Pronouns - types of.ppt - Liberty Union High School District
advertisement
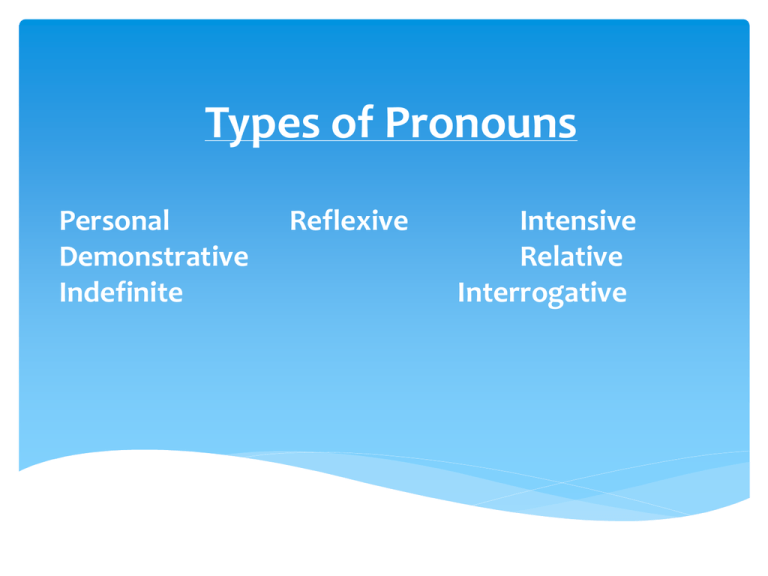
Types of Pronouns Personal Demonstrative Indefinite Reflexive Intensive Relative Interrogative 1. Personal Pronouns A personal pronoun refers to the one speaking, the one spoken to, or the one spoken about. Karen ate pizza. She was hungry. The word "she" is a personal pronoun that refers to "Karen." Examples Singular Plural First Person I, me, my, mine We, us, our, ours Second Person You, your, yours You, your , yours Third person He, him, his, They, them, she, her, hers, their, theirs it, its 2. Reflexive Pronouns A reflexive pronoun is a pronoun that refers to the subject and is necessary to the meaning of the sentence. It ends in "-self" or “-selves” Bob enjoyed himself at the gym. “Himself” is a reflexive pronoun; it is necessary for the sentence to make sense. 3. Intensive Pronouns An intensive pronoun emphasizes a noun or another pronoun. It is not necessary to the meaning of the sentence. Did you decorate the room yourself? “yourself” is not necessary to include. Reflexive and Intensive Examples Singular Myself Yourself Himself Herself itself Plural Ourselves Yourselves Themselves 4. Indefinite Pronouns An indefinite pronoun is a pronoun that refers to persons, places, or things, in general. It may or may not be specifically named. Someone stole my wallet! The word "someone" is the indefinite pronoun. Indefinite Examples Singular Anybody, anyone, Each, either, Every, everybody, Everyone, Neither, nobody, No one, nothing, one Plural Both Many Few several 5. Demonstrative Pronouns A demonstrative pronoun is a pronoun that replaces and points out a person, place, thing, or idea. These lemons are sour. These are sour. The word "these" is a demonstrative pronoun; it replaces the word lemons. Demonstrative Pronoun Examples This That These Those 6. Interrogative Pronouns An interrogative pronoun introduces a question. Who, whom, and which are interrogative pronouns. Who wrote Twilight? The word “Who" is an interrogative pronoun. Relative Pronouns Relative and interrogative pronouns are similar. who which whom that whoever whichever whomever whose Who, Whom, Whose Relate to people. THAT Relate to things and persons (only when a class or type of person is meant). Restricts the meaning of the sentence, making the words that follow necessary to the meaning of the sentence. The Internet service provider that installed our network provides 24-hour online assistance. We received an e-mail attachment that contained video files. Which Refers primarily to things. Introduces nonessential clauses Some e-mail services provide instant messaging systems, which allow you to chat with your friends. This e-mail software, which I downloaded from the Internet, eliminates junk e-mail.