surface • Low vertical wind shear between surface and troposphere (of less than 23mph). The Eye of a Hurricane Conditions for a Hurricane 1. What causes your temperature to rise? What gets under your skin? 2. Something happens to “cool” your spirits or 3. You are not in the safest place 4. Something disturbs you 5. A vertical wind shear 6. What takes the wind out of your sail Troposphere Photo by Nick Juhasz http://www.miamisci.org/hurricane/h owhurrwork.html Coriolis Effect • • • • Paper plates Ruler Tack Pen or Pencil Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale Dr. Simpson is on the left. Category 1 (119-152 kph) • All hurricanes are dangerous. If it is a Category 1, you will need a raincoat. The man in the middle will be very wet by the time the bus comes. 74 – 95 mph Category 1 Hurricanes • Mobile homes could be damaged. • Small trees could be blown over. Category 2 (152 – 177 kph) • If it is a Category 2 hurricane, you should leave and drive inland. Flooding is associated with hurricanes and a Category 2 hurricane produces lots of water and damaging winds. (96-110 mph) Category 2 • Windows and roofs will be damaged. • Some trees and street signs will be blown down. • There will be a lot of damage to mobile homes. Category 3 (177-209 kph) • A Category 3 hurricane is very dangerous. (111-130 mph) Category 3 • Roofs and porches will be damaged. • Some trees will be blown down. Category 4 (209-250 kph) Category 4 • In a Category 4 hurricane there will be major damage to roofs, windows, and street signs. • Mobile homes will be destroyed. Category 5 (above 209 kph) Category 5 is the most destructive rating for a hurricane. Category 5 storm surge could be well over 5.5 meters. George Hilldegard portrays “hurricane” Earthquakes in the Southern US Rock Slides Jobs Associated with Natural Disasters • • • • • • • Can any job relate to natural disasters? Meteorologists • Water Resources and Energy Directorate Norwegian Meteorological Institute • Engineering Mathematics • Emergency Services County Government • Writers Directorate of Public Roads • Artists, Newscasters Environmental Science • Reporters Singer/songwriters • Fishermen Words • • • • • • Hurricanes Flooding Equator Atmosphere Troposphere Dangerous • Coriolis Effect • Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale • Categories Today’s Objective • • • • Where do hurricanes form? What conditions do hurricanes need to form? How are hurricanes classified? What are the damages associated with each category of hurricanes? • How does geography affect natural disasters? Your Task • Using the knowledge you have or the ideas this presentation has given you…. • Choose a medium (art, music, drama, poetry) to illustrate your understanding of how natural disasters are impacted by geography. References • Førland, E. (2006). Climate change and natural disasters in Norway – An assessment of possible future changes. Meteorologisk Institutt met.no. Retrieved from http://met.no/Forskning/Publikasjoner/Publikasjoner_2007/filestore/slf-keypoints.pdf • Flood forecasting system Retrieved from: http://www.nve.no/en/Floods-andlandslides/Flood-forecasting-system/ • NOAA (2011) Retrieved from: