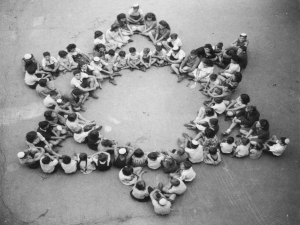Which countries made up the Allied Powers in WWII?
advertisement

Born in Austria, 1889 Not accepted into Art school Fought in WWI, got interested in politics Leader of Nazi party Dictator Anti-semitism Committed suicide April 30, 1945 Territorial expansion to assert superiority and strength promotes political violence and war as actions that create national spirit “corporatist” economy- big business and state work together to set national economic policies Authoritarian democracy- rule of the most qualified seeks to represent the different interests of a society United States – joined in 1941 Great Britain France Soviet Union Over 50 countries worldwide Germany Italy Japan Others: Hungary, Romania, etc EUROPE THE PACIFIC Instigated by Nazi’s who Instigated by the Japanese invaded Poland Major battles in France, Belgium, Italy, Northern Africa Ended in spring of 1945 when the Axis powers were unable to regain the Western Front. During this time Mussolini was killed by his own people and Hitler committed suicide. who bombed Pearl Harbor in 1941 Major battles: Midway, Iwo Jima, Okinawa Ended in August of 1945 after the United States dropped two atomic bombs on Japan at Hiroshima and Nagasaki. *There were also battles fought in Northern Africa (French colonies) Schutzstaffel Protective Squadron Hitler Heinrich Himmler leader of S.S.. Created concentration camps Extreme loyalty Geheime Staatspolizei, "Secret State Police“ Formed in 1933 sub-group of the S.S. 1936 the Gestapo Law no judicial oversight 46,000 members during the war In charge of investigating accusations made by German citizens against others systematic genocide the “Final Solution” Influenced by feelings of superiority and blame placed on the Jews for WWI and its aftermath Eugenics improving genetic composition of a population. Nazi idea of “cleansing” Included the execution of: *German descent did not protect the victims of the holocaust Jews gypsies communists Soviet POWs Polish and Soviet civilians homosexuals people with disabilities Jehovah's Witnesses political and religious opponents of the Nazi Party Born in Sighet, Transylvania (Romania) , 1928 Lived in a ghetto in Sighet before being shipping to Auschwitz with his family Sent to a work camp with his father where he stayed for over 8 months and was shuffled between 3 different camps Was released when Buchenwald was liberated in April 1945 10 year vow of silence after the war Wrote about his experiences during the Holocaust in the book Night and many other books Won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1986 Still speaks and makes appearances today Jews moved from their homes to ghettos Walled off or surrounded by barbed wire Leaving = death Conditions *In the Warsaw Ghetto, there Crowded Bad sanitation were 400,000 people crammed into 1.3 sq. mi. *Approx. 7.2 people per room Starvation Jews either killed in ghettos or sent to concentration camps A network of concentration and extermination camps in Nazi-occupied Poland 1940 first camp built “Selections” – 2 groups Work Medical experiments