total quality management
advertisement

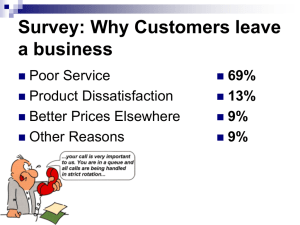
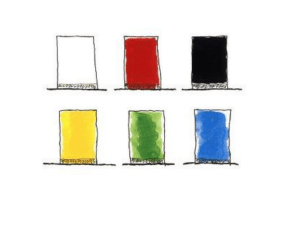
TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT BERNA AKSU İSMET SIDKI UYAR MERT ZORER HISTORY • First published in 1926 and was used by Henry Ford, My Life and Work (all my life and my job) described his book as a new form of government. However, this management style is unpopular at that time, started to be adopted by the Japanese. TQM can be said fully implemented by the Japanese in 1950. Japanese managers at all levels of quality and integrated circuit ; • all the business units spread awareness on this issue provided by training. With this method, low-quality, well-known Japanese products within five years conquered the whole world market. This methods for implementing this approach come from people such as Philip B. Crosby, W. Edwards Deming, Armand V. Feigenbaum, Kaoru Ishikawa and Joseph M. Juran. FREDERİCK W.TAYLOR • There is a quality system based on Taylor's philosophy. According to Taylor, whoevaluate their work with the workers, did not have the capacity to control. Therefore, thecontrol elements of the finished products had to investigate. Quality control was working on the finished product. • Unsuitable products, scrapped leaving, re-processed or sold to the customer by providing the minimum requirements. Inspection activities, depending on the factorymanager or production manager check was conducted by the department. WHAT İS QUALITY? • Quality is the ability of a product or service to consistently meet or exceed customer expectations. Or • Quality is the fitness to the customer requirements. TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT • Total Quality Management is a philosophy that involves everyone in an organization in the quest for quality, with customer satisfaction as the driving force. ELEMENTS OF TQM • Continuous Improvement • Competitive Benchmarking • Employee Empowerment • Team Approach PRINCIPLES OF TQM • Customer focus -Customers' views be taken into account, the datum of the various methods used in the production of knowledge. • Mutually beneficial (win / win principle) -Suppliers, employees and customers a competitive advantage can be achieved through co-operation. • Employee participation -Employees should be given the freedom to participate in the management, training and motivation-enhancing techniques, explained the importance of employees within the organization. Spread improvements and enhancements to the base. • Leadership PRINCIPLES OF TQM • Process approach (Process Management) -Processes should be defined, all the processes for identifying and measuring the effects of each other developed. • Continuous improvement -Continuous improvement must become a habit, a long-term effects of changes should be considered. • Factual approach to decision -Total quality management is decision making tools. Through these means theenvironment are analyzed and decisions are made within the limits of feasibility. System approach to management -Evaluation done the organization as a whole, the interaction of the environment should be considered. DIMENSIONS OF QUALITY • Performance; Primary operating characteristics • Features; Secondary operating characteristics added touches Perceived Quality • Times; -Waiting in line -Concept to production -To complete a service DIMENSIONS OF QUALITY • Reliability; Extent of failure – free operation • Durability; Amount of use until replacement is preferable to repair • Conformance; • Uniformity; • Service, after sale; • Aesthetics; BENEFITS OF TQM 1. Advantages unique to TQM: It makes the company a leader. Fastens the team work. Makes the company more sensitive to customer needs. Makes the company adapt more readily to changes. 2. Benefits to company Quality improves. Increased productivity. 3. Benefits to customer Fewer problems with product/services. Better customer care. Greater satisfaction. 4. Benefits to staff Empowerment. More training and more skills. More recognition of achievement. ELEMENTS OF TQM • Be customer focused It requires the company to check customers' attitudes regularly and includes the idea of internal customers as well as external ones. • Do it right the first time This means avoiding rework, i.e., cutting the amount of defective work. Constantly improve Continuous improvement gradually to get better. allows the company Quality is an attitude Every one has to be committed to quality. That means changing the attitude of the entire workforce, and altering the way the company operates. Telling staff what is going on This involves improved communication. Typically, it includes team briefing. ACCEPTABLE QUALITY LEVEL • Is there something called “AQL” • For example; If 99% the quality level in America 200 000 prescriptions incorrectly 30 000 new-born baby's risk of humiliation at least 4 days per year of unhealthy drinking water daily 15-minute power failure Therefore, the quality of the target must 100% CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT • The improvement is never enough • The performance should always be measured and improved at all times. • KAI – ZEN Plan (değişim) (daha iyi) ACT Represent: Edward Deming DO CONTROL PROBLEM SOLVING TECHNIC • Brainstorming -Is a method for generating a large number of creative ideas in a short period of time -No critism, no evoluation, no discussion of ideas -All ideas are recorded • PMI: Plus, Minus, Interesting -Review the action or the problem -Brainstorm pluses -Braintstrom minuses -Brainstrom interesting points -Calculate the outcome PROBLEM SOLVING • Nominal Group Technique -Is a structured method for group brainstorming that encourages contributions from everyone • Six Thinking Hats -Six thinking hats; is a powerful technique that helps you look at important desicions from a number of different perspectives. -Everyone argues that different views of a plug hat. HATS White Hat: Facts, Neutral, Objective, Information Red Hat: Emotions, Intuition Black Hat: Critic, Analst, Logical negative Yellow Hat: Sunshine, Optimism, Logical Positive Green Hat: Creative growth, Possibilities ideas Blue Hat: Cool agenda, Process • Six Sigma is a business management strategy, originally developed by Motorola in 1986. Six Sigma became well known after Jack Welch made it a central focus of his business strategy at General Electric in 1995, and today it is widely used in many sectors of industry. • Six Sigma seeks to improve the quality of process outputs by identifying and removing the causes of defects (errors) and minimizing variability in manufacturing and business processes. • With six sigma quality processes, and whether the numerical value of the desired qualitycan be seen. This approach is a process of improving the performance of the error rate of the unit aims to reach 3.4 million.