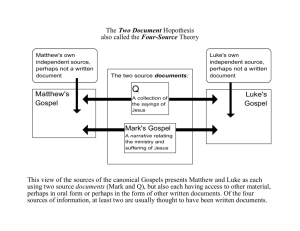
Choose the best definition for the meaning of CANON. Answer: Standard (Answer can be found on page 63 in ITNT.) Exegesis is the careful study of Scripture to discover the original, intended meaning. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 27 in How to Read.) Two basic kinds of questions one should ask of every biblical passage are related to context and content. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 30 in How to Read.) The questions of context are also of two kinds: historical and _________________. Answer: Literary (Answer can be found on page 30 in How to Read.) The From-the-Bible Application view holds that what is written in Scripture is wholly sufficient for guiding Christian life and ethics. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 177 in A Beginner's Guide.) The concept that God chose to reveal himself, his will, and his plan for redemption over time such that earlier stages show a less-complete picture of this than later stages is called what? Answer: Progressive Revelation (Answer can be found on page 179 in A Beginner's Guide.) Textual Criticism is the analysis of various manuscripts of the New Testament that have been preserved over the centuries, comparing them, dating them, and employing various techniques to determine which are the most reliable. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 66 in ITNT.) There are four gospels in the New Testament. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 60 in ITNT.) There are letters from Paul to various Roman governors and magistrates in the New Testament. Answer: False (Answer can be found on pages 60-61 in ITNT.) The titles of the New Testament documents reflect ancient church traditions. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 61 in ITNT.) One of the criterion that was used after the time of Bultmann to sort through the layers of historical and fantastical material in the Gospels is the criterion of embarrassment. Answer: True (Answer can be found on pages 18-19 of A Beginner's Guide) One of the key factors that weighs heavily into how one looks is the sources of information. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 21 of A Beginner's Guide) The purpose in a "quest" for the historical Jesus is to analyze all of the information available about Jesus so that we might know his life and significance. Answer: True (Answer can be found on pages 15-16 of A Beginner's Guide) The Sadducees believed in life after death. Answer: False The Pharisees emphasized faithfulness to Torah. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 42 of ITNT) Jews, for the most part, did not desire to maintain their Jewish identity. Answer: False (Answer can be found on pages 54-56 of ITNT) Stoicism was a philosophy that emphasized free will, questioned fate, and avoided anxiety - and believed joy was found everything, but in moderation. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 25 of ITNT) The pivotal social value in the New Testament world (especially the Roman world) was honor. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 33 of ITNT) Each Gospel has its own unique voice when it talks about Jesus. Answer: True (Answer can be found on pages 85-87 of ITNT) The New Testament presents Jesus as both human and divine/exalted. Answer: True (Answer can be found on pages 80-84; 90-92 of ITNT) Matthew's gospel is the only gospel that talks about "the church." Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 125 in ITNT.) The author of Matthew's gospel is anonymous. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 123 in ITNT.) The role of Jesus as Jewish teacher or rabbi is not very prominent in Matthew's gospel. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 131 in ITNT.) Mark's gospel is distinct, not in content, but in perspective and style. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 147 in ITNT.) Mark's gospel has an overly positive view of the disciples. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 156 in ITNT.) Most scholars believe Mark's gospel to be the last one written. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 144 in ITNT.) Scholars believe that the version of John's gospel that we possess today is a 2nd, 3rd, 4th, or even 5th edition. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 186 in ITNT.) Just about everything is unique in John's gospel. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 191 in ITNT.) A major theme of John's gospel is Jesus as the true revelation of God. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 195 in ITNT.) In John's gospel Jesus's crucifixion is viewed as a tragic moment only. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 196-197 in ITNT.) Matthew's gospel is the only gospel that talks about "the church." Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 125 in ITNT.) The author of Matthew's gospel is anonymous. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 123 in ITNT.) The role of Jesus as Jewish teacher or rabbi is not very prominent in Matthew's gospel. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 131 in ITNT.) Mark's gospel is distinct, not in content, but in perspective and style. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 147 in ITNT.) Mark's gospel has an overly positive view of the disciples. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 156 in ITNT.) Most scholars believe Mark's gospel to be the last one written. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 144 in ITNT.) Scholars believe that the version of John's gospel that we possess today is a 2nd, 3rd, 4th, or even 5th edition. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 186 in ITNT.) Just about everything is unique in John's gospel. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 191 in ITNT.) A major theme of John's gospel is Jesus as the true revelation of God. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 195 in ITNT.) In John's gospel, Jesus's crucifixion is viewed as a tragic moment only. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 196-197 in ITNT.) With certainty, we know Luke to be the author of the Gospel that bears his name. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 163 in ITNT.) The author of Luke's gospel has done research in order to write it. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 164 in ITNT.) About half of Luke's gospel is unique to his gospel alone. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 166 in ITNT.) Women are not very prominent in the unique material of Luke's gospel. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 167 in ITNT.) Food is a major theme in Luke's gospel. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 173 in ITNT.) In Luke's gospel, Luke never directly links salvation to the death of Jesus on the cross. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 178 in ITNT.) In Luke's gospel, Luke says a great deal about how Jesus's life provides salvation. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 179 in ITNT.) The author of Luke's gospel is also the author of Acts. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 209 in ITNT.) Acts is usually regarded as an example of "ancient biography" as it reports on the lives of Peter and Paul. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 212 in ITNT.) In Acts, Jesus remains present, even though he is absent. Answer: True (Answer can be found on pages 222-223 in ITNT.) One of the most difficult parts of hermeneutics is dealing with cultural relativity. Answer: True (Answer can be found in How to Read on page 84.) The typical pieces to a letter are the salutation; the thanksgiving; the main body; and the closing. Answer: True (Answer can be found in ITNT on pages 234-237.) The typical salutation in a letter would only identify the sender(s). Answer: False (Answer can be found in ITNT on page 235.) Authors in the ancient world, including those of the New Testament letters, likely used an "amanuensis" to compose their letters. Answer: True (Answer can be found in ITNT on page 233.) Paul studied "at the feet of Gamaliel." Answer: True (Answer can be found in ITNT on page 251.) Paul went on 2 missionary journeys. Answer: False (Answer can be found in ITNT on page 258.) Paul sees the gospel as a dynamic force. Answer: True (Answer can be found in ITNT on page 264.) There are notable differences between Jesus and Paul, in NT scholarship today, most scholars fall somewhere on a spectrum between Paul and Jesus having zero cohesion and complete cohesion. Answer: True (Answer can be found in A Beginner's Guide chapter 4.) Salvation history is one approach of understanding what Paul's theology is. Answer: True (Answer can be found in A Beginner's Guide on pages 60-62.) The New Perspective on Paul opposes the attitude that the Judaism of Paul's day was legalism and driven by works righteousness. Answer: True (Answer can be found in A Beginner's Guide on page 73.) It is possible that Paul wrote the letter of Galatians to the people in the northern part of the province of Galatia because in his salutation he addresses them as Galatians. Answer: True (Answer can be found on pages 326-327 in ITNT.) It appears that the situation going on in Galatians concerns them listening to a "rival version" of the Christian faith. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 328 in ITNT.) According to Powell, Paul makes three critical points in Galatians concerning the relationship between Christ and the Law. Answer: False (Answer can be found on pages 332-335 in ITNT.) Much of Paul's letter to the Romans is devoted to discussing implications of Paul's claim that the Gospel puts Jews and gentiles on the same footing, with regards to both their need for salvation and God's provision of that salvation through Christ. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 275 in ITNT.) In Paul's letter to the Romans, Paul declares that people are justified by good works and obedience to "works of the law." Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 278 in ITNT.) In the latter half of Paul's letter to the Romans, he addresses a number of themes, one of which concerns Christian's relationship with civil government. Answer: True (Answer can be found on pages 283-284 in ITNT.) In Paul's letter to the Ephesians, one of the themes Paul discusses is the "mystery" of the gospel. Answer: True (Answer can be found on pages 349-351 in ITNT.) Many scholars wonder if Ephesians was really written by Paul. Answer: True (Answer can be found on pages 347-348 in ITNT.) The city of Philippi was the second place in Europe that Paul founded a church. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 360 in ITNT.) Justification by faith alone in Christ alone is a major theme of Paul's letter to the Philippians. Answer: False (Answer can be found on pages 363-368 in ITNT.) Colossians bears many close parallels with Philippians. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 376 in ITNT.) The textbook mentions how scholars notice that Paul writes Colossians to address a particular problem - this problem is often referred to as the "Colossian heresy." Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 375 in ITNT.) One of the major themes in Colossians the reading discusses is suffering. Answer: False (Answer cannot be found in Colossians; this theme belongs to Philippians.) In the reading on Philemon, the author concludes saying that most scholars today believe Paul did not approve of slavery. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 440 in ITNT.) Paul's letter to Philemon is the shortest of all his letters. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 431 in ITNT.) In 1 Corinthians sexual morality is a big theme - from the reading it appears that there were people who believed that there is nothing wrong with having sex with prostitutes and people who believed sex is always wrong even for married couples. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 301 in ITNT.) In 1 Corinthians Paul's conclusion about "spiritual gifts" was that they were to be used for the benefit of the church. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 306 in ITNT.) According to the author, Paul's letter of 1 Corinthians was written to "spiritually mature" Christians. Answer: False (Answer can be found on page 289 in ITNT.) In 2 Corinthians Paul addresses apostolic authority - that he has it and those who have come to them do not have it. Answer: True (Answer can be found on pages 316-319 in ITNT.) In 2 Corinthians Paul discusses an opportunity for the Corinthian church to give an offering for the poor in the Jerusalem church. Answer: True (Answer can be found on page 315 in ITNT.) Two basic kinds of questions we should ask when studying a text in the Bible are questions related to content and context. The answer is 'True'. The Gospels are loosely categorized by scholars as... The correct answer is: Ancient Biography. From the graphic below, which "Synoptic Puzzle/Problem" theory is represented? The correct answer is: The 2 Source Theory. According to the Two Source Theory, what is Q? The correct answer is: Q is a collection of sources used by Matthew's Gospel and Luke's Gospel. According to the Two Source Theory, what does Q help explain? The correct answer is: Q explains the shared material between the Gospels of Matthew and Luke. Which Gospels are considered the "Synoptic Gospels?" The correct answer is: The Gospels of Matthew, Mark, and Luke. The synoptic puzzle, or problem, concerns the issue of explaining why the synoptic gospels share so much of the same material. The answer is 'True'. The most important quality in Roman culture was religious duty. The answer is 'False'. The Maccabean Revolution sits in the "back of the mind" of Jewish culture at the time of Jesus. The answer is 'True'. What was the most important quality in Roman culture? The correct answer is: Honor/Status. Each language has their own preferred structures as to how words and ideas are related to each other in sentences; so, it is at these points where translation by functional equivalence is to be preferred. The answer is 'True'. (Answer can be found on page 51 of How to Read.) Jesus was fond of teaching in parables. The answer is 'True'. Jesus often transgressed (that is, crossed over or went outside) social boundaries. The answer is 'True'. The authors of all four Gospels are anonymous. The answer is 'True'. A unique literary device used in Luke's Gospel to teach discipleship is a travel narrative. The answer is 'True'. Matthew's gospel is the only gospel where Jesus talks about "the church." The answer is 'True'. What episode is recorded in each of the Synoptic Gospels that serves as a kind of "hinge point" in the narrative? The correct answer is: Peter's confession that Jesus is the Christ. Word choices in Matthew's gospel appear to be intended to make the book more appealing to Gentiles than to Jews. The answer is 'False'. Luke's Gospel does not mention anything about Jesus's death on the cross as something that is needed for accomplishing salvation. The answer is 'True'. This Gospel has a unique prologue about the Word being with God and the Word being God. The correct answer is: John's Gospel. This Gospel depicts Jesus's disciples in a very negative light. The correct answer is: Mark's Gospel. Most scholars believe Mark was the first gospel written. The answer is 'True'. Scholars think that John's gospel has gone through a number of editions. The answer is 'True'. Which Gospel begins with a genealogy? The correct answer is: Matthew's Gospel. Which Gospels contain genealogies. The correct answer is: Matthew's Gospel and Luke's Gospel. Which Jewish group believed in the resurrection of the dead? The correct answer is: Pharisees. In many cases, New Testament authors would use an ______________________ to transcribe the letter. The correct answer is: Amanuensis (secretary). The salutation of a New Testament letter would identify what two different parties? The correct answer is: Sender(s) and Recipient(s). Where in a NT letter is the thanksgiving prayer placed? The correct answer is: Between the Salutation and the Body. Which Jewish sect did Paul belong to? The correct answer is: The Pharisees. How many missionary journeys did Paul go on? The correct answer is: 3. What system did the Pharisees develop during the intertestamental period to teach and train the people in Torah? The correct answer is: Synagogues. What is the Greek translation of the Old Testament called? The correct answer is: The Septuagint. Exegesis is the careful study of Scripture to discover the original, intended meaning. The answer is 'True'. Many modern scholars think that the Gospels can be placed loosely into the genre of "ancient funeral oration," since they describe in great detail Jesus's death. The answer is 'False'. There are only 3 parables in John's gospel. The answer is 'False'. The word synoptic means "seeing together." The answer is 'True'. One feature of Mark's style that has attracted a lot of attention is his abundant use of the "historical present." The answer is 'True'. The author of Luke's gospel did research to some extent by drawing on the previous work of those who were "eyewitnesses and servants of the word." The answer is 'True'. Many scholars have said that Luke envisions salvation as primarily liberation - meaning freedom from worldly forces that enslave people (like wealth). The answer is 'True'. Acts is usually considered by scholars to be "ancient biography." The answer is 'False'. The person who wrote Acts was also the person who wrote what other gospel? The correct answer is: The Gospel of Luke. What is missing from the list of parts to a Greco-Roman letter: the thanksgiving, the main body, the closing and ___________________. The correct answer is: The salutation. In Greco-Roman letters, the author of the letter would identify themselves in the closing portion of the letter. The answer is 'False'. According to Paul’s worldview as a Christian, we live “between the ages,” with Jesus inaugurating the “new creation age” with the “present evil age” still here. The answer is 'True'. For Paul, the heartbeat of God is that he is a God of self-expenditure, as demonstrated through Jesus Christ. The answer is 'True'. All of Paul's theology, at the end of the day, is very practical in that everything he believes about God and Christ has direct implications for how people live in the present world. The answer is 'True'. REL236 Final Review First Semester Review 1. Be familiar with the religious atmosphere of the Roman world. 2. Be familiar with the history leading up to the New Testament. 3. Be familiar with the different groups of people within the New Testament (i.e., Pharisees, Sadducees, etc.). 4. Be familiar with the many ways in which scholars study the New Testament (i.e., source criticism, textual criticism, etc.). 5. Know and understand the Synoptic Problem/Puzzle – pages 109-116 ITNT Be very familiar with the chart on page 113 in ITNT Review of Paul and His Letters I. Understand who Paul is and his history – pages 247-269 in ITNT and lectures Be familiar with his cosmic perspective Be familiar with his conception of the resurrection and how that changed through Jesus Be familiar with his relative timeline within the NT Be familiar with his three missionary journeys II. Know about the various aspects of NT letters – pages 231-245 ITNT Be familiar with the aspects of the three main parts to a letter: opening, body, closing Be familiar with how letters were written Be aware of the views concerning which of Paul’s letters are universally accepted as authored by him vs. those that are suspect Be familiar with the six issues concerning if a letter may be pseudepigraphic (know what pseudepigraphic means) III. Be familiar with each overview and the themes from each discussion of Paul’s letters 1. 1 Corinthians pages 289-307: is a letter where Paul addresses reports of division in the first half and in the second half, he addresses questions they have written to ask him; know that there are at least 4 letters to the Corinthians – we have #’s 2 and 4 2. 2 Corinthians pages 309-321: address some of the same things as 1 Cor. This letter reveals a lot about him as a pastor, but it is within a context of defending his apostolic ministry. 3. Paul’s prison letters: not sure from what imprisonment he wrote these – Caesarea or Rome, my thought is Rome. Beyond where Paul wrote them, these letters share a common bond in that they are apocalyptic (a word you need to know). Paul desires to let them in on a divine reality. a. Ephesians pages 339-355: kind of odd, no greetings to people, so one thought is that this is a letter that was to be circulated to churches around the western part of the province of Asia (modern day Turkey) i. Paul lays out Ephesians as a drama – focusing on the Triumph of God that is in Jesus Christ, the church participating in that triumph and how we are yet working in this world to defeat the cosmic powers of sin, death, and Satan b. Philippians pages 357-369: a letter of joy in many respects. A major theme in is Paul connecting the two points of salvation, the now and the not yet, through participation in suffering and servanthood i. In this letter Paul shows how his situation is not weakness or defeat, but it has not only been a good thing but that it is an opportunity for him to participate in the shame and suffering of Jesus ii. Chapter 2: Probably Paul’s central theological concept – not just for this letter but for all of his theology. vv. 5-11 show the humiliation of Christ something all the Philippians should imitate – participation in the shame of Jesus iii. Paul shows that he and others ae examples of what it is to have the “mind of Christ” – he once thought God noticed and honored those who accumulated credentials (practices and ideologies of the present evil age), but what God really takes notice of and the one whom God honors is the one who makes themselves a servant (slave), the lowest social place – Jesus gave up his privileges to become a slave and to be put to death and cursed on a cross c. Colossians pages: pages 371-385: a letter to a church Paul has never visited. It concerns the Christian’s existence in a hostile cosmic setting (similar to Ephesians) i. Paul sees salvation as cosmic realm transfer (see the Ven diagram) ii. He calls the Colossians to live according to the new age d. Philemon pages 431-441: a letter to a slave owner named Philemon about a runaway slave named Onesimus i. The same concepts or themes as Ephesians, Philippians, and Colossians ii. Paul encourages Philemon not to inhabit practices of the present evil age but to inhabit the practices of the new creation age iii. Philemon does this by welcoming Onesimus – showing lavish hospitality and receiving him as an equal 4. 1 and 2 Thessalonians pages 387-411 a. Paul’s response to questions the Thessalonians had concerning the resurrection b. They were a model church – suffered persecution and yet remained faithful 5. The Pastoral Letters: 1 and 2 Timothy, Titus pages 413-429 6. Galatians pages 323-337: the letter does not have a thanksgiving prayer – ouch – and the tone of the letter is abrasive and direct a. The trouble seems to be the Galatians embracing a message from Jewish Christian missionaries who believe and teach that the Gentile Christians are to take on a Jewish ethnic identity by converting to Judaism through Torah practices (circumcision, dietary laws, Sabbath, ect.). b. Paul tells the Galatians that the “gospel” they are believing is no gospel at all c. What Paul sees is the Galatians defecting from the gospel d. Paul tells the Galatians that Peter did something similar and he confronted Peter to his face publicly e. Some phrases to know: “works of the law” = deeds done in obedience to the Mosaic Law that mark a person out as Jewish; “justification” = more than a legal term referring to God’s act of setting people right, it is a term that sees God doing something – snatching us from the present evil age and thrusting us into the new creation age (cosmic realm transfer); transgress = someone who will be cut off, not ever forgiven f. For Peter, he left the boundaries of his ethnic identity and had fellowship with Gentiles, for him to retreat back into the boundaries he broke (which was right and good to do) would then make him a transgressor g. Paul proclaims that the Galatians have been co-crucified with Christ which frees them to live into the fulness of God’s new creation people h. One comes into being God’s people through being justified, any other way is a nullification of the death of Christ i. “the curse of the law” – classic understanding: under curse for trying to earn salvation by works, we cannot keep the whole law; a better understanding: a gentiles do not need to be pressured to take on the practices of the Mosaic Law j. To the Jewish Christian Missionaries: Paul says that they are cursed because they are outside the law because of their Christian faith k. The promise: Abraham would bless the nations – Jesus is the one who inherits this promise; the Mosaic Law was added for a different purpose, and it serves the Abrahamic promise l. Jesus created a new family, and everyone is free to associate with everyone else – this is what Paul calls the “Law of Freedom” 7. Romans pages 271-287: this is a letter written to the Roman house churches by a pastor trying to bring unity to the church – this is not Paul’s “magnum opus” of theological work a. What is the nature of the conflict? Starting from the end of Romans and working backward there appear to be two groups that Paul calls the “strong” and the “weak” – the issue appears to be the weak group claiming to be superior to the strong group because they have a Jewish ethnic identity and they are pressuring the strong to also take on this identity (this could be because the weak group is comprised of Jewish Christians or they could be gentiles who have taken on a Jewish ethnic identity [it is my opinion that both groups are gentiles and where the weak have taken on a Jewish ethnic identity]) b. Paul’s first major movement is 1:18-5:11 i. Here Paul brings both groups together as one group where he argues that they all share in humanities rebellion and depravity, and they all share in God’s justification in Christ ii. 1:18-3:26 – Paul’s focus is on all of them share in rebellion and all of them have been made right (rectified) iii. 3:27-5:11 because all of them have been justified there is no basis for any group to take on a new/different identity to be justified and hold that over the other group – so there is no basis for boasting in their “superior identity,” justification eliminates boasting; Paul further explains that the weak cannot claim superiority in Abraham as their father, since all who are justified can claim Abraham as their father; they should boast together in the hope of the future transformation, boast in their suffering, and boast in God c. The second major movement is 5:12-8:39 – Paul now sets their church conflict in terms of cosmic conflict; he theologizes in cosmic terms i. In chapter 5 Paul calls the two realms Adam = old humanity = enslavement to sin and death and Christ = new humanity = redemption and renewal – there is life and life spreads ii. In chapter 6 the context is Paul telling the community that they, as the people of God, have been living in the wrong realm; their division is because they have been inhabiting the realm of that is enslavement to sin iii. In chapter 7 Paul talks about the relationship of Torah and sin, because they have been inhabiting the realm of sin and death they have inadvertently used Scripture for great harm, Torah has become Torah of sin and death; the Law was a good gift from God, but as it is being used by the Roman Christians within the realm of sin and death, these cosmic forces have hijacked God’s good law and it produces destruction; what the Roman Christians need to do is use the Law within the realm of Christ so that it can do its unifying work iv. Chapter 8 continues this line of thought and Paul uses the phrases “law of sin and death” and the “law of the Spirit and life” – Torah used in these two different cosmic realms are going to produce very different effects; later in chapter 8 Paul clarifies Christian identity – being Christian is cosuffering, they are united together and is they co-suffer, they will be coraised with Christ and if they do this then nothing can separate them from God’s love, no cosmic power can sperate them from the love of God that is in Christ Jesus d. Paul’s third movement in his letter to the Romans is chapters 9-11 i. Paul made a couple of statements earlier about God’s righteousness is being worked out in the gospel apart from Torah, and he talks about Israel being unfaithful ii. With these comments Paul now turns to explain this central question: How can God being doing a work in the world through a new agent? 1. Because God’s righteousness was to be worked out in the world through Israel 2. If God is now renewing the nations apart from Israel, what does that say about God’s faithfulness? 3. Israel was God’s chosen people; how can God just switch agents? iii. Chapter 9 takes up the question of Israel’s election, he frames it as recognizing that God elected Israel, but has now set them aside and is now doing a new work with some other agent – Jesus being the new agent 1. This is not a chapter about individual election for salvation 2. It is about God setting aside the people that he chooses 3. Paul’s point, God has the right to change agents when the agent gets in God’s way to accomplish his mission a. So, Paul’s comment about choosing Jacob over Esau is God is about God choosing a new agent b. And he has chosen a new agent because that agent, Israel, has harden its heart and stands in God’s way e. Paul’s third movement is chapters 12-15 i. There are slightly more generalized exhortations concerning community life ii. In chapter 15 Paul’s entire rhetorical movement comes to its highpoint in vv. 5-8 – where Paul exhorts the two groups to receive one another 1. Receiving one another is more than tolerance – it is acceptance 2. It is showing lavish hospitality and warmly embracing one another 3. It is an honor to be related to one another iii. By receiving one another they become unified as the one new people of God; through which they can glorify God The Rest of the NT 1. Understand the various issues with the letter of Hebrews Unknown author Unknown audience Unknown situation Unknown date Understand the professors view of these things Know the themes Know the issues concerning the “stern warnings” 2. Know what the letter of James is about Themes Topics discussed o Specifically concerning his view of trials as temptation o And the issue of works and faith 3. Be familiar with 1 and 2 Peter Understand 1 Peter is a letter of encouragement to Christians suffering persecution in regions outside Palestine 2 Peter is a warning to be on the lookout for false teachers 2 Peter 1 calls the Christian to make an effort to increase in character 4. Know what Jude is about It is very similar to 2 Peter Warning about false teachers and the judgment awaits 5. 1, 2, 3 John – Know what the letters are about 1 John stands out, as the largest of the three letters, and that it focuses on love for God and love for others 2, 3 John focus on conflicts in the house churches 6. Revelation – know everything about it, LOL Know the big picture of Revelation Themes Various interpretative perspectives