The Anasazi People: A Native American Tribe
advertisement

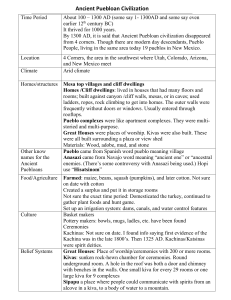
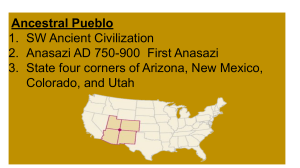
Their tribes evolved from nomadic to sedentary They are the ancestors of the modern- day Pueblo Indians. They were made up of about 20 different Tribes found in Arizona, Utah, New Mexico and Colorado. • Archaeologists identified the Anasazi culture through artifacts found in the ancient dwellings • The earliest traces of the Anasazi were discovered to be from year 1 A.D. to 1300 A.D • By 1000 AD the Anasazi People were establishing permanent villages • Between 1275-1300 AD they had abandoned their Mesa Verde dwellings and moved south, east and west along the Rio Grande River The Anasazi created what Archeologists refer to as “Kivas”. Kivas are communal, above ground buildings that belonged to an individual families or entire clans Probably used as working and/or sleeping quarters • Switched from Kivas between 1200-1300 AD to the “Cliff-Dwelling” style of architecture • Large storerooms became prominent features in Anasazi villages in order to store surplus crops • It is believed they were governed by Clan Elders. • Their society is matriarchal, meaning that homes and farm land are owned by and inherited from the mother • However, some kinds of civil and religious authority were reserved for men. The village chief or kikmongwi was usually a man. Anasazi Farming Practices • At first, they were only hunters and gatherers. • The Anasazi improved their techniques by using terrace farming along Rio Grande River. Anasazi Symbol for fertilization • They farmed mesa tops, plains and canyon bottoms • They captured rain water runoff for agricultural uses • Farming supported as many as 20,000 people • Primary food sources- corn, beans and squash, grown during 7 months. • The Anasazi relied heavily on hunting mountain sheep, elk, mule deer, black bear, antelope and squirrels. Hunting parties also brought back wild plants to supplement the tribe's diet. • They wove blankets, shirts, robes, aprons, kilts, breechcloths, socks, and belts using various plant fibers, animal hair, and human hair. • Shoes- sandals, moccasins, and possibly snowshoes. • Jewelry defined social status- Necklaces, earrings, bracelets, arm bands, hair combs, and pins were made from wood, bone, shell, coral, coal, and stone beads. • Pueblo religion-maintaining harmony with the natural world, which was the key to survival for ancient people. Pueblo Feast Day in NewMexico • Religious concepts/events linked with seasonal tasksfarming (in spring and summer), hunting (in fall and winter) • Animal figures pecked or painted on rockpossibly prayer/rituals for successful hunting. •Public and Private Ceremonies were held. • YES, the Anasazi Did trade with Other Tribes! • They were not isolated from other tribes and participated in trading with other tribes from as far as the Pacific Coast, Gulf of Mexico and the Great Plains. • Theories- starvation, war, civil war, poor sanitation and environmental degradation. • A major drought between 1275 and 1300 possibly forced the Anasazi to abandon their Mesa Verde villages. • The Anasazi Mystery Website- Further information Mesa Verde National Park Website Anasazi State Park Museum Website (in Utah) Present day Pueblo cultural center