Mammalia Phylogeny Powerpoint
advertisement
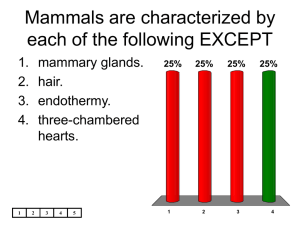
Stuart S. Sumida Biology 342 (Over) Simplified Phylogeny of Mammalia Memorize this. Just kidding. Proboscidea Perissodactylia Cetcacea Artiodactylia Carnivora Chiroptera Primates Rodentia Lagomorpha Edentata Marsupalia Monotremata Proboscidea Perissodactylia Cetcacea Artiodactylia Carnivora Primates Rodentia Lagomorpha Edentata Marsupalia Monotremata Chiroptera Mammalia: •Mammary glands •Hair •Dentary-squamosal jaw-joint •Dentary – single bone of lower jaw •Three middle ear ossicles •Muscles of facial expression •Muscular diaphragm MONOTREMATA: •Most basal of living mammals. •Retain primitive anmiote feature of laying eggs. •Includes only a few relict living forms including duckbilled platypus and spiny anteater. Theria: •Mammals with internal development •Placenta Proboscidea Perissodactylia Cetcacea Artiodactylia Carnivora Chiroptera Primates Rodentia Lagomorpha Edentata Marsupalia Monotremata METATHERIA (Marsupalia): •The pouch mammals •Choriovittiline (chorion + yolk sac) placenta •Living forms have epipubic bones (the primitive placentals probably did as well.) •Restricted primarily to Australi currently, though one form remains in North America (Didelphis; the Virginia oppossum). Kangaroos can be almost orthograde Eutheira: “True placental mammals” With extended internal development Chorioallantoicplacenta Proboscidea Perissodactylia Cetcacea Artiodactylia Carnivora Chiroptera Primates Rodentia Lagomorpha Edentata Marsupalia Monotremata Mammalian Highlights / Features of Note: •Primates are a very early offshoot within Mammalia. •The relationships of basal mammals are not terribly clear – as noted by the polychotomy between edentates, glires (rodents + lagomorphs), primates, and bats. •Cetaceans are actually most closely related to artiodactyls (pigs actually)! •Elephants and their kin are amongst the most derived of mammals Many, many taxa are left out here.