Russia Pre-1917
advertisement

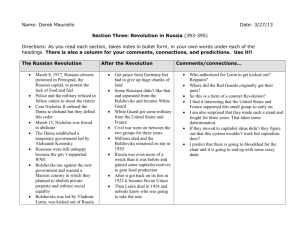
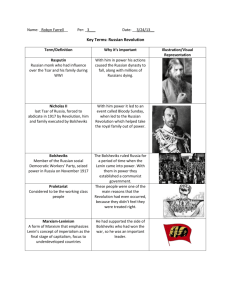
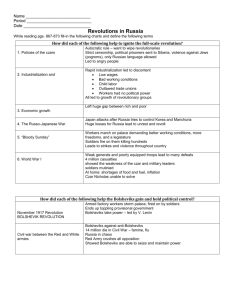
Russia Pre-1917- Revolution History 12 Ms Leslie Very very beginning Russia has been around since the 10th century Mostly made up of Ethnic Slavs who went north escaping the Turkish empire These migrating Slavs clashed with Mongolians and Tartars 15th century - Grand Duchy of Moscow established = creation of a strong Tsardom or Czardom The first Tsars were the likes of Ivan the terrible and Ivan the Great Took a lot of territory from the Tartars, Kazans and Crimeans Imperial Russia 17-19th Century A great time for Russia Grew culturally and territorially Rulers = Peter the great and Catherine the Great The people were mostly illiterate farmers Feudal system Czar Alexander II abolished slavery in 1861 Factories had horrid working conditions Alex II assassinated in 1881 and replaced by this son Alexander III 1881-1894 Authorities shifted attention from the failings of the government by creating scapegoats and encouraging pogroms Pogroms - Was physically intimidating - a body builder to make up for his 5’6” height Died of kidney failure from trauma from a train accident Nicolas II Started his reign in 1894 Autocratic and ineffective Romanov family very wealthy Population of 165 million Secret police (OKHRANA) Censorship of the press Czar’s word was law Despite this, the people loved Nicolas II Believed he was appointed by God Kept pictures of him in their homes and worshipped him Related to heads of Greece, UK, Denmark, Germany What was Nicholas II like? Not very smart Easily manipulated by his advisors Relied on His son, His allowed Rasputin to gain dangerous control of the government. Population of the 1910’s 1910 1914 Only 40% 80% Life expectancy = 40 years Well educated middle class - had the most books per capital in 1913 Most lived on communal farms called Obschina or Mir. The Obschina organized taxes and allotted land to households Peasants could not Punishment = Agricultural reforms had not caught on eg crop rotation famine Lots of famines 1891 - famine +cholera + typhus = 400,000 dead 1890 - 64% of conscripts declared unfit to serve Revolutionary movement 1. Nihilists – 2. Populists – 3. Marxists 4. Liberals - Problems with Industrialization Far behind rest of Europe Because of late start industry was modern and they lacked skilled workers Relied heavily of foreign loans and taxes for growth France owned 2/3rd Germany owned Britain owned Biggest problem - massive, abused proletariat Industry 5th Average hard labour work day Child labour common. Start age 4 Kids worked in cotton mills. Injuries common, rickets, cotton lung Unions Banned Labour Problems Industrial workers small in number Exploited Demanded Started to demand Peasant Problem 3/4 of the population Although no longer serfs, still had a separate administration and courts Illiterate and superstitious Excessively taxed - main source of tsarist revenue. 1896 the people had enough and rioted in St Petersburg 1902 street demonstrations 1901-1907 arson in rural areas common 1904 a social revolutionary assassinated the minister of the interior 1905 Revolution causes 1. - 2. 3. 4. - 5. 6. Liberals organized the Constitutional Democratic Party (Cadet). Wanted democratic reform 7. Bolsheviks (Majority) – Mensheviks (minority) - 1905 Rebellion/Revolution Jan 22/Jan 9 Workers under the leadership of Father Gapon marched on the Winter Palace Wanted: Bloody Sunday Result Showed tsar’s incompetence Tsarist supporters changed their minds creation of the ‘Shildlovski Commission’ Oct 1905 Oct 20-30 – First soviet formed in St Petersburg Soviet (council) = The Tsar responded with the October Manifesto promising: Extremists not appeased, but moderates happy and a full revolution didn’t happen The Duma Russian Parliament Long term impact 1905 Tsar used him powers to arrest and harrass opposition 1906-07, 4,400 deaths due to terrorism Catch 22 - Marxism Came to Russia in the 1880s Lenin knew revolution would happen in Russia first as it was the weakest capitalist state (contrary to Marxism) 1903 the Russian Marxist movement split in two Bolsheviks Professional revolutionaries Majority Mensheviks Moderate Feared Lenin would become a dictator Minority WWI and the revolutionary movement Bolsheviks opposed the war from the start Lenin exiled in Zurich, Switz. Most Bolsheviks banished to Siberia Home front War meant more food shortages 1914 1915 This left the Tsarina in charge - she let Rasputin make decisions… War stats 15.5 million man army 1.65 million died 3.85 million wounded 2.41 million POWs 1917 1.5 million deserted Lack of medical attention Not enough equipment for soldiers. 1 in 3 didn’t have a gun Beginning of the collapse 1917 Little transportation February Police joined rioters and a general strike formed Army called in and they shot the rioters Fear of civil war causes Czar to resign and the provisional government is formed But more on all that later The end