Fronts and Air Masses
advertisement

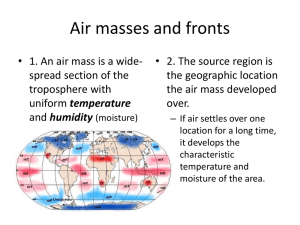
Dr. Hooda What is an air mass? A large body of air having nearly uniform conditions of temperature and humidity at any given altitude. • Warm air forms over tropical regions near the equator. • T- Tropical • Cold air forms over polar regions. P- Polar • Wet air masses form over water m- maritime • Dry air masses from over land. c- continental 3 • Moisture content is noted by the first letter. m – maritime – wet c – continental – dry • Temperature is noted by the second letter. P – polar – cool T – tropical - warm 4 • Continental Polar (cP) , “cold and dry” – closer to the Poles over land-locked regions. • Continental Tropical (cT), “warm and dry” – closer to the Tropics over land-locked regions. • Maritime Polar (mP), “cold and damp” – closer to the Poles over water. • Maritime Tropical (mT), “warm and humid” – closer to the Tropics over water. 6 7 8 The advancing edge of a mass of cold or warm air. • A front is a boundary between air masses. Four types of fronts and map symbols The directions that the bumps face is the direction the front is moving. 1. Cold front 2. Warm front 3. Stationary front 4. Occluded front 10 When a fast moving cold air mass runs into a slow moving warm air mass and the thicker cold air slides under the lighter warmer air. • Bring thunderstorms, rain or snow. • Most tornadoes develop from thunderstorms on the edge of a cold front. • Cold front followed by cooler drier air. • http://www.mesoscale.iastate.edu/agron 206/animations/05_cnWfronts.html 12 When a moving warm air mass collides with a slowly moving cold air mass and the warm air moves over the cold air. • Brings drizzly precipitation. • Followed by clear warm weather. http://www.mesoscale.iastate.edu/agron206/animations/05_c nWfronts.html 14 When a cold air mass and warm air mass meet, but neither air mass has enough force to move the other air mass. • Many days of cloudy, wet weather. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VwI1NmESxss 16 When a warm air mass is caught between two cooler air masses and the thicker cold air masses move underneath the thinner warm air mass and push it upward. • Brings cool temperatures with large amounts of rain or snow http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4gc7puH279s 18 Cold Front, Warm Front and Occluded Front Animation • http://www.phschool.com/atschool/phsciexp/active_art /weather_fronts/ • http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/c ontent/visualizations/es2002/es2002page01.cfm?chap ter_no=visualization 19 20 Quiz 1. Describe a maritime polar (mP) air mass, in terms of moisture and temperature. 2. What is the name of an air mass that forms over water? 3. What is the name of an air mass that forms over land? 4. What is the name of an air mass that forms in a cold region? 5. What is the name of an air mass that forms in a warm region? 6. Describe a continental tropical (cT) air mass, Moisture and temperature. 21 Quiz 7. The boundary between two air masses is called a ______________________. 8. A cold air mass meets and pushes a warm air mass out of the way. What type of front am I? 9. A warm air mass is trapped between to cold air masses. What type of front am I? 10. A warm air mass meets and pushes a cold air mass out of the way. What type of front am I? 11. I am a front that brings drizzly rain and am followed by warm clear weather. Name me. 12. A cold air mass meets a warm air but neither is very strong. They are separated and many days of wet , cloudy weather occur. Which types of fronts can you find on this map?