Male sexual organ consisting of the root,
shaft, and glans, also contains the urethra,
through which urine is excreted.
Keeps testes cooler than the normal body
temperature (to help make sperm)
When a man gets too hot, the testes fall away
from the body.
When a man gets too cold, the testes pull into the
body.
The location where sperm are stored in the
testes and where nutrients are provided to
help the sperm develop.
Tip of the penis and is very sensitive.
Parental choice.
Called the foreskin, covering the head (Glans)
of the penis. In circumcision, the foreskin is
surgically removed, exposing the end of the
penis.
The inside of a penis is filled with spaces and
fill with blood during an erection
This is why the penis gets larger, and harder
during an erection.
The tube through which the bladder empties
urine outside the body and through which the
male ejaculate exists (Semen).
The ‘duct’ that transports sperm from the
epididymis to the urethra
Prostate Gland:
Walnut sized gland surrounds a portion of the
urethra and produces some of the fluids in semen
Seminal Vesicle:
Located at the base of the bladder, the 2 seminal
vesicles secrete a thick fluid that nourishes sperm
Cowper’s Gland:
A pea-sized gland in the male located behind and
to the side of the urethra that discharges a
component of seminal fluid into the urethra
STRUCTURE: Each of the ovaries contains hundreds of
thousands of immature eggs (ova) from the time of birth
(~40,000-400,000)
FUNCTION: Produce the two hormones; Estrogen and
Progesterone. Holds the immature eggs until puberty. Then
one egg matures each month and is released in a process
known as OVULATION.
LOCATION: A few inches below the waist. One on each side
of the body.
PROGESTERONE:
A hormone that signals the endometrium to
develop in preparation for a zygote (fertilized egg)
ESTROGEN:
A hormone produced by the ovaries; levels in the
blood helps control the menstrual cycle.
Matures egg, builds up endometrium
LH
Makes ovulation occur
FSH
Choose an egg in ovaries
Helps with ovulation
STRUCTURE: Thin, soft tubes. The end that lies on the
ovary has finger-like structures called FIMBRAE that help
sweep the egg into the tube. Tiny cilia line the tube to move
the egg along.
FUNCTION: Carry the released egg from the ovary to the
uterus. If sperm are present, fertilization MUST occur in the
tube!!
LOCATION: Begin at the ovaries and end at the uterus
STRUCTURE: AKA ‘The Womb’ A pear shaped hollow organ
with very thick, muscular walls lined with ENDOMETRIUM
(a rich supply of blood vessels). The base of the uterus is
called the CERVIX. The cervix opening must expand
dramatically during labor/birth.
FUNCTION: To nurture the developing embryo and
fetus.The fertilized egg will implant in the endometrium and
continue to develop in the uterus. If no egg implants, the
lining is shed during MENSTRUATION.
LOCATION: At the top of the Vagina behind the bladder
between the two ovaries.
STRUCTURE: A hollow, tunnel like structure,(~4.5 inches)
very muscular passage that has the ability to expand
dramatically during birth to allow baby to come through, and
provides and exit for menstrual flow. Also, is coated with
vaginal secretions that are slightly acidic to control infection.
FUNCTION: The“birth canal”, and a passage way for sperm
and menstrual blood.
LOCATION: Leads from the base of the uterus (cervix) to the
outside of the body.
Mouth of the uterus, through which the
Vagina extends
Inner most layer of uterus and is loaded with
blood vessels to provide nourishment
necessary to sustain a developing fetus.
Fertilized egg attaches and is nourished as it
develops before birth.
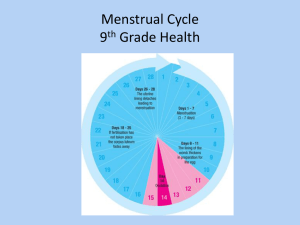
MENARCHE:
The time when a female begins her first menstrual
cycle, usually 8 to 16 years old.
Blood is discharged (endometrium) from uterus
through the vagina for several days.
Latin origin: Menstruation is mensis, meaning
‘month’
Absence of menstruation in a woman who
should be menstruating.
http://kidshealth.org/misc/movie/bodybasics/
bodybasics_female_repro.html
Preparation for a healthy pregnancy begins far
before conception.
Concerns Before Pregnancy:
Men as well as women’s health habits before
conception are important
Both should prepare healthy bodies; limit drinking,
smoking, drugs of all sorts, increase exercise and eat
a proper diet.
Females- born with all eggs- release ONE every
month starting at puberty
Males- produce millions of SPERM everyday starting
at puberty.
If a female and male have sex within several
days of the female's ovulation (egg release),
fertilization can occur.
YES, SEVERAL DAYS!!!
When the male ejaculates (which is when
semen leaves a man's penis), between 0.05
and 0.2 fluid ounces (1.5 to 6.0 milliliters) of
semen is deposited into the vagina.
Between 75 and 900 million sperm are in this
small amount of semen, and they "swim" up
from the vagina through the cervix and
uterus to meet the egg in the fallopian tube.
It takes only ONE sperm to fertilize the egg.
About a week after the sperm fertilizes the
egg, the fertilized egg (zygote) has become a
multi-celled blastocyst
A blastocyst is about the size of a pinhead,
and it's a hollow ball of cells with fluid inside.
The blastocyst burrows itself into the lining of
the uterus, called the endometrium.
The hormone estrogen causes the
endometrium to become thick and rich with
blood. Progesterone, another hormone
released by the ovaries, keeps the
endometrium thick with blood so that the
blastocyst can attach to the uterus and
absorb nutrients from it. This process is called
implantation
Gestation- THE PERIOD FROM CONCEPTION TO
BIRTH-about 38-42 weeks
ZYGOTE-Fertilized Egg- 3 weeks
-cell division
-3 layers from different organ systems of the body
Nervous system and skin
-Muscles and internal organ systems
-Glands and linings of the digestive, respiratory and
urinary tract system form
EMBRYO- 3rd week to 8th week
-Number of cells double approximately every
24 hours
- At 8 weeks embryo is a little more than an
INCH long but already has complete CNS and
digestive system, a beating heart, well
defined fingers and toes, beginnings of facial
features
FETUS- 9 weeks until Birth
-Gain weight and size during this time
-Critical periods for each organ occur
-If any organ is limited by some factor, that
organ will be permanently damaged
-During the critical period, the fetal brain
increases by 100,000 cells a minute.
PLACENTA:an organ that develops during
pregnancy- permits the exchange of
materials between maternal and fetal blood
Has 2arteries and 1 vein
No direct exchange of blood, only nutrients
Fetal wastes are also carried away by the
mother’s blood here
UMBILICAL CORD- Rope-like structure
through which the fetus’s veins and arteries
extend to and from the placenta
AMNIOTIC SAC- Bag of water in the uterus in
which the fetus floats
LIGHTENING: Sensation woman experiences
when the fetus settles into the birth position
1st Sexual intercourse or sperm come close to the
vaginal opening
2nd OVULATION
3rd Sperm must meet egg
4th ONE sperm out of millions must penetrate the
EGG
5th Once one sperm gets in, a protective coating
surrounds egg and no other sperm can get in.
6th Genetic material of the 2 cells unite with in the
fertilized egg
7th Must implant itself into the UTERINE WALLimplantation
8th Cell DIVISION- form a baby
Signs One is Pregnant
Missed Period- Not always an accurate
measure
Breasts become tender and swollen
Nausea
Can take a home Pregnancy Test
Can take a blood or urine test at the doctor’s
office
As cells from the blastocyst take in nourishment,
the embryonic stage, begins.
The inner cells form a flattened circular shape
called the embryonic disk, which will develop
into a baby.
The outer cells become thin membranes that
form around the baby. The cells multiply
thousands of times and move to new positions
to eventually become the embryo
After approximately 8 weeks, the embryo is
about the size of an adult's thumb, but
almost all of its parts — the brain and nerves,
the heart and blood, the stomach and
intestines, and the muscles and skin — have
formed, complete CNS and digestive system, a
beating heart, well defined fingers and toes,
beginnings of facial features
Lasts from 9 weeks after fertilization to birth,
development continues as cells multiply, move, and
change.
The fetus floats in amniotic fluid inside the amniotic
sac.
The amniotic fluid and membrane cushion the fetus
against bumps and jolts to the mother's body.
The fetus receives oxygen and nourishment from the
mother's blood via the placenta, a disk-like structure
that sticks to the inner lining of the uterus and
connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord
Pregnancy lasts an average of 280 days — about
9 months.
When the baby is ready for birth, its head
presses on the cervix, which begins to relax and
widen to get ready for the baby to pass into and
through the vagina.
The mucus that has formed a plug in the cervix
loosens, and with amniotic fluid, comes out
through the vagina when the mother's water
breaks… YES, the Water does BREAK!
When the contractions of labor begin, the walls
of the uterus contract as they are stimulated by
the pituitary hormone oxytocin.
The contractions cause the cervix to widen and
begin to open.
After several hours of this widening, the cervix is
dilated (opened) enough for the baby to come
through.
The baby is pushed out of the uterus, through
the cervix, and along the birth canal.
The baby's head usually comes first; the
umbilical cord comes out with the baby and is
cut after the baby is delivered.
Stage one:
Dilation: cervix is opening
Contractions become harder and harder and
closer together
Crowning: Baby’s head is seen
Episiotomies: surgical cut made in the vagina to
help so the vagina does not rip
Cesarean Section: Surgical birth, in which the
infant is take through a cut in the women’s
abdomen
Stage Two:
Baby is born
Stage Three:
Afterbirth is delivered, placenta and membranes
are expelled
Constipation
Shortness of breath
Frequent urination
Backaches
Morning sickness
Nutrition during pregnancy is important:
Gain 25-35 pounds
7 ½ lb infant at birth= Average
1lb-placenta
4lbs mother’s added blood
4lbs Mother’s added fluid
2 ½ lbs Growth of Uterus
3lbs Growth of breasts
2lbs fluid surrounding infant
7lbs Mother’s fat stores
-Pregnant for 38-42weeks.
When it becomes too cramped for the fetus- Labor
Begins….