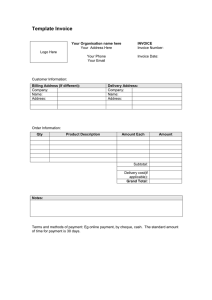
LECTURE 11 BUSINESS DOCUMENTS Why Documentation is Necessary in Business Transactions o Record Keeping: Maintain accurate history of transactions and business activities. o Efficiency: Streamline operations and prevent errors. o Legal Compliance: Meet government regulations and contract requirements. o Communication: Facilitate clear communication within the business and with customers, suppliers, etc. o Decision-Making: Provide data for financial analysis and informed business choices. Transaction – A transaction is the complete process of supplying goods or services from the initial enquiry through to eventual payment. Source Document – A source document is any document that provides evidence of a transaction, such as an invoice, receipt, or bank statement. Auditing - Auditing is a process of evaluating and verifying the financial information presented in a company's financial statements. It involves a systematic and independent examination of a company's financial records, transactions, and operations to ensure that they are accurate, reliable, and in compliance with accounting standards and regulations Credibility - Credibility is the quality or characteristic of being trusted, believable, and reliable. In essence, it is the perception or reputation that someone or something has for being truthful, honest, and dependable. 1 Types of Documents Sales & Ordering o Letter of Enquiry: A formal request for information about products or services. o Quotation: A document outlining the price, terms, and conditions for a potential sale. o Order Form: Specifies the goods or services a customer wants to purchase. o Delivery Note: Confirms the items included in a shipment. o Invoice: Request for payment, listing goods or services provided and total amount due. o Receipt: Proof of payment received from a customer. Financial o Credit Note: Issued to reduce an invoice amount due to returns or errors. o Debit Note: Used to adjust an invoice upwards, such as for additional charges. o Statement of Account: Summarizes transactions and balance due over a period. Stock Control o Purchase Requisition: An internal request to buy goods or materials. o Stock Card: Records the movement of inventory in and out of a business. Imports & Exports o Bill of Lading: A contract between a shipper and carrier, detailing goods shipped. o Import/Export License: Government permits required for certain goods. o Certificate of Origin: Indicates where goods were manufactured. o Airway Bill: A receipt and contract used for air cargo. Payment 2 o Cheque: Order to a bank to pay a specific sum of money. o Banker's Draft: A guaranteed payment drawn on the bank's own funds. o Bill of Exchange: A written order for payment at a future date. o Telegraphic Money Transfer: Electronic transfer of funds Business Documents for Various Purposes Stock cards are used to keep a record of all stocks entering and leaving the stockroom. This procedure ensures that stock level do not fall below a minimum resulting in the depletion of stocks. Purchase requisition – This is a document sent by the purchaser or buyer to the seller requesting goods that may be available. MAKING ENQUIRIES 1. Letter of Enquiry is a letter or standard form that is sent by persons who wish to be informed of what goods and services and the prices of these that a company offers for sale. The requesting information includes of this letter or standard form. includes : Specifications of the product Prices Despatch and delivery arrangements Payment procedures 3 What is a tender? A TENDER refers to a formal written offer to provide goods or services, usually submitted in response to a request for proposal (RFP), request for quotation (RFQ), or other formal solicitation issued by a company, organization, or government agency. The tender typically includes detailed information about the goods or services to be provided, the terms and conditions of the contract, and the price and payment terms 4 Cover letter (information received) – A response to a letter of enquiry with the supplier providing details of their products through mediums such as catalogues. Request for quotation – A request to quote for specific goods. 2. Quotation – A quotation is a formal document outlines the price and other terms and conditions that a vendor or supplier is offering to a potential customer for goods or services. It typically includes details about the quantity and specifications of the products or services, the delivery or completion time, and the payment terms. Basically it answers the lettefr of enquiry The quotation includes : Trade discount – is given to sellers in similar trade to to make a profit on resale Quantity discount – it encourages buyers to place a larger order Cash discount – this is usually shown as “ terms “ Carriage paid – the seller pays the cost of transportation for the goods Carriage forward – Buyer pays for c everything else but transport which is an extra charge The company may resend either a quotation or a catalogue Purchase 3. Order (information provided) – If the buyers find satisfaction in the quotation order form or letter requesting the supply of specific goods. Required goods The agreed prices The date the delivery is required THE ORDER HAS GREEN WRITING 5 A catalogue is a booklet with a brief description and pictures of articles for sale. Since a catalogue is costly, some companies opt to send a quotation instead. A quotation lists all the goods in stock along with their prices. (c) If there is an interest to purchase an item in the catalogue then an order letter is sent requesting goods to be supplied. Requisition A requisition is a formal request or demand for something that is needed, often used in the context of requesting goods or services for a business or organization (internal request for suppliers) Acknowledgement of Order Having received an order from a byer, the seller will usually send an acknowledgement stating: That the order have been received Order is accepted and will b supplied When dispatched is anticipated 4. Despatch and Delivery 6 The following three documents accompany goods delivered: Delivery Note is a document used by businesses to confirm that goods have been delivered to a customer. It serves as proof of delivery and contains important information about the shipment, such as the quantity and description of the goods, the date of delivery, and the names and addresses of the seller and buyer A copy of the delivery note is given to the buyer. Consignment/Advice note is sent when the firm does not have its own transportation. A transport company is paid to deliver the goods. A consignment note will be prepared by the consignor (the sender) and given to the transport company. It contains information about the destination of goods and the name of the consignee (the receiver). (Proof of receipt by Transport Company) 7 5. Charging An Invoice is a document that lists the goods or services provided by a seller(creditor) to a buyer (debtor), along with the prices and terms of payment. This invoice states: Quantity of goods supplied. Individual prices Total amount owed. Discounts offered for prompt payment. The individuals invoice number The buyer’s order number. 8 Terms 5% 30 days – A Discount of 5% will be given if the customer pays within 30 days. E & OE – means E & OE ‘Errors and Omission Expected’ , i.e. if any mistakes were made on the invoice the company will make the correction. Pro forma Invoice A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that is sent to a customer before the completion of a transaction. It is to help facilitate and streamline the transaction process by providing a clear understanding of the terms of the sale before it is completed just there isn’t credibility within the customer (secure payment). If the customer is interested in the items sent, an actual invoice is sent. 9 Credit note is the reduction in prices. It is issued to a customer when there has been an overcharge on an invoice due to faulty arithmetic, when goods have been returned because of damage or refunds requested for goods not received. Which can reduce the debit which the buyer owes the seller A credit note is printed in red. Debit note is also known as a supplementary invoice and it makes additional charges. It is sent to the customer whenever there is an undercharge or omission on the invoice. It makes an additional charger Debit note is printed in red Tax on purchases Indirect Taxes are taxes that are levied on goods and services, rather than on individuals or businesses directly. These taxes are typically included in the price of the goods or services and are paid by the consumer at the point of purchase( point of sale terminal). It is not directly paid to the government but is collected by the business and then passed on unto the government. \ Statement of Account (which is the demand for payment) represents a compilation of all financial activities that have taken place within a specified period, typically ranging from a month to a year. Which basically summarises a customer’s outstanding account (amount the owed) in the company’s accounts and books. This information can include deposits, withdrawals, purchases, and other financial transactions, as well as any fees or charges incurred during the period in question A receipt is given for cash payment. PAYMENT OF DEBTS CASH Cash Payment : Cash is the most traditional and commonly used method for making debt payments. It is a physical exchange of money between the debtor and the creditor. Cash are legal tenders which refers to the universal acceptance of certain methods of p87u7ayments. 10 CHEQUE A cheque is an order to the bank to transfer payments from an individual’s account (the payer’s/drawer’s account) to credit another individual’s account (the payee’s account) or to pay the payee on presentation of that cheque. DEBT CONSOLIDATION Debt consolidation is a financial strategy that involves combining multiple debts into a single loan or payment. The goal of debt consolidation is to simplify the repayment process and potentially lower the overall interest rate or monthly payment, making it easier for the borrower to manage their debt and pay it off over time. STOCKS Stocks are capital or assets of a firm. It is used for to support internal operations as well as meet orders from customers Holding stocks can adversel affect cash flow because it can drain on a business financial resources STOCK LEVELS Stock levels refers to the amount of capital within in business. Maximum and minimum stock levels are often established to ensure 1) Sufficient stocks are available for internal operations 2) Stock is readily available to meet customers’ order 3) Too much stock is not held Maximum stock level - Greatest figure of stock of a particular item which is allowed to rise It is used to ensure stock does not rise above what is considered to be an economic level To avoid tying up capital unnecessarily 11 Minimum stock level - Lowes level of stock which is allow to fall It is to safeguard running out of stock When stocks fall to this level, immediate supplies are ordered to arrie before an internal financial decline crash. 12