Industrialization and Nationalism
advertisement

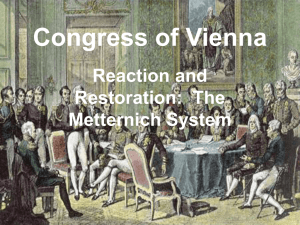
Industrialization and Nationalism Chapter 19 Test Review The production of this was one of the first industries to be affected by the Industrial Revolution. What is cotton cloth? Where did the Industrial Revolution begin? What is Great Britain? By 1830, two-thirds of the British cotton factory’s workforce were a. Rural farm families who had moved to the city from Canada. b. Immigrants from France and Belgium. c. Women and children d. Slaves from Africa and South America. Answer: C Women and Children The factory system created a new labor system in which a. Products were produced by an assembly line of workers and animals. b. Workers had to adjust to periods of hectic work, followed by periods of inactivity. c. Machines were valued more highly than the men who ran them. d. Workers had to work regular hours and do the same work over and over. Answer: D Workers had to work regular hours and do the same work over and over. The ___was crucial to Britain’s Industrial Revolution? a. Bicycle b. Flying shuttle c. Water-powered loom d. Steam engine. Answer: D Steam Engine Who developed a steam engine that could drive machinery? Who was James Watt? What social change brought by the Industrial Revolution was evident? a. Emergence of the middle class and the working class. b. Growing death rates, due to accidents on the highways. c. Thick air pollution that choked the British Isles. d. Widespread famines caused by families abandoning their farms. Answer: A The emergence of the middle class and working class. The pitiful conditions created by the Industrial Revolution gave rise to a. The Iron Workers’ Revolt of 1886. b. The organization of charitable groups. c. Socialism, in which society owns and controls the means of production. d. A cry for rights for animals that worked in coal mines. Answer: C Socialism People interested in finding new business opportunities and new ways to make profits. What are entrepreneurs? Labor for factories during the Industrial Revolution came mostly from the ________. Farm. Built the first paddle-wheel steamboat. Robert Fulton. Production done by individuals in their homes. Cottage industry. Economic system based in industrial production. Industrial capitalism Meeting in 1814 of the great powers of Europe. Congress of Vienna. Leader of the Congress of Vienna in 1814. Prince Klemens von Metternich Prince Metternich’s claim that he was guided by the principle of legitimacy meant a. Territories would only be retuned to those who had a legitimate claim to them. b. Lawful monarchs from the royal families that had ruled before Napoleon would be restored to power. c. He was the legitimate and lawful heir to the throne of Denmark. d. The old tensions that had existed prior to Napoleon would resurface. Answer: B Lawful monarchs would be restored to power. ____is the belief that people should be as free as possible from government restraints. What is Liberalism? According to the principle of intervention, the great powers of Europe had the right to a. Borrow food from one another in times of economic crisis within their countries. b. Send armies into countries where there were revolutions in order to restore legitimate monarchs to power. c. Take one another’s territories without asking. d. Have responsibilities with voting privileges in one another’s governments. Answer: B They could send armies into countries where revolutions in order to restore legitimate monarchs to power. Liberals in Europe believed in the protection of ________liberties. Civil Political philosophy based on tradition and social stability. Conservatism Belief that people owe loyalty to a nation. Nationalism Meetings of the great powers of Europe to maintain peace. Concert of Europe The Congress of Vienna had created ___independent German states. 38 The independent German states recognized by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 were called the ____________________________________. German Confederation The __________Assembly met to draft a constitution for a unified Germany. Frankfort The unification of Germany was accomplished by the Prussian prime minister _______________________. Otto von Bismarck. Politics based on practical matters rather than theory or ethics. realpolitik a. b. c. d. One of the leaders of the Italian unification effort was Giuseppe Garibaldi Giovani Bernini Otto von Bismarck Klemens von Metternich Answer: A Giuseppe Garibaldi The Crimean War was a long-standing struggle between _____________and the ___________Empire. Russia and Ottoman Empire a. b. c. d. In 1848, revolutions took place in all of the following EXCEPT Britain France The German states Italy Answer: A Britain The first president of the Second Republic in France was a. Napoleon Bonaparte b. Louis-Napoleon c. Metternich d. Louis-Philippe Answer: B Louis-Napoleon After Napoleon, France was governed until 1830 by a. A king b. An emperor c. An constitutional monarchy d. The Constituent Assembly Answer: A A King. Collection of different peoples under the same government, as in the Austrian Empire. Multinational Voting rights for all adult men Universal male suffrage. True or False? The government of Napoleon III was authoritarian. True! A _________is a popular vote of the people. Plebiscite. When the Germans failed to achieve unification in 1848 and ‘49, they looked to _______for leadership in the cause of German unification. Prussia What territories were given to Prussia as a result of the Franco-Prussia war in 1870? Alsace and Lorraine She reigned from 1837 to 1901, the longest in English history! Queen Victoria The German “Emperor” Kaiser True or False. During the 19th century, Russia was falling hopelessly behind the western European powers. True. a. b. c. d. The ____established a self-governing Canadian nation. Treaty of France in63 British North American Act Canadian Revolution Declaration of Canadian Liberty Answer: B British North American Act Russia wanted to expand its power into this region of Eastern Europe. The Balkans The Compromise of 1867 created dual monarchies in ______and ________. Austria and Hungary a. b. c. d. Who proposed the germ theory of disease? Farhid Molotof Michael Faraday Louis Pasteur Charles Darwin Answer: C Louis Pasteur Literary and visual art movement that rejected romanticism. realism Published On the Origins of Species by Means of Natural Selection. Charles Darwin The brutal life led by the urban poor in England was described in literature by ___________________. Hint: “It was the best of times it was the worst of times...” Charles Darwin