Kansas Journey PPT Ch. 1
advertisement

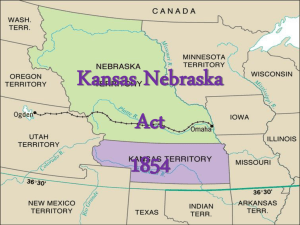
The Kansas Journey Chapter 1: Home on the Range History and Geography History tells us about the people who came before us while geography introduces the natural features of Earth. Geography studies location, place, regions, movement, and the interaction between humans and the environment. Both history and geography look at where and how people live. Location Kansas is called “America’s heartland”, because it truly is the center of the United States. We use latitude and longitude to find the absolute location. Kansas is between the 37th and 40th parallels north latitude and between 94 and 102 degrees west longitude. The relative location explains where a place is in relation to other places. Place All locations have different physical features, which are the natural landforms and characteristics of a place. Kansas has rivers, hills, soil, and rocks. Kansas rises at an incline of 10 feet per mile, east to west. About 1/3 of Kansas is prairie, on of the most complicated ecosystems. A Kansas prairie. The Permian Sea The physical features of Kansas are the result of an inland sea. Kansas was covered by a shallow ocean of salt water, the Permian Sea. The creatures that lived in the sea died and organic material decayed and compressed to form limestone. Deposits of natural resources like coal, oil, and natural gas formed. This is a picture of the Permian sea floor. Tallgrass prairie National Preserve Land that looks like a sea of grass was formed out of the floor of the Permian Sea. The Flint Hills are formed with limestone and shale deposits. Visitors of the National Preserve can see land much like early American Indians and explorers did. 400 different plants, 150 species of birds, 39 reptiles and amphibians, and 31 species of mammals live in the preserve. Water Underground in western Kansas lies a reservoir called the Ogallala Aquifer. It runs under other states, too. It is commonly used for irrigation. Cheyenne Bottoms is one of the few natural lakes in KS. But, it no longer is completely natural. Water levels of Cheyenne Bottoms have to be altered. Half of the bird species of the US can be found here on their seasonal migrations. These birds include endangered whooping crane, peregrine falcon, and bald eagles. Lakes Kansas has few natural lakes. All the lakes we see today are the result of flood-control projects. Some lakes are for drinking water and irrigation. Cheyenne Bottoms One of the few natural lakes in Kansas. Half the bird species can be found here on their seasonal migrations. Protecting Our Water Kansas sued Colorado over water rights. The U.S. Supreme Court ruled in favor of Kansas. Vs. Grasslands Characterized by tall or short grasses. Big and Little Bluestems are most common. The grasses protect the soil from erosion. Kansas is home to 1,600 varieties of blooming plants. Prairie Fires Fires are part of the life cycle of the prairie. Today they are set by man. Promotes growth. Animals 700 species of fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals can be found in Kansas. Insects 3,500 different Insects can be found in Kansas. Only 1% are harmful to plants. Many insects help pollinate flowers. The most destructive insect is the grasshopper. In the 1870’s grasshoppers destroyed most of the Kansas crops. Climate The climate of Kansas is dramatic because it is changeable, extreme, and unpredictable. Wind chill is a dominant feature of Kansas climate. How the temperature feels is affected by the speed of the wind and the moisture in it. Precipitation is measuring the amount of moisture that reaches the ground from rain, snow, sleet, hail, and mist. The average is around 40 inches in eastern KS, and less than 18 inches in western KS. Regions of Kansas A region is an area with one or more features that make it different from surrounding areas. Kansas is divided into 11 physiographic regions. High Plains – Flatlands formed by sediments Red Hills – Hills red with iron oxide. Glaciated Region – Glaciers that once covered part of the US. Ozark Plateau – Oldest surface rock in the state. Arkansas River Lowlands – Formed of rocks from the Rocky Mountains. Wellington-McPherson Lowlands – Grass covered sand dunes. Underground water and salt. Cherokee Lowlands – Fertile soil. Regions of Kansas Chautauqua Hills – Osage Cuestas – Low hills topped with East facing cliffs with sandstone. gentle slopes to the west. Smoky Hills – Sandstone, limestone, and chalk. Flint Hills Uplands – Erosion of limestone and shale formed rolling hills. Interaction of Humans and the Environment From the beginning people have used natural resources from the earth. Trees were cut down, stone removed from the ground, and people drank the water from the rivers. The Pawnee built earth lodges and the Wichita made grass homes. Settlers came to Kansas and built homes of sod and wood. Today we change the environment to meet our needs by removing oil, gas, coal, zinc and other resources with the help of technology. Strip mining. Movement of People, Products, and Ideas People travel from place to place, to share what they know and ideas. Kansas is a crossroad. As people travel through a place, so do ideas and information.