Earth in Space2 - Moore Middle School
advertisement

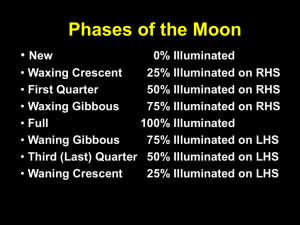
People once thought the Earth was Today we know it’s shape is a Earth’s Location Earth is located in a collection of stars called a The kind of galaxy is called a spiral galaxy and Earth is located on one of the arms. The name of the galaxy that Earth is located in is the Solar System rd The Earth is the 3 planet of nine planets that revolves around the sun. The Earth’s orbit is the curved path it follows as it travels around the sun. Earth’s Travels People once believed everything traveled around the Earth. Now we know it is the Earth that moves. It both rotates and revolves. The spinning of the Earth on it’s axis which causes day and night is called The motion of the Earth around the sun which takes about 365 ¼ days or one year to complete is called a Figure the Speed The moon is 240,000 miles from of the Earth and it travels around the Earth once every 27 days. How fast is it traveling? x diameter= circumference The Earth’s Tilt The Earth has 4 seasons. Summer, Spring, Autumn, and Winter. These seasons are caused by Earth’s The Earth’s axis is the imaginary line around which the Earth spins (rotates) causing the Earth to tilt toward and away from the sun during different times of the year. The seasons depend on which side of Earth is tilted toward the sun. When the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the sun it is summer in the north and winter in the south and vice versa. Day vs. Night During the summer the number of hours of daylight is longer and the number of hours of darkness is shorter. •During the winter it is just the opposite. Longer nights and shorter days. Solstices The solstices are the longest and shortest days of the year. The Summer Solstice is the longest and the winter solstice is the shortest. Northern Hemisphere During the Summer Solstice, the Earth is tilted as far toward the Sun as possible. During the Winter Solstice, the Earth is tilted as far away from the Sun as possible. Winter Solstice for Northern Hemisphere Summer Solstice for Southern Hemisphere Summer Solstice for Northern Hemisphere Winter Solstice for Southern Hemisphere Equinoxes During the Equinoxes the Earth is neither pointing toward or away from the Sun. During the Spring and Fall equinox the length of day versus night is equal. Moon Phases The phase of the moon you see depends on how much of the sunlit side of the moon faces Earth Moon Phases New Moon Full Moon Waxing Crescent Waning Gibbous 1st Quarter 3rd Quarter Waxing Gibbous Waning Crescent Moon Phases The shadow on the moon always disappears from right to left when the moon is growing. If you can see the right side of the moon, then it is growing. The moon always disappear from left to right as well. So if you can see the left side then it is getting smaller. What phase? When the moon grows it is said to be When the moon gets smaller it is said to be