chapter 2 slides
advertisement

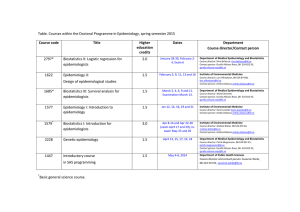
What is a population? What is population health? Epidemiology matters: a new introduction to methodological foundations Chapter 2 A brief introduction to the graphical notation used in Epidemiology Matters Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 2 Diseased Non-diseased Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 3 Set of individuals 100 individuals 20 diseased individuals Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 4 Multiple sets of individuals Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 5 1. Defining a population of interest 2. Dynamic versus stationary populations 3. Summary Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 6 Seven steps 1. Define the population of interest 2. Conceptualize and create measures of exposures and health indicators 3. Take a sample of the population 4. Estimate measures of association between exposures and health indicators of interest 5. Rigorously evaluate whether the association observed suggests a causal association 6. Assess the evidence for causes working together 7. Assess the extent to which the result matters, is externally valid, to other populations Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 1 7 1. Defining a population of interest 2. Dynamic versus stationary populations 3. Summary Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 8 Defining a population of interest A population is a collection of individuals, at moments in time, defined by at least one organizing characteristic The definition of a population has implications for analysis, interpretation, and generalizability of results from epidemiologic studies . Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 9 Two axes of population definitions 1. Populations are defined by eligibility criteria 2. Populations are defined by whether individuals move in and out of eligibility; i.e., populations can be dynamic or stationary . Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 10 What could be eligibility criteria? 1. Geographic area and time period of interest 2. Characteristics of persons, events, or exposures for which health-related factors are of interest 3. Factors that promote successful study completion Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 11 Population, defined by geographic space and time Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 12 Dynamic population of Farrlandia over 1 year Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 13 Dynamic population of Farrlandia over 1 year Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 14 Dynamic population of Farrlandia over 1 year Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 15 Examples of populations, defined by characteristic, event, or exposure If we are interested in understanding determinants of neonatal health, the population of interest is all newborn infants. Therefore, the defining event for inclusion is date of birth, and eligible individuals for population can be those within a year of their birth. Pregnant women Individuals over the age of 65 Individuals exposed to a natural or human-made disaster Individuals of certain races or ethnicities Individuals subject to particular laws Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 16 An example After the World Trade Center 2001 attack, a study considered neonatal outcomes among offspring of women in California who gave birth six months after the attack comparing them to women who gave birth six months before the attack This study therefore defined population of interest defined by a. Event or exposure = pregnancy b. Geographic location = California c. Time period = six months before and after September 11, 2001 Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 17 Populations, defined by study considerations Population of interest may be select group collected specifically to achieve successful study Good responders to our surveys Likely to continue to attend the health facility for followup visits Individuals who are healthy so that they are unlikely to die during the course of the study outside scope of inquiry Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 18 An example The Women’s Health Initiative is a study that assesses health benefits and risks of hormone replacement therapy after menopause. Eligibility is limited to women who had undergone menopause. The study excludes a. Women with a history of certain medical conditions b. Women who were unlikely to be adherent to study protocol c. Women who failed to meet other criteria Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 19 1. Defining a population of interest 2. Dynamic versus stationary populations 3. Summary Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 20 Dynamic vs stationary populations Dynamic eligibility criteria for the population: allow movement in and/or out of the population. For example, people may move out of geographic region and no longer be considered part of the population of interest. Stationary eligibility criteria for the population: do not allow movement in and/or out of the population. For example, population may include all those born on a particular date only and follow them forward in time, never losing any nor adding others. Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 21 1. Defining a population of interest 2. Dynamic versus stationary populations 3. Summary Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 22 What is a population? What is population health? Epidemiology is concerned with understanding the health of populations Populations of interest can be defined by geography, space, time or by characteristics of participants or of events of interest Regardless of eligibility criteria, population may be dynamic or stationary Careful definition of the population base from which we conduct an epidemiologic study underlies many of the core methods in epidemiology Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 2 23 Seven steps 1. Define the population of interest 2. Conceptualize and create measures of exposures and health indicators 3. Take a sample of the population 4. Estimate measures of association between exposures and health indicators of interest 5. Rigorously evaluate whether the association observed suggests a causal association 6. Assess the evidence for causes working together 7. Assess the extent to which the result matters, is externally valid, to other populations Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 1 24 epidemiologymatters.org Epidemiology Matters – Chapter 1 25