340_13HistoricalLinguistics-1
advertisement
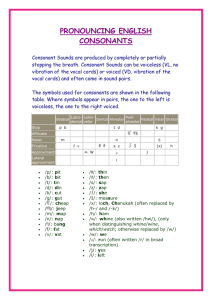
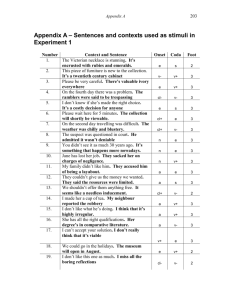
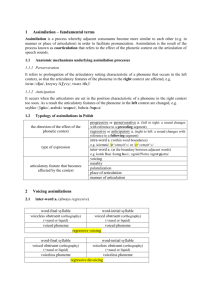
Historical Linguistics Historical Lingustics Definition: the study of how languages change over time. Reasons for Language Change The nature of society geography and isolation of groups, invention/discovery of new things, imperfect learning, and social status. Example: Martha’s Vineyard, Massachusetts Move to lower socioeconomic status to show membership in year-round resident group Example: Children learn imperfectly and transmit their errors to younger children. Reasons for Language Change The nature of language ease of articulation, analogy, and metaphor Example: Metaphors eventually change the meaning of words into their metaphorical meaning (arms (on the body) to arms (weapons) and brazo (arm) to braceros (laborers)) Language Change Occurs in Phonetics Phonemics Morphology Syntax Semantics Phonetic Changes Regular sound shifts that occur over time in many languages bh dh gh Grimm’s Law (1822) b b p p d d t t g g k k Voiced voiced aspirated plosive aspirated EG. Latin pater piscis tres voiced voiceless plosive plosive English father fish three voiceless f th x voiceless plosive p-f, t-th p-f t-th Verner’s Law When the stress/accent falls on the root syllable of the word, Grimm’s law works; when it does not, then Verner’s Law works: p t k b d g Types of Sound Change Assimilation – one sound influenced by the pronunciation of a neighboring sound. (Don’t be silly – Dombe silly) Dissimilaton – when the same consonant sound appears close together, one will disappear (surprise – supprise, governor – govenor) Haplology – the loss of one of two repetitive syllables (probably – probly, Anglaland – England) Loss – a sound disappears – Old English eahta (8) Prothesis – introduction of an extra sound at the beginning of a word – Latin scola to Spanish escuela. Apocope – the loss of final sounds – Old English helpe to help. Etc……… Types of Morphological Change Analogy – irregular forms change to conform to regular patterns – helpan, healp, holpen to help, helped, helped Gender changes – Early Indo European masculine, feminine and neuter to French - masculine and feminine Dutch - common and neuter English - none German and Greek – masculine, feminine and neuter Types of Semantic Change Lexical history (etymology) Borrowing - French from English - weekend, parking Loan Translation - German from English – telephone to ferensprecher fern=distant, sprecher=speaker Obsolescence - Concept no longer useful – English telex Extension - A word widens its meaning – Latin virtue is a male quality, English is used for both males and females Amelioration – loss of negative connotation, English mischievous used to mean disastrous Reconstructing Past Languages Contemporary accounts – writings by authors who described language at the time Poetic evidence – rhyming Alphabetic evidence – alphabets had added symbols for sounds Comparative reconstruction based on families of languages In future – tape recordings and video recordings. Reconstruction of Proto Indo European - Romance Reconstruction of Proto Indo European (Germanic) Patterns of Language Change Change from above – attempts to rise in status Change from below – using language as an indication of membership in a particular group S-shaped curve – slow beginning, rapid center, slow ending Wave Model – movement through social and geographical space. Language Families Two kinds of family trees : Morphological – from the grammar of the languages Genetic – from historical documentation of how languages evolved http://www.danshort.com/ie/iecentum.htm http://www.danshort.com/ie/iesatem.htm Study Guide Historical Linguistics Geogrphical isolation Culural invention/discovery Imperfect learning Status differences Grimm’s Law Verner’s Law Assimilation Dissimilaton Haplology Loss Prothesis Apocope Analogy Gender changes Borrowing Loan translation Obsolescence extension Amelioration Contemporary accounts Poetic evidence Alphabetic evidence Comparative reconstruction Tape and video recordings Proto Indo European Change from above Change from below S-shaped curve Wave model Morphological language families Genetic language families