Change by Other Means - RunningStart Forms
advertisement

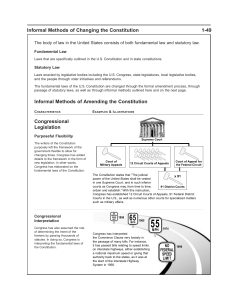
Change by Other Means Government/CWP Chapter 3, Section 3 Mrs. Huston Five Methods • Legislation—passing laws • Executive Action—using powers to define and interpret • Court Decisions—interpreting and applying the Constitution to Court Cases • Party Practices—shaping the processes of government through party politics • Custom—establishing precedents, shaping processes of government Basic Legislation • Congress has passed laws to clarify several Constitutional provisions • It began with the Judiciary Act of 1789 • Only the Supreme Court was established by the Constitution • Congress has added other Federal Courts through the years Commerce Powers • The Constitution gives Congress the power to regulate commerce • By adding additional laws, Congress has clarified and expanded those powers through the years Presidential Actions • Executive Agreements—a pact made by the President directly with the head of a foreign state • Treaty—a formal agreement between two or more sovereign states • Main difference—treaties must be approved by the Senate • Both are legally binding Conflicts • The Constitution says that only Congress can declare war, yet the President has sent troops into combat many times in history without the approval of Congress Court Decisions • The courts, especially the Supreme Court, interpret and apply the Constitution • Example: Marbury v. Madison • Established the principle of Judicial Review • Courts only review when a case is brought, not automatcially Supreme Court • President Woodrow Wilson called the Supreme Court a Constitutional Convention in continuous session • This is because they apply the Constitution in many ways in the cases they decide and so they have a large influence Party Practices • Political parties not mentioned in the Constitution at all • They have had a large impact anyway • Example: the nomination process for the office of President, using party conventions • Example: both houses of Congress are organized based on political party Custom and Usage • Long-standing customs become almost as powerful as written laws • Example: the President’s Cabinet is not mentioned in the Constitution, but has become a significant advisory body Senatorial Courtesy • Although not written down, it is customary for the President to seek the recommendations of the Senator or Senators from the state in which he intends to make appointments for positions such as federal judges, US marshals, etc. When a Custom is Violated • For nearly 150 years, Presidents followed a “no third term” tradition • But in 1940 and again in 1944 Franklin Delano Roosevelt broke that tradition by seeking, then winning first a third, then a fourth term • As a direct result, the 22nd Amendment was added to the Constitution limiting the President to two terms Presidential Succession • A VP has taken over 8 times in history after the death of a President • This wasn’t actually in the Constitution until the 25th Amendment in 1967 • Before that, the powers and duties of the president, but not the office itself, were given to the VP according to the Constitution The End