File
advertisement
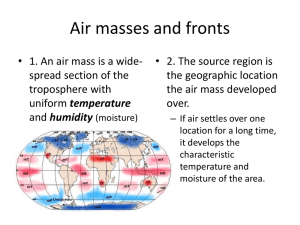
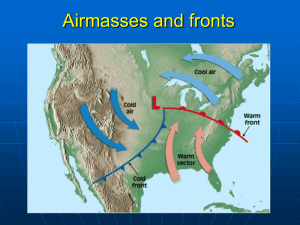
Air Masses and Fronts Air Mass • Large body of air with uniform temperature and humidity • Air masses take on the characteristics of the region from where they originate • Continental (dry) • Maritime (moist) • Polar (cold) • Tropical (warm) Fronts A front is the boundary separating air masses of different densities Fronts extend both vertically and horizontally in the atmosphere Classified by what type of air mass is replacing another Where most weather takes place NSF North Mississippi GK-8 Types of Fronts • • • • • Cold front Warm front Stationary front Occluded front Dry Line front • Each represented by these symbols on a weather map Fronts: Five Types of Fronts 1. Cold Front: The zone where cold air is replacing warmer air • In U.S., cold fronts usually move from northwest to southeast • Slope of front is steep so warm air forced up abruptly • Creates rain and thunderstorms along front • Air gets drier after a cold front moves through NSF North Mississippi GK-8 Fronts: Five Types of Fronts 2. Warm Front: The zone where warm air is replacing colder air • In U.S., warm fronts usually move from southwest to northeast •Slope of front is gentle so creates a line of stratus clouds and precipitation • Air gets more humid after a warm front moves through NSF North Mississippi GK-8 Fronts: Five Types of Fronts 3. Stationary Front: When either a cold or warm front stops moving ( they are in a standoff) •Bring several days of cloudy, wet weather that can last a week or more. • When the front starts moving again it returns to either being a cold or warm front NSF North Mississippi GK-8 Fronts: Five Types of Fronts 4. Occluded Front: Formed when a cold front overtakes a warm front • This occurrence usually results in storms over an area • In U.S., the colder air usually lies to the west NSF North Mississippi GK-8 Fronts: Five Types of Fronts 5. Dry Line (Dew Point Front): Boundary separating a dry air mass from a moist air mass This occurrence can result in tornadoes being formed Usually found in western part of U.S. NSF North Mississippi GK-8 • New Area of Focus: Fronts • Warm Fronts and Cold Fronts are caused by air pressure. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Remember: Cold sinks, warm rises • Cold Front: Form where cold air moves towards warm air. – Creates rain storms. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Cold Front: Form where cold air moves towards warm air. – Creates rain storms. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Cold Front: Form where cold air moves towards warm air. – Creates rain storms. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Direction of travel Direction of travel Cold Cold Warm Cold Warm m Cold Cold Cold Cold Cold Warm Cold Warm Cold Wa Cold “Honey, I think it’s time to get our stuff together.” Cold Air Warm Air Cold Air Warm Air Cold Air Rain • Video (Optional) Cold Front Time Lapse. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i8zq0UXPLX0 • Warm Front: Form where warm air moves towards cold air. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Warm Warm Cold old Warm Warm Warm • Occluded front: When a cold front overtakes a warm front and forces it up (Mix) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Occluded front: When a cold front overtakes a warm front and forces it up (Mix) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Stationary Front: When a cold front and warm front cannot overtake each other (tie) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Stationary Front: When a cold front and warm front cannot overtake each other (tie) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Stationary Front: When a cold front and warm front cannot overtake each other (tie) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Stationary Front: When a cold front and warm front cannot overtake each other (tie) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Stationary Front: When a cold front and warm front cannot overtake each other (tie) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Stationary Front: When a cold front and warm front cannot overtake each other (tie) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Stationary Front: When a cold front and warm front cannot overtake each other (tie) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Stationary Front: When a cold front and warm front cannot overtake each other (tie) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Stationary Front: When a cold front and warm front cannot overtake each other (tie) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Stationary Front: When a cold front and warm front cannot overtake each other (tie) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Stationary Front: When a cold front and warm front cannot overtake each other (tie) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Stationary Front: When a cold front and warm front cannot overtake each other (tie) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Please match the name of the front to the picture. – Warm Front, Cold Front, Occluded Front, Stationary Front A B C D • Please match the name of the front to the picture. – Warm Front, Cold Front, Occluded Front, Stationary Front A B C D • Please match the name of the front to the picture. – Warm Front, Cold Front, Occluded Front, Stationary Front A B C D • Please match the name of the front to the picture. – Warm Front, Cold Front, Occluded Front, Stationary Front A B C D • Please match the name of the front to the picture. – Warm Front, Cold Front, Occluded Front, Stationary Front A B C D • Please match the name of the front to the picture. – Warm Front, Cold Front, Occluded Front, Stationary Front A B C D • Please match the name of the front to the picture. – Warm Front, Cold Front, Occluded Front, Stationary Front A B C D • Please match the name of the front to the picture. – Warm Front, Cold Front, Occluded Front, Stationary Front A B C D • Please match the name of the front to the picture. – Warm Front, Cold Front, Occluded Front, Stationary Front A B C D • Please match the name of the front to the picture. – Warm Front, Cold Front, Occluded Front, Stationary Front A B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents a warm front? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents a warm front? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents a cold front? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents a cold front? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents an occluded front? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents an occluded front? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents an occluded front? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents a stationary front? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents a stationary front? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents a stationary front? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents high pressure? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents high pressure? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents low pressure? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents low pressure? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents a cyclone? F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents a cyclone? Answer: A F A E B C D • Challenge Activity! Which letter best represents a cyclone? Answer: A F A E B C Weather fronts. Learn more at… http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/At mosphere/front.html Weather map fronts. See more at… http://www.nws.noaa.gov/outlook_tab.php D • Video Link Before Quiz – Weather forecasting, fronts, Isobars and more. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lITCF3UPVu4 • Quiz 1-10 Name the Front. Warm, Cold, Occluded, Stationary, Other. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy 6 • Bonus -1 pt for each character (1 minute) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answers: Name the Front. Warm, Cold, Occluded, Stationary, Other. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy 6 6 Weather Maps How to read Weather Maps • There are weather stations all over the world • These stations report on their current weather using symbols • This data is plotted and a view of conditions are seen Station Model How to read • • • • Temperature Weather conditions Dew point Atmospheric pressure • Wind direction and speed Wind Barbs • Wind Direction is stated where it is blowing FROM • This is blowing from southeast • Feathers show how fast blowing – Full feather = 10 knots – Half feather = 5 knots – Little feather = 1 knot Isobars Temperature Maps Isobars • ‘iso’ = equal • “bars” = barometeric pessure • • • • Shows line of equal atmospheric pressure Lines close together = strong winds Lines further apart = gentler winds Generally measured in 4 millibar increments • Can also have isotherms on weather maps (measured in 10 degree increments) Wind Directions • Low pressure system aka “cyclone” – Winds blow in a counterclockwise direction • High pressure system aka “anticyclone” – Winds blow in a clockwise direction