German Unification
advertisement

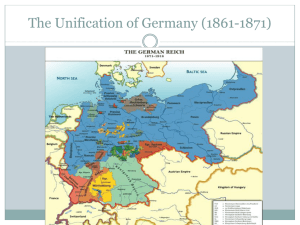
GERMAN UNIFICATION From the Napoleonic Era to 1871 CHAPTER 22: SECTION 2 GOALS 1. Identify major events in Germany’s unification 2. Describe the system of government of the German Empire BACKGROUND: LIBERALISM AND NATIONALISM • The French Revolution causes the ideals of liberalism and nationalism to spread • Liberty, equality, fraternity • Classical Liberalism • Man has inalienable rights (U.S. Declaration of Independence.) Freedom of movement, association, minimal government, could develop himself to the fullest • Social Contract: Sovereignty resided in the people and rulers had to respect that. *FRENCH REVOLUTION AND NATIONALISM • A nation of equal citizens • Secular state recognizing no higher authority • Citizen enjoyed certain rights but also had to give to the state (his life included) DEFINE THE FOLLOWING IN DETAIL IN YOUR NOTES • Look up the following event, person, or concept and write a brief summary of why it is important to German Unification: Include important dates when applicable • Battle of Jena • Stein-Hardenberg Reforms • Congress of Vienna • Carlsbad Decrees • Hambach Festival • Pan-Germanism • Zollverein • Frankfurt Parliament • Erfurt Union • Kleindeutschland-Grossdeutschland • Otto Von Bismarck • The Danish War • The Seven Weeks’ War GOAL 1: MAJOR EVENTS *NAPOLEONIC WARS • War with large parts of Germany by 1793-94 • Western Germany conquered • 112 German states disappeared • Ideas of Nationalism and Liberalism forced on Germany • *1806 Confederation of the Rhine created by Napoleon • Holy Roman Empire eliminated. • 15,000,000 subjects • Counter to Prussian and Austrian Power *GOAL 1. CONFEDERATION OF THE RHINE Prussia France---- Austrian Empire How would the geographic position of the Confederation aid France? Goal 1. Confederation challenges Prussia *Battle of Jena 1806 Battle of Jena: Prussia defeated • Treaty of Tilsit • Massive payments to be made to France (reparations) • Reform necessary to pay it RESULTS: *STEIN-HARDENBERG REFORMS GOAL1 • Uniform tax systems • Efficient Government stressed (bureaucracy developed) • Education reforms encouraging the teaching of history and language • Power of nobility curtailed but land left in their hands • Serfs freed to encourage agricultural growth and landownership • Guilds power broken and industrial competition encouraged • *Military reform was geared toward war with France. • Conscription • 3 years with line regiment • 2 years reserve • 7 years landwehr • Promotion on merit not birth WHAT DOES THIS PAINTING TELL US? The military was held in the highest esteem in Prussia following the Napoleonic wars and Wars of Unification! GOAL 1: CONGRESS OF VIENNA • As a result of Stein-Hardenberg, Prussian forces helped defeat Napoleon • 1815 Congress of Vienna • Confederation of the Rhine becomes the German Confederation • Prussia most powerful N. German state • Rival is Austria • German Nationalism strongest in the North (Why?) • Austria was divided among several nationalities • 39 independent states still exist *PAN-GERMANISM • Idea of a peaceful unification of all German-speaking areas including Austria • Grossdeutschland (Large Germany) • *May 1832 Hambach Festival • 30,000 attend to hear speeches about unification and democracy. First time in GER. • Brothers Grimm! HAMBACH GOAL 1: ZOLLVEREIN: ANALYZE THIS! *ZOLLVEREIN (1834) • Tariffs: tax on imported goods • Hurt sales (How?) • 1818-1834 gradually German states end tariffs and form Customs Union • Lower-uniform prices • Standardized weights and measures • Increased Industrialization How did Stein-Hardenberg make this last bullet possible? GOAL 1: TECHNOLOGY, FINANCE, AND UNIFICATION • Railroads: • 1835 (3.5 miles of track) • 1848 (3,000 miles of track) • 1855 (8,500 miles of track) • 1880 (1880, 9,400 locomotives pulling 43,000 passengers and 30,000 tons of freight • Telegraph • Stock Companies INDUSTRIAL GROWTH • Coal • Iron • Steel • Chemicals Description of Krupp Industries: 1900; “A great city with its own streets, its own police force, fire department and traffic laws. There are 150 kilometers of rail, 60 different factory buildings, 8,500 machine tools, seven electrical stations, 140 kilometers of underground cable and 46 overhead." Population of Berlin (1907) doubles from 1,000,000 to 2,000,000 in 30 years!!!! *1848 REVOLUTIONS (WANTED UNIFICATION AND PARLIAMENT) CONFEDERATION DISSOLVED • Democratic and Nationalistic • Middle class and Working Class led • Elected National Assembly in Frankfurt attempts to unify Germany • Constitution: Kleindeutschland model • Failure due to…. • Rivalry between Pr. And Aus. • Middle class and Working Class Rivalry ERFURT UNION (1849) • Prussian attempts to form a union with German states excluding Austria • Prussia humiliated by Austria • Adds to Prussia’s desire to eliminate Austrian influence PRUSSIAN GOVERNMENT BEFORE UNIFICATION • Frederick Wilhelm issued Prussia's first constitution in 1850. (Goal 1) • two-house parliament. • lower house (Landtag) elected by all taxpayers • divided into three classes -votes were weighted according to the amount of taxes paid. • Women and those who paid no taxes had no vote., • The Upper House: Herrenhaus ("House of Lords") appointed by the king. He retained full executive authority and ministers were responsible only to him. • the landowning classes, the Junkers, remained powerful OTTO VON BISMARCK • "The great questions of the time will not be resolved by speeches and majority decisions—that was the great mistake of 1848 and 1849—but by iron and blood." BISMARCK AND WILHELM I • Prussian military reforms create a powerful force • Railroads • New artillery • Other Weapons • Long service and large reserves • Telegraph • Bismarck named chancellor 1862 Dryse Needle Gun UNIFORMS OF THE DAY Color Print Actual Photo BISMARCK’S GOALS 1.limit democracy 2.Unify Germany under Prussian leadership 3.Destroy Austrian power 1. Believed foreign policy could unify the people or at least distract them from dissent THREE WARS OF UNIFICATION • Danish War: 1864 • Austria and Prussia take SchleswigHolstein • Seven Weeks War(1866) • Treaty of Prague ends Austrian domination of Germany What is going on here? Hint: What other traditional enemy of Austria might gain from her loss in the 7 Weeks War? Italy! The Lion of St. Mark is the symbol of Venice FRANCO-PRUSSIAN WAR • 1870 Spain seeks a new King related to the Prussian Royal family • France protests • Bismarck edits the Ems dispatch and War is declared by France • Major French defeats at Metz and Sedan, Paris surrounded • Reparations to be paid to Germany • Alsace-Lorraine lost • Large indemnity (5 billion gold francs in 5 years • Pays for further growth of railroads, etc…. In Germany WHAT IS HAPPENING HERE? JANUARY 1871 GERMAN EMPIRE DECLARED JANUARY 18TH 1871 GERMAN EMPIRE DECLARED Analyze this…. Look closely!