ppt - AADL - Aakash Application Development Lab
advertisement

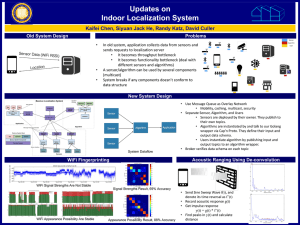
Village Communication Network Leveraging on Fibre to the Village Researcher: Vishal Sevani Faculty: Bhaskaran Raman, Abhay Karandikar TCOE IITB Researcher: Jyoti Purohit Faculty: Ashok Jhunjhunwala TCOE IITM Motivation: Rural Broadband Scenario Tablet (Aakaash) House Fibre optic access close to village: ~5km Community centre Tablet (Aakaash) School Village: 2-3km diameter Need: cost effective last mile connectivity Applications: rural education, healthcare, IT services Solution Choices • Running cables High cost • WiMAX, LTE High cost Requirement of tall tower High power consumption • Wi-Fi based network License free band Low equipment cost Low power consumption: <10W, solar power possible Long-Distance WiFi versus WiFi Mesh High cost of tall tower Hidden terminal issues Fault tolerance issues “On the Feasibility of the Link Abstraction in (Rural) Mesh Networks”, D. Gokhale, S. Sen, K. Chebrolu, and B. Raman, INFOCOM 2008 Insight: outdoor mesh network links can be stable, TDMA MAC feasible Solution Choices • Running cables High cost • WiMAX, LTE High cost Requirement of tall tower High power consumption • Long-distance WiFi High cost of tower • Wi-Fi based multi-hop mesh network License free band Low equipment cost Low power consumption: <10W, solar power possible Low cost installation on light poles, roof-tops Self configurable Potential to enable “sustainable village franchise” model Solution Approach: WiFi Mesh (1) Low-cost commodity WiFi hardware (2) WiFi-PHY based link Fibre optic access close to village: ~5km (3) Multi-hop mesh network running TDMA-based LiT MAC Tablet (Aakaash) House Community centre Tablet (Aakaash) School Village: 2-3km diameter Technical Challenges and Solution • Commodity Wi-Fi has CSMA/CA • Poor performance in multi-hop mesh • Poor throughput, delay: cannot support realtime applications • Solution: TDMA-based MAC called LiTMAC – Light-weight TDMA MAC Accomplishments • Implementation of TDMA based LiTMAC protocol for WiFi-PHY based mesh network – Modifications to open source ath9k driver – Testing and bug-fixing of LiTMAC implementation – Code runs stably for long durations of time – Implementation of the per-hop ack: performance improvement in presence of wireless packet losses • Ported the software on the low cost Ubiquiti bullet M2HP platform • Testing the solution in lab setting & test deployment Performance Evaluation Setup LitMAC WiFi Ethernet Root LitMAC WiFi Infra1 Ethernet CSMA WiFi LitMAC WiFi Infra2 Ethernet Ethernet CSMA WiFi Aakash Tablet Infra3 Aakash Tablet CSMA WiFi Aakash Tablet Performance Results Aakash 1 Aakash 2 Aakash 3 3.72 Mbits/s 3.54 Mbits/s 3.49 Mbits/s UDP 4.15 Mbits/s, throughput, 4.09 Mbits/s 4.10 Mbits/s, 3.812ms, 3.653ms, 3.549ms, 0% 0.047% 0% TCP throughput jitter, packet loss Future Work • Other features in LiTMAC implementation – Ease of configuration of various LiTMAC parameters – Dynamic routing, dynamic scheduling • Identify solar-power solution for the WiFi nodes • Detailed field deployment evaluation of LiTMAC in rural settings • Identify any modifications required in LiTMAC to further improve the efficiency • With LiTMAC code, run pilot commercial network, in co-operation with ISP to provide broadband Internet connectivity