Six Years as One: Planning the Geography Curriculum for Junior
advertisement

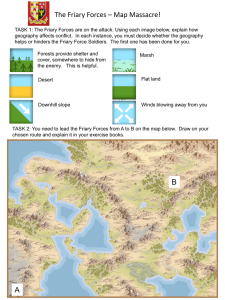
Six Years as One: Planning the Geography Curriculum for Junior and Senior Secondary Education How do I plan the Geography curriculum of my school? Task 1 Case Study: S1 S2 S3 City Natural Hazards Food Problem The Trouble of Water Manufacturing Industry Energy S4 S5 S6 Opportunities & Risks Managing River & Coastal Environment Dynamic Earth Changing Industrial Location Building a Sustainable City Transport Combating Famine Disappearing Green Canopy Global warming Task 2 What did the Curriculum Guide said? Case Study: S1 S2 S3 City Natural Hazards Food Problem The Trouble of Water Manufacturing Industry Energy Core Modules Themes: From HK to the World – Variations in space, people and places From China to the World – Enquiring regional problems arising from humanenvironment interactions Challenges for our world – Managing global issues in a sustainable way Case Study: S4 S5 S6 Opportunities & Risks Managing River & Coastal Environment Dynamic Earth Changing Industrial Location Building a Sustainable City Transport Combating Famine Disappearing Green Canopy Global warming Themes: Living with our physical environment Facing change in the human environment Any other Confronting global challenges considerations? General guidelines to planning • Concepts, knowledge and skills – from simple to complex, easy to difficult • Choice of case study – a balanced coverage from local to global examples • Progression: Breath of study Depth of study Spatial scale Development of skills Increasing opportunities for pupils to examine social, economic and environmental issues Needs of students (interest / strength / weakness) Planning of Junior Geography Curriculum Different mode of junior form PSHE curriculum Integrated Mode (Geography is not an independent subject) Mixed Mode (S3 Geography) Independent subject Mode (S1-3 Geography) Planning of Junior Geography Curriculum • Enquiry learning • Essential learning elements Knowledge, concepts and skills, values and attitudes Integrated & mixed mode Curriculum Auditing for the Integrated curriculum • Check whether the integrated curriculum has covered the essential learning elements Topics related to Geography Find out the knowledge, concepts or skills covered • Find out the missing elements Task 3 Planning of Junior Geography Curriculum Characteristics of each topic: Topic Characteristics City • Illustrate the knowledge & concept of “landuse”, “urban problems”, “sustainability” • Introduce the map reading skills • Conduct simple fieldwork task Natural Hazards • Introduce physical geography • Introduce prior knowledge on “Plate Tectonics” / “Geological Hazard” • Train map reading skills Characteristics of each topic: Topic Characteristics Tourists • Interesting topic • Illustrate the concept “sustainability” & “global interdependence” • Train elementary map reading skills and use atlas / Google Map Changing Climate • A very hot global issue • Introduce climatic pattern • Illustrate the concept of “peopleenvironment interaction” & “global interdependence” Characteristics of each topic: Topic Characteristics Food problem • Understand the knowledge and concepts related to “Farming” • Conduct simple fieldwork The trouble of water • Learn about the physical characteristics of China • Illustrate the concept of “management” • Train map reading and graphic skills Characteristics of each topic: Topic Characteristics Population problem • A topic that will not be taught in higher level • Illustrate the concept of “spatial distribution” • The problem is related to other issues, e.g. disease, urban problems • Learn about the physical characteristics of China • Illustrate the concept of “desertification”, “management” • Interpret satellite and aerial photographs Taming the sand Characteristics of each topic: Topic Characteristics Manufacturing industry • Develop global perspective and the concept of “global interdependence” & “place and region” • Train statistical and graphic skills Energy • A very hot global issue • Illustrate the concept of “global interdependence” • Train statistical and graphic skills Characteristics of each topic: Topic Disease Ocean Characteristics • Illustrate the concept of “spatial distribution” & “global interdependence” • Illustrate the concept “ecosystem” • Interpret satellite photographs What do you think about this curriculum? School background: Characteristics of students: average ability, rather passive, come from lower socio-economic class No. of Geography lessons: two 40-minute lessons per week Task 4 What do you think about this curriculum? 1.The choice of the topics 2.The time available to cover the content 3.Students’ learning of these knowledge and skills 4.Any other comments? What do you think about this curriculum? • Good points: Follow what the Curriculum Guide suggests Choice of topics: interesting, related to daily life • Bad points: Content is too much Map reading skills are too difficult for S1 students Sequence of the modules Curriculum design of S1-3 Geography Curriculum Core Core Core Core Elective Other considerations 1. Trimming the curriculum Number of specific examples Content Example Sustainable City: 1. Do all cities look the same? (choose any 1-2) • Western city • SE Asian city • South American city 2. What problem is our city facing? • Traffic congestion problem • Urban decay problem 3. Specific examples (choose any 1-2) • Guangzhou • Tianjin • Seoul • Helsinki Example The Trouble of Water: • Major water problems in China (overall view) • Water cycle • Major rivers in China • Concentrate on only one/two kind(s) of water problem: causes, impacts and solutions • Water management experience of one country Other considerations 2. Progression • Knowledge Breath of study Depth of study Spatial scale • Skills • Choice of case studies Principles that guide the planning of progression • Build upon students’ existing knowledge and previous experience; • Match carefully to pupil’s capabilities and interest • Take into account of the ways in which pupils’ mature (intellectually, socially and physically) • Be important in pupils’ future learning S1 Student’s common mistake 計算坡度 (直線比例尺): 垂直距離 = 150-100 = 50米 水平距離 = 1.3 x 10000 50÷50 13000÷50 = 1:260 Mix up R.F. and linear scale Example Other considerations 3. Provision of fieldwork experience 4. Formative assessment Planning of Senior Geography Curriculum • Prior knowledge • Related topics Opportunities & Risks Dynamic Earth River & Coast Planning of Senior Geography Curriculum Tropical Rain Forest Global Warming Combating Famine Weather & Climate Planning of Senior Geography Curriculum Sustainable City Transport Zhujiang Delta Transport Planning of Senior Geography Curriculum Concept and knowledge • Simple to complex • Easy to difficult • Concrete to abstract Example: City Opportunities & Risks Planning of Senior Geography Curriculum Map reading skills • Lower order to higher order Example: Lower level Urban maps Map symbols Higher level Maps with contour lines Interpretation of features As a start…… More typical features Simple contour line map GeoInfo Map http://www2.map.gov.hk/gih3/view/index.jsp Hypothetical example – S4-6 Geography 1.Industry 2.Sustainable city (Transport) (Zhujiang Delta) 3. Opportunities 5. Tropical rain & risks forest 4. River & coast 6. Global (Dynamic Earth) warming (Weather & climate) 7. Famine Interface between Junior & Senior Geography Curriculum Issue-based enquiry Interface between Junior & Senior Geography Curriculum • Development of spatial perspectives Interface between Junior & Senior Geography Curriculum • Essential learning elements (curriculum auditing) Interface between Junior & Senior Geography Curriculum • Data response enquiry Information / Data: Question: 1a. 根據圖一所示,2013年五月和六月的雨量與該兩個月的 平均雨量有甚麼不同? 1b.這個現象與2013年6月發生的山泥傾瀉有何關係? 2. 根據圖二所示的資料,解釋為何那裡會發生山泥傾瀉? Interface between Junior & Senior Geography Curriculum • Writing skills • High order thinking skills Graphic organizer Interface between Junior & Senior Geography Curriculum Framework for essay writing Interface between Junior & Senior Geography Curriculum High order thinking skills – problem solving Questions & answer 2009 H1N1 Flu Outbreak Map Google map 1. Which three countries have been most affected by swine flu? 2. Which regions have been most affected by swine flu? 3. Which regions have been least affected by swine flu? Software for calculating gradient and identifying relief features http://diy.fwg.hk/download/geog/map/Map-S.html http://diy.fwg.hk/download/geog/map/Map-TC.html Software for calculating gradient and identifying relief features Calculation of gradient Software for calculating gradient and identifying relief features Drawing of Cross-section Contour lines – from 2D to 3D http://www.rgs.org/webcasts/activities/contours/contours.html Contour lines – from 2D to 3D Contour lines – from 2D to 3D