Competencies for Diabetes Patient Education: Pilot study results
advertisement

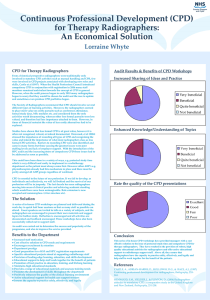
Competencies for Diabetes Patient Education: Pilot study results Joan McDowell National Education Co-Ordinator NHS Education for Scotland Development of competencies 88 competencies from TREND, RCN, DUK, NHS Education for Scotland (Skills for Health, RCGP, Consensus) – Knowledge based – Skills based – Philosophy Reduced to 18 Pilot study • DENS conference May 2012 • NHS Colleagues (total responses 10) • QISMET • DESMOND • Paediatric representation Results • 10 Diabetes Specialist Nurses and Dietitians England and Wales • Delivering structured patient education • Mean 6.8 years, median 7 years (18 months – 20 years) Competencies (1 of 4) • 1. Assess person’s self management needs: 10 yes; 8 keep; 3 lose this one; • 2. Learning styles: 9 yes; 5 keep; 4 need for own CPD • 3. Identify barriers to self management : 9 yes; 5 keep; 9 need for own CPD • 4. Facilitate self management goals: 10 yes; 5 keep; 1 change; 6 need for own CPD Competencies continued (2 of 4) • 5. Manage groups: 9 yes; 5 keep; 2 need for own CPD • 6. Personal reflection: 10 yes; 5 keep; 3 need for own CPD • 7. Effective communication skills: 10 yes; 5 keep: 1 need for own CPD • 8. Special needs: 7 yes; 6 keep; 1 change; 2 need for own CPD Competencies continued (3 of 4) • 9. Theoretical frameworks: 8 yes; 5 keep; 2 lose; 1 change • 10. Learning theories: 8 yes; 5 keep; 4 lose; 2 need for own CPD • 11. Actively involve participants: 10 yes; 5 keep; 3 need for own CPD • 12. Learning plan: 9 yes; 5 keep; 1 lose; 3 need for own CPD Competencies continued (4 of 4) • 13. Family/support: 9 yes; 4 keep; 2 lose; 1 need for own CPD • 14. Teaching methods: 6 yes; 5 keep; 4 lose; 1 need for own CPD • 15. Educational resources: 8 yes; 5 keep, 1 change • 16. Relationships: 10 yes; 4 keep; 6 lose • 17. Peer support: 10 yes; 5 keep; 4 lose • 18. Non judgemental advice: 10 yes; 5 keep; 4 lose Competencies 1-18 Majority currently think that they could personally demonstrate competence in them all. 14. (Teaching method) lowest at 6 responses 8. (Special needs) next lowest with 7 responses Competencies and own professional development • 3. (Barriers to self management) 9 responses • 4. (Facilitate self management goals) 6 responses • 6, 9, 11, 12 3 responses • 5, 8 10 2 responses • 7, 13, 14 1 responses • 1,15,16,17,18 0 responses How would YOU use competencies • • • • Professional development Appraisal/annual review Develop a business case Promote services to others • Change practice • Quality assurance • Raise awareness of role 6 6 1 2 1 4 2 How would you like your LINE MANAGER to use competencies • • • • • • • • • • Professional development Appraisals/annual review Develop a business case Promote services to others Setting objectives Quality assurance Developing role awareness Peer review Recruitment of staff Training new staff 3 4 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 Importance of establishing competencies • • • • • • 0 (not important) 1 2 3 4 5 (most important) 4 6 Individual Comments • Competencies need: – a context – definitions of terms used – evidence the outcomes – to include emotional skills • Focus on ‘teaching’ as opposed to diabetes educator The Scottish Context www.diabetesinscotland.org.uk • Publications: APEDS&TAPEDS and Reviewer’s Handbook • 12 competencies to be a trained educator • List of other desirable skills • Trained educator evidenced by teaching qualification; training for national programmes PLUS providing evidence through peer review, self reflection and written support DENS Competencies Where to now?