Social Motives - Grand Junction High School
advertisement

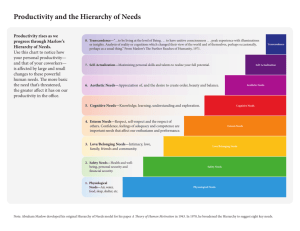
Social Motives David Skinner, Nicole Stoddard, Liz Heaps, Heather Hutchinson, and Max Martinez Psychology 3rd hour Different Theories Fear of Success Will cause people to do all in their power to avoid success Women tend to suffer more so than men Raised to believe that to succeed was not acceptable for women Example: A woman in college may feel it is ok to do well on her finals, but it would not be ok for her to be at the top of her class, above all the men. Different theories Expectancy-Value Explains goal-directed behavior Estimated likelihood of success to what the goal is worth How likely is it that a student barely passing high school will become a doctor when that goal means little to them? How about a straight B student who wants to be a lawyer, and who really works toward that? Different theories Competency Also explains goal-directed behavior How good at something we are determines how difficult or achievable tasks we choose Too easy and we don’t learn anything Too hard and we can’t learn anything We choose moderately difficult tasks so we learn from both failure and success Example: A C-average student won’t take 5 AP classes just for fun Different theories Intrinsic The knowledge you gain and fun you have is enough reward for doing a task Example: Reading a Harry Potter book because you enjoy that activity Extrinsic Getting some form of external reward for an activity Example: Getting paid to deliver phone books in the summer Tidbits Social motives can be learned from interactions with others Can be measured One of the main tools for this is a TAT (Thematic Apperception Test) Was a series of pictures The person taking the test had to come up with a story to explain each one There were no “correct” answers David McClelland, the man who developed the TAT, came up with a scoring system to determine the highest motivator for that person Similar to personality aptitude tests Stats from TATs McClelland tested college students in 1947 He found that 11 years after graduation, 83% of the entrepreneurs (business people, salesmen, real estate, etc.) scored high on the TAT Only 21% of non entrepreneurs scored high Decided not all of us should aim to be high achievers Such people are not always interesting Aren’t usually artistically sensitive, and are less likely to value intimacy in a relationship; they prefer to associate themselves with successful people rather than friendly people Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Image found at http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/58/Maslow's_hierarchy_of_needs.svg/80 0px-Maslow's_hierarchy_of_needs.svg.png Maslow’s Fundamental Needs Bottom of the hierarchy; biological needs that must be satisfied in order to maintain life Examples Food Water Safety/Security Breathing Sleep Maslow’s Psychological Needs Next level in the hierarchy; if these are shorted, it will be difficult for a person to achieve fulfillment in the top level Examples include Belonging/giving and receiving love Friendship and family Self-respect Confidence Respect for and from others Maslow’s Self-Actualization Needs Top level of the hierarchy; whatever may be required to sustain the realization of one’s unique potential Examples Morality Creativity Pursuit of knowledge and beauty Prejudices or the lack thereof Accepting or rejecting facts The Monkey Wrench… Other, more recent studies have shown that the lower level of needs do not necessarily have to be met before the higher levels Any particular need may dominate at any time, depending on the person, situation, and time Example: Christopher Columbus risked safety, but may quite possibly have achieved self-actualization So which hierarchy level is dominate? A bum in the Park hasn’t had food for 5 days, has been drinking out of the River, and has to worry about where he’s going to sleep safely each night. However, he has a girlfriend who loves him, and whom he loves in return. Psychological (Second) So which hierarchy level is dominate? Vincent Vangough cut off his own ear, was dirt poor, and lived in what could scarcely be called a shack, but he was a phenomenal painter and was very pleased with his work. Self-Actualization (Third) So which hierarchy level is dominate? A CEO has all of his physical needs met, and finds his job very fulfilling. He has reached his current job level by his sheer determination, hard work, and creativity. But he lives by himself, has never been able to date anyone for longer than a couple months, and has no living family. Self-Actualization (Third) So that was all as clear as mud, right? Well, hopefully you caught some of that because here comes the evil, much dreaded POP QUIZ!!!!