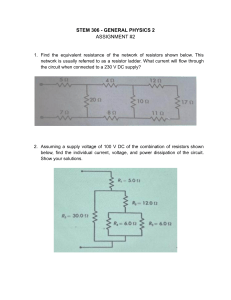
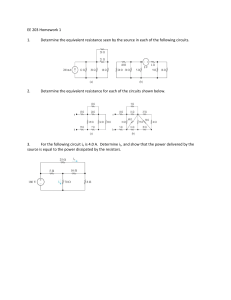
General Physics 2 – 4th Quarter Ohm’s Law – describe the relationship among electric current, potential difference, and electric resistance. Electric Current – A charge per unit time measured by ammeter. “intensité de courant” – French translation Formula: 𝐈 = 𝐪 𝐭 where: I = electric current q = charge (C) Coulomb t = time (s) Seconds Unit: C/s or A (Ampere) Other formula: 𝐈 = 𝐕 𝐑 where: I = electric current V = voltage (V) Volts R = resistance (Ω) Ohms Ω – omega Georg Simon Ohm (March 16, 1789 – July 6, 1854) André-Marie Amperé (January 20, 1775 – June 10, 1836) Two Types of Current Flow 1) Conventional (+ -> -) – from positive to negative terminal 2) Electron (- -> +) – negative to positive terminal Electrical Resistance – it is the opposition of a material to the flow of electric current. Most electrical connections used devices called resistors. Problem 1: A steady current of 2.0 A flows in a wire for 16.0 s. How many coulombs of charge flow through the wire? Solution: q = It q = (2.0 A) (16.0 s) q = 32.0 C Problem 2: Calculate the current through the circuit in which the voltage and resistance be 20V and 4Ω respectively. Solution: I = V R I = 20V 4Ω I = 5A Problem 3: The voltage and resistance of a circuit are given as 25V and 5Ω respectively. Calculate the current through the circuit. Solution: I = V R I = 25V 5Ω I = 5A Resistor Color Code Chart Color Digit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Multiplier x 100 x 101 x 102 x 103 x 104 x 105 x 106 x 107 x 108 x 109 Tolerance ± 1% ± 2% ± 0.5% ± 0.25% ± 0.1% ± 0.05% ± 5% ± 10% For easier remembering: BB ROY of Great Britain had a Very Good Wife RMA (Radio Manufacturers Association) – 1920s Color Bands –> Resistor Color Codes Resistors – it is the component that is used to limit or regulate the flow of electric current. Tolerance Formula: 𝐓 = (𝐑 ∗ 𝐏)/𝟏𝟎𝟎 Example: Brown-Black-Red-Gold Brown – 1 Black – 0 Red – x 102 Gold – ± 5% Translation of Color Code: 10 x 102 ± 5% 1000Ω ± 5% Resistance: 10 x 102 = 1000Ω Tolerance: 𝐓 = (𝐑 ∗ 𝐏)/𝟏𝟎𝟎 𝐓 = (𝟏𝟎𝟎𝟎Ω ∗ 𝟓)/𝟏𝟎𝟎 𝐓 = 𝟓𝟎Ω Another example: Find the resistor color code of the given resistance, 3450000Ω, assuming that the tolerance is 10%. (3 digits) Orange – 3 Yellow – 4 Green – 5 Yellow - x 104 Silver - ± 10% Answer: Orange-Yellow-Green-Yellow-Silver DC and AC Circuits Direct Current (DC) – refers to the unidirectional propagation of electric charge. Thomas Edison – proponent DC Circuit can be divided into two categories: 1) Series DC Circuit – A series circuit is a circuit that contains more than one electrical component connected one after the other in a single path. 2) Parallel DC Circuit – A parallel circuit is a circuit in which two or more electrical components are connected across each other. Quantity Series Resistors Parallel Resistors Current (I) I = I1 = I2 = I3… I = I1 + I2 + I3… Voltage (V) V = V1 + V2 + V3… V = V1 = V2 = V3… Equivalent Resistance RTotal = R1 + R2 + R3… (RTotal) 1 1 1 1 = + + … 𝑅𝑇 𝑅1 𝑅2 𝑅3 Formulas: 𝐈 = 𝐕 𝐑 𝐕 = 𝐈𝐑 𝐑 = 𝐕 𝐈 Example: 1000V IT = 1.33 A VT = 1000V RT = 750Ω IT = I1 = 1.33 A V1 = 266V R1 = 200Ω I2 = 1.33 A V2 = 532V R2 = 400Ω 1000V 750Ω IT = 1.33 A V1 = I1 R1 V1 = (1.33 A) (200Ω) V1 = 266V V1 = I1 R1 V1 = (1.33 A) (400Ω) V1 = 532V V1 = I1 R1 V1 = (1.33 A) (150Ω) V1 = 199.5V The answers are approximation only, especially in voltage. I3 = 1.33 A V3 = 199.5V R3 = 150Ω Physics – Major Instruments and Their Uses 1) Accelerometer – Measures acceleration 2) Ammeter – Measures electric current flow 3) Anemometer – Measures wind speed 4) Barometer – Measures atmospheric pressure 5) Bolometer – Detects electromagnetic radiation 6) Caliper – Measures distances and diameters precisely 7) Calorimeter – Measures heat exchange 8) Electrometer – Measures electric charge or voltage 9) Gravimeter – Measures gravitational field variations 10) Galvanometer – Detects and measures small electric currents 11) Hydrometer – Measures liquid density or specific gravity 12) Inclinometer – Measures angles of inclination 13) Magnetograph – Records changes in Earth's magnetic field 14) Manometer – Measures pressure in gases and fluids 15) Ohmmeter – Measures electrical resistance 16) Seismometer – Detects and measures seismic waves 17) Thermometer – Measures temperature 18) Viscometer – Measures fluid viscosity 19) Voltmeter – Measures electric potential difference