Decolonization of India and Indo
advertisement

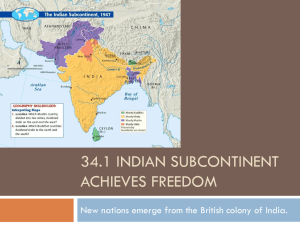
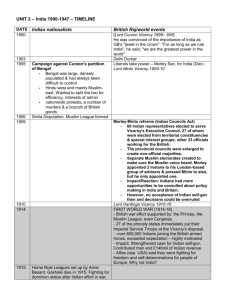
History 12 Ms Leslie Britain and France bankrupt after WWII. 2. Colonial subjects do not was things to return to how they were. 3. New super-powers were ideologically opposed to the concept of empires 1. India is a colony of Britain for 200 years Provides Britain with cotton The Indian Civil Service was the most desirable of all foreign service postings. Britain provided education for the middle class Included modern states of: Pakistan India Bangladesh Burma Islands in the Indian Ocean Huge country = lots of bureaucracy So educated Indians ran the country This fostered nationalism Formed in 1885 Nehru and Gandhi’s political party Want independence for India Britain does not think they are able to govern themselves he opposed western industrialization – it brings misery Satyagraha Concerned with the poverty of the peasants Wanted to abolish the caste system – help the untouchables People in the lowest caste Jobs: butcher, removal of rubbish, manual labourers, cleaning latrines and sewers. segregated, and banned from full participation in Hindu social life. could not enter a temple or a school, Indian contribution made nationalism stronger Woodrow Wilson’s talk of selfdetermination and Lenin’s views on national self-determination provided ample encouragement. 1917 promised self-government in the future Churchill opposed to this 1919 Created a diarchy More government control provincially but not federally Promise to consider more concession sin 10 years Gandhi called for a country wide general strike on April 6, 1919 April 13, 1919, in the Punjab Province, 5 Europeans were killed in riots. General Dyer, commanding the security forces in the area resorted to lethal force in trying to disperse a crowd of 5,000. The machine gun fire killed 379 Indians Dyer is forced to retire over this. Gandhi organizes peaceful protest Sit down strikes Non-payment of taxes Boycotts non-co-operation Other Indians are more violent Soon Indians of all backgrounds echoed the slogan of the Congress Party, “Quit India”. The Simon Commission in 1928 recommended self government for the Provinces. The Congress wanted dominion status to be on par with Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa. March 12, 1930 – Salt march begins. He goes to the sea with 80 people to make salt illegally. The Costal people follow his example. 60,000 Indians are imprisoned. http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=WCvuo_NZcj o&feature=related Gandhi, recently released from jail, led his famed march to the sea to produce salt – in violation of the law. Gandhi returned to jail where he goes on a hunger strike to protest the treatment of the untouchables. London Congress not present as they’re in jail Gandhi shows up for the last one, in traditional dress Churchill calls him “this malignant and subversive fanatic.” Nothing comes of the conferences and Muslims and Hindus can’t agree on government Only Defense and Foreign affairs was to remain in British hands. Yet, once again Congress was unsatisfied. The Princes who continued to rule their own states within India also refused to cooperate. Though Congress desired a united India (dominated by a Hindu majority), Jinnah and his Muslims sough a separate Pakistan. In a region where Muslim and Hindus had intermingled under the British a division could be easily managed. 1 million Indians fought for Britain Gandhi supported as he thought it would help Britain give independence Britain responded with the Defense of India Act and the Rowlatt Act which made independence movements illegal. India was put into WWII but Viceroy Linlithgrow with out approval from domestic political leaders. Britain is distracted by the war to pay any attention to India By 1942 Britain is forced to consider independence Congress leaders and thrown in jail for speaking against the British As the Congress leaders re-emerged from jail, negotiations were opened again, but Congress leaders found that the Muslim League had now established themselves in important political positions in several provinces. The struggle between the two parties intensified. Gandhi was opposed to the very concept of division. Nehru found it distasteful, but accepted the political necessity. Jinnah would consider nothing else. Struggle between the Muslim minority and the Hindu majority Britain turned heir back on India and instructs Viceroy Mountbatten to prepare India for Independence India to divide into 2 – India for Hindus and Sikhs and Pakistan (East and West) for Muslims. Gandhi against this. With the formation of an interim government under Nehru in 1946 (included 2 Muslims), violence broke out. Jinnah inflamed the situation, calling for ‘direct action’ to ensure the formation of Pakistan. 5,000 people were killed in Calcutta, and the troubles spread to Bengal. Muslims killed Hindus, who retaliated and were in turn retaliated against. The British announced, in early 1947, that the British would withdraw no later than June 1948. Viceroy Mountbatten was now well aware that partition was the only thing that could prevent civil war. Fearing that delay would only foster greater violence, Mountbatten shortened the length of time before independence, settling on August 1947 – Gandhi opposed, but most of the Congress Agreed the problem of how to divide the intermixed religious groups was a nightmare. Hindu and Muslim minorities existed in practically all parts of the sub-continent. The majority Muslim areas were furthermore located in two sections, more that 2,000 miles apart. The Punjab and Bengal, with mixed populations, had to be divided. Millions of people were stranded on the wrong side of the boundary. 10 million flee Pakistan. Violent clashes occurred and horrendous slaughter took place. In the Punjab about ¼ million people were killed. About 1 million die in Bengal. Gandhi is able to stop the violence by going a hunger strike. It was not until the end of 1947 that the violence began to die down it was the assassination of Gandhi (by a Hindu fanatic) in 1948 during a second hunger strike against violence that brought the terrible cost of the violence home to all. The Indian Civil Service, one of the finest organization of its kind anywhere, was split in two. 80% when to India and 20% to Pakistan. So too was the Indian army Officers and men were given the choice of which successor state they would serve. All assets – cash and material goods – along with India’s national debt, were divided between the two Some Muslims even called for the Taj Mahal to be dismantled and shipped to Pakistan, since a Muslim ruler had constructed it. No consideration given to Sikhs o In 1962 India fought a border conflict with China In 1965 war broke out between the two states. Border clashes escalated into full scale war. With China threatening India on its northern borders, India was unable to press the full weight of its superior military strength against Pakistan. Eventually the USSR helped arranged a peace based on a return to the status quo. In 1971 Pakistan was divided by civil war. East Pakistani opposition to the political dominance to the West encouraged a call for separation. The ravaged of a disastrous cyclone and tidal wave increased the misery. India intervened, launching an invasion of East Pakistan in December, 1971, winning easily to make Bangladeshi independence a reality. - - Democracy Mass unemployment, poverty and corruption AIDS 80,000,000 Untouchables Army loyal to government Gandhi honoured for how he was not his politics A Nuclear power After WWII, the French wanted to return to their South East Asian colony, but their subjects in French Indo-China really did not want them North Vietnam had an effective resistance movement to the occupying Japanese had been organized by Ho Chi Minh. Ho’s Vietminh simply continued the struggle when the French retuned, Ho declared an independent Vietnam in 1945. Ho’s communist guerillas earned the support of the peasants with land reform. The success of the Chinese revolution brought a steady stream of supplies from Mao’s China. The French, unable to finance the war against the Vietminh themselves, turned to the USA for help and were granted financial and military aid to assist in the cold war struggle against communism. The Americans were not in favour of a continued colonial presence, favouring independent non-Communist governments in the Area. After the French defeat at Dien Bien Phu in 1954, the French gave in to the inevitable and withdrew. Formal settlement between Indochina and France Laos and Cambodia were given independence, while Vietnam was temporarily partitioned at the 17th parallel, until elections in 1956 could determine its future. Elections never happened the Communist regime of Ho Chi Minh in the North faced the South Vietnamese of Ngo Dinh Diem Ngo Dinh Dien was a catholic governing a mostly Buddhist population. Neither could be properly described as democratic Diem’s policies were anti-Buddhist. The led to the famous self-immolation of a monk in June of 1963 Thích Quảng Đức was protesting the religions oppression of Diem His protest didn’t work A guerilla war (Viet Cong) began in the south, with the Southern Vietminh forming the basis of the new NLF (National Liberation Front), armed and supported Ho’s North. The North never accepted a divided Vietnam. Diem came increasingly to rely on American support against the spread of communism. End :)