Power Point For Chapter Four - semo.edu
advertisement
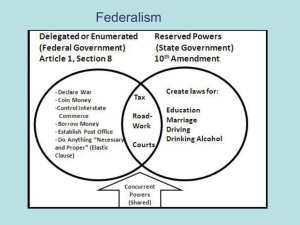
Chapter Four Federalism Instructor: Kevin Sexton Course: U.S. Political Systems Southeast Missouri State University What is sovereignty? & Who has it? Sovereignty: who has ULTIMATE AUTHORITY. In this class we will discuss GOVERNMENTAL SOVEREIGNTY. • which government has the ultimate authority over a specific geographic region or area. To better understand the concept lets look at the three most common forms of governmental structures found in the world: 1. Unitary 2. Confederation 3. Federal Unitary Government Unitary Form of Government: • Sovereignty rests with one central government. • The central government has the authority to create and disband all other levels of government. • Most common of the three forms of government. •Great Britain and France are examples of this form. • There are local governments in Great Britain and France, but they act primarily as administrative arms of the national/central government. • In addition, they receive their legitimacy, or right to exist from the national/central government. Confederation Confederation Form of Government: • Sovereignty rests with each individual member of the group. • National/central government receives its power or authority from the group of individual members. • United States under Articles were an example of this. • Southern States during the Civil War were another example. • Many other examples of this type of relationship. • European Union • O.P.E.C. • A.F.L.C.I.O • SEMO’s Greek Council Federalism Federal Form of Government: • Sovereignty is shared between a national/central government and other levels of government (State Governments). • The United States and Germany are examples of this form of government. • Least common of the three forms of government. • Sovereignty over the same geographic regions is shared by more than one governmental unit. Shared Sovereignty Here are SOME of the governments that have sovereignty and/or power over you If you live in Cape Girardeau, Missouri: & United States Govt & Missouri State Govt Cape Girardeau County Govt & • City of Cape Girardeau • Cape Girardeau Public School District • Levee District • Water and Sewer District • Fire District • PLUS OTHERS Federalism & Democracy Federalism strengthens America’s democratic ideals by: 1. Allowing many levels for issues to be addressed. 2. Allowing many levels for individuals to be involved the political process. 3. Allowing many level for varying opinions and values to be expressed, and represented. (In elected bodies) Paradoxically, Federalism has also been a large part of why we continued to have racial discrimination well into the 1970s. What do you do when the local opinions and values Support discrimination? i.e. – voting laws, Jim Crow laws,……. State & National Governments The State and National (federal) governments are the two major levels of government that we will focus on this semester. Why not include local governments in our study: Dillion’s Rule states that local governments are the creation of states, and that state legislatures can create, alter or abolish them at their discretion. Federalism in the United States In the United States there are actually 51 different major governments. One Federal Government & Fifty State Governments Each of one us, regardless of where we live are represented by elected officials, at both the Federal and State Level. SIMULTANEOUSLY How People Are Represented in a Federal Form of Government Since each level of government (federal & state) is sovereign each has its own rules and regulations (laws) and each has individuals that are elected to create and manage those laws. & You have individuals elected at each level to represent you, at that level of government. The Elected Officials Assignment is designed to ensure you are aware of the organizations (state and national legislatures) in which you have people that represent you at each level of government, and who those people are. National Representation Each American citizen has people elected/appointed to represent them in the national government, These people represent their constituents in Washington, D.C. President (Executive Branch) Legislative branch U.S. Senate (2 from each state) U.S. House of Representatives (9 from Missouri) Judicial Branch U.S. Supreme Court •They represent their constituents on Federal Issues. • They Do not have the authority to tell states what to do on state and local issues. State Representation Each state citizen has people elected/appointed to represent them in the state Government. These people represent their constituents in their state capital (Jeff City). Executive Branch Governor Legislative Branch A State Senate & A State House of Representatives All states, except Nebraska, have bi-cameral legislature Judicial Branch State Supreme Court •They represent their constituents on state issues. •They do not have the authority to tell the federal government what to do on federal issues, even if they take place within their state. Shared Power Federalism is based on the concept of SHARED POWER. Anytime you share ANYTHING there must be rules and definitions that outline how the item will be shared. i.e. shared custody of a child Our political system has rules that define how power will be shared between the various levels of government. WHERE DO WE FIND THOSE RULES? U.S. Constitution Supreme Court Decisions Have been needed to clarify some issues. U.S. Constitution and Federalism Article VI, Paragraph 2 of the United States Constitution is known as the Supremacy Clause: "This Constitution, and the laws of the United States which shall be made in Pursuance thereof; and all Treaties made, or which shall be made, under the authority of the United States, shall be Supreme Law of the land; and the Judges in every state shall be bound thereby, any thing in the Constitution or Laws of any state to the contrary notwithstanding.“ In short it states that: The U.S. Constitution will the SUPREME LAW of the land & Federal Laws will take precedence over State Laws Supremacy Clause This does not mean that the Federal government is always supreme. The Federal government is only supreme on issues that the Federal government has authority or when the State and Federal governments share power. If the Federal government does not have the power to regulate an issue, then the state will be supreme. In short: When a State and Federal law conflict with each other The Federal law will be supreme. U.S. Constitution and Federalism (CONTINUED) Article I, Section 8, Clause 3 of the U.S. Constitution is known as the Commerce Clause: "To regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and among the several States, and with the Indian Tribes." There is no question that the Federal government has the power to regulate INTERSTATE Commerce. But….. What is considered INTERSTATE COMMERECE. It has changed over the years. As the definition has changed the power of the Federal government has grown. Powers of the Federal and State Governments There are three basic types of powers dealt with in relation to the U.S. Constitution: Enumerated Implied Reserved HINT!!! YOU WILL SEE THESE AGAIN!!! (ON THE FIRST EXAM) TAKE GOOD NOTES ON THESE!! Enumerated Powers Those specific powers of the U.S. Congress listed in the U.S. Constitution. There are 18 specific powers of Congress listed. They include (but are not limited to): • Coin Money • Declare War • Tax • Create and operate Post Offices SEE THE HANDOUNT AVAILABLE ON THE COURSE WEBSITE Implied Powers IMPLIED: To involve or indicate by inference, association, or necessary consequence rather than by direct statement. OR…. Something that is assumed to exist, even though it is not expressly stated. There are a number of powers that the Congress have that are not enumerated or expressly listed. Why then does Congress have those powers? THE NECESSARY AND PROPER CLAUSE The 18th power on the list of ENUMERATED POWERS THE NECESSARY AND PROPER CLAUSE “To make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers, and all other Powers vested by this Constitution in the Government of the United States, or in any Department or Officer thereof” Examples: Why, in the 1960s, could you burn and American flag, but not your draft card? McCullough v. Maryland (1818) Could the State of Maryland NULLIFY the federal law creating A national bank? Reserved Powers Tenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution “The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the states, are reserved to the states respectively, or to the people”. Examples of Reserved Powers 1. Voting 2. Education Three Eras of Federalism in the U.S. The relationship between each level of government in the U.S. has changed or evolved over the course of our history. The Evolution of U.S. Federalism Can Be Broken Down Into Three Eras are: 1. Dual Federalism (Layer Cake Federalism) 2. Cooperative Federalism (Marble Cake Federalism) 3. Fiscal Federalism (Modern Federalism) Dual Federalism Both Levels of government (nation and state) are completely sovereign within their own SPHERES of authority. Each level’s SPHERE OF AUTHORITY was determined, primarily by the U.S. Constitution as was discussed on the previous slides. Federal Sphere of Authority From ratification of The Constitution Until F.D.R. (Great Depression) •18 Enumerated Powers State Sphere of Authority •10th Amendment VERY CLEAR LINE BETWEEN THE TWO LEVELS Cooperative Federalism Both levels of government continue to maintain sovereignty Over many or most issues within their SPHERES OF AUTHORITY. BUT….. They begin to work together on some issues that are of Interest to both LEVELS. i.e. – Welfare of citizens during the Great Depression Math and Science education after Sputnik Begins with F.D.R. (Great Depression) and continues through World War II into present day. Cooperative Federalism (Continued) No Clear Line Between Two Levels Of Gov’t Begins with F.D.R. (Great Depression) and continues through World War II into present day. Fiscal Federalism The STATE governments still maintain AUTHORITY over Many of the issues that had in the past, but the POWER over many of those issues have been transferred to the FEDERAL government. WHY HAS THIS TRANSFERE OF POWER TAKEN PLACE? $$$$$$$$$$$$ It started in late 1930s, gained a lot of momentum and strength in the 1960s and 1970s and we continue to be in this era of federalism. Federalism Today Much of the relationship between the state and federal governments today are influenced by money. It is how the federal government “got their foot in the door” of state issues, and it is how they keep pressure on the states to do what they would like them to do. Examples: Helmet Laws Blood Alcohol Levels Affirmative Action Fiscal Federalism How Does It Work The Federal Government passes money on to the State and local governments through a system Known as GRANTS IN AID. Three Basic Types of Grants in Aid: 1. Categorical Grants 2. Block Grants 3. Revenue Sharing Categorical Grants Used to address specific issues. Group Receiving the funds are limited on what they can use the funds for. Allows the federal government more control over how the Funds are used. Preferred method of grant in aid of the federal government. About 90% of all federal grants dollars. Example: • AFDC in 1960s thru 1980s. • Aid To Families With Dependent Children • Program designed to help address poverty. • Federal government gave funds to state, but they had to be administered in very specific manner. Block Grants Used to address general topic area. Group receiving funds are given much more flexibility in how they spend the funds. Federal government has given less control. Preferred method of grants for those conservatives favoring DEVOLUTION of more control back to the states. Examples: CSBG, CDBG, TANF, ……. Revenue Sharing Federal Government simply gives (shares) a certain percentage of the tax Revenue it gathers with each of the states. This was the least restrictive of the grants in aid. The money could be used For whatever the state wanted to use. It was a method created by conservative lawmakers (primarily Pres. Ford) in An attempt to DEVOLVE more power back to the states. No longer used. Block Grants are the method now used to DEVOLVE more Power back to the states. Unfunded Mandates What are they? Rules and regulations created by the federal government Calling for state or local governments to do something, Without providing the funds to carry it out. i.e. – A.D.A. Why do the states stand for them? Fear that not doing this will cause them to lose money for This program, or worse yet, other programs as well. EXAMPLE OF THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN POWER AND AUTHORITY