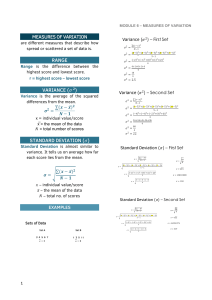
INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGICAL TESTING AND ASSESSMENT - 1905 – Alfred Binet and colleague published - a test designed to help place Paris school children appropriate classes. WWI and WWII: psychological testing for military. Psychological Testing - Measuring psychology related variables by means of devices or procedures designed to obtain a sample or behavior. - Objective: obtain some gauge, numerical in nature, with regard to ability and attribute. - Process: may be individual or group in nature; adding up the number of correct answers or the number of certain types of responses. - Role of Evaluator: one tester may be substituted for another tester without appreciably affecting the evaluation. - Skill of Evaluator: technician-like skills in terms of administering and scoring a test, and interpreting a test result. - Outcome: testing yields a test score or series of test scores. Psychological Assessment - Gathering and integration of psychology related data for the purpose of making a psychological evaluation. - - - - Through use of tools: tests, interviews, case studies, behavioral observation. Objective: to answer a referral question, solve a problem, or arrive at a decision through use of tools of evaluation. Process: individualized; focuses on how an individual processes rather than simply the results of that processing. Role of Evaluator: assessor is key to the process of selecting tests and/or other tools of evaluation. Skill of Evaluator: educated selection of tools of evaluation, skill in evaluation, and thoughtful organization and integration of data. Outcome: logical problemsolving approach. VARIETIES OF ASSESSMENT • Psychological Assessment • Therapeutic Psychological Assessment • Educational Assessment • Retrospective Assessment • Remote Assessment PROCESS OF ASSESSMENT Referral - Initial Contact - Selection of Tools - Formal Assessment - Report Writing Feedback Sessions Collaborative Psychological Assessment Therapeutic Psychological Assessment Dynamic Assessment: Evaluation – Intervention – Evaluation TOOLS OF PSYCHOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT 1. Psychological Tests - may differ in content, format, administration procedures, scoring, interpretation, and technical quality or psychometric soundness. Score: code or summary statement, not necessarily numerical in nature, reflects an evaluation of performance on a tests, task, interview, or some other sample of behavior. Scoring: process of assigning such evaluative codes or statements to performance on tests, tasks. Interviews, or others. Cut Score: reference point, usually numerical, derived by judgement and used to divide a set of data into two or more classifications. Psychometrics: science of psychological measurement Psychometrician or Psychometrist: professional who uses, analyzes, and interprets psychological test data 2. Interview - Taking note of verbal and nonverbal behavior - May be conducted in other formats. - Through direct communication involving reciprocal exchange. - Motivational Interviewing – therapeutic dialogue that combines person-centered listening skills such as openness and empathy, with the use of 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. cognition-altering techniques designed to positively affect motivation and effect therapeutic change. Portfolio – work products, canvas, film, video, audio, or some medium. Case History Data records, transcripts, and other accounts in written, pictorial, or other form that preserve archival information. Behavioral Observation – monitoring actions of others by recording quantitative and/or qualitative information. Role-play Test – acting an improvised part in a simulated situation. Computers/Computer-Assisted Psychological Assessment (CAPA) PARTIES IN THE ASSESSMENT ENTERPRISE • Test Developers – publishers, creators, distributors. • Test Users – Levels A, S, B, and C. • Test Takers – psychological autopsy HISTORICAL, CULTURAL, LEGAL, AND ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS Chinese Imperial Examinations 2200 BCE - Music - Archery - Horsemanship - Writing and Arithmetic - Agriculture - Geography - Civil Law - Military Strategy (Song Dynasty) 960 – 1279 CE - Tests: knowledge of classical literature. - Wisdom of the past. ➢ Privileges: wearing of special garb, exemption from taxes, exemption from government-sponsored interrogation by torture. Middle Ages - Ancient Greco-Roman writings: indicative of attempts to categorize people in terms of personality types – overabundance or deficiency in some bodily fluid. Charles Darwin - Natural Selection (1859) - Chance variation in species would be selected or rejected by nature according to adaptivity and survival value. - Individual Differences Francis Galton - Classified people according to their natural gifts and to ascertain their deviation from an average. Wilhelm Max Wundt - Experimental Psychology Laboratory - General description of human abilities with respect to variables such as reaction time, perception, and attention span. James McKeen Cattell - Coined the term mental test (1890). - Psychological corporation – advancement of psychology and the promotion of the useful applications of psychology. Charles Spearman - Originating the concept of test reliability as well as building the mathematical framework for the statistical technique of factor analysis. Victor Henri - With Alfred Binet: how mental tests could be used to measure higher mental processes. Emil Kraepelin - Word association technique Emil B. Titchener - Psychological school of thought: Structuralism. - Coined the word empathy. G. Stanley Hall - First president of American Psychological Association (APA) Lightner Witmer - Succeeded Cattell as director of Psychology Laboratory in Pennsylvania. - Founded the first clinic in the US. 20TH CENTURY: MEASUREMENT OF INTELLIGENCE 1895 – Alfred Binet and Victor Henri: Measurement of Abilities (memory and social comprehension). 1905 – Binet and Theodore Simon: 30-item measuring scale of intelligence. 1939 – David Wechsler: measure adult intelligence. 1914 – Robert S. Woodworth: emotional fitness – Woodworth Psychoneurotic Inventory: personality test. Self-Report – process whereby assesses themselves supply assessmentrelated information by responding to questions, keeping a diary, or selfmonitoring thoughts or behaviors. Projective Test – an individual assumed to project onto some ambiguous stimulus. (inkblot, drawing, photograph) Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) – use of pictures as projective stimuli. CULTURE AND ASSESSMENT Culture - The socially transmitted behavior patterns, beliefs, and products of work of a particular population, community, or group of people. Cultural Considerations - Culture-Specific Tests – for people from one culture but not from another. - Culture-Fair Tests – to be free of cultural bias. LEGAL AND ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS Law – body of rules thought to be for the good of society as a whole. Ethics – body of principles of right, proper, or good conduct. STATISTICS ➢ Range of techniques and procedures for analyzing, interpreting, displaying, and making decisions based on data. ➢ Figures and facts. ➢ Central component: Math Psychological Statistics - Based on Psychological Data - Psychological constructs or variables. Types of Data • Data – set of qualitative and quantitative values, made up of variables. • Variable – can be measured, different values between individuals or in the same individual at different time points. Types of Variables • Independent Variable – can control, not affected by the state of any other variable in the experiment, may have different levels. • Dependent Variable – can be measured. • Qualitative Variable – qualities, does not imply numerical ordering. • Quantitative Variable – measured in terms of numbers. • Discrete Variable – possible scores are discrete points on the scale. • Continuous Variable – possible scores are continuous. Level or Scales of Measurement • Nominal – differentiates between items or subjects based on categories, CLASSIFICATIONS. • Ordinal – ranking, spectrum of values. • Interval – degree of difference between observations, equal distances. • Ratio – fixed intervals between scores, has TRUE ZERO POINT. Types of Statistical Analyses • Descriptive Statistics – summarizing, graphing, and describing quantitative information. • Inferential Statistics – drawing of conclusions and generalizations, testing hypothesis and deriving estimates. Describing Data Qualitative Variables - Frequency Tables - Pie Charts - Bar Charts - Comparing Distributions using Bar Charts Quantitative Variables - Histogram - Frequency Polygon - Commulative Frequency Polygon - Bar Charts - Line Graph Shape of Distribution • Symmetrical – can be cut down to form 2 mirror images, never a perfectly symmetrical distribution. • Asymmetrical/Skewed – one of the 2 tails of the distribution is disproportionately longer than the other: positive or negative. • Normal Distribution – 2 sides are roughly the same shape, single peak: center, 2 tails extends out equally, bell shaped or bell curved. • Kurtosis – degree of flatness of peakness of a distribution, higher peak: data is clustered around the middle, flat: data is spread around evenly. Measures of Central Tendency ➢ Mean – sum of the numbers divided by the number of numbers. ➢ Median – midpoint, counting all numbers in the data set. ➢ Mode – most frequently occurring value, qualitative data only. Measures of Spread or Variability - How spread out a group of scores is within a distribution. - Range – simplest measure of variability; highest score minus lowest score. - Interquartile Range (IQR) – divides data set into 4 parts (25% of data), range of the middle 50% of the scores in a distribution. - Variance – average squared difference of the scores from the mean. - Standard Deviation – square root of variance. Standard Normal Distribution 1. Symmetrical around their mean. 2. Mean, median, mode is equal. 3. Area under normal curve is equal to 1.0. 4. Denser in the center, less denser in the tails. 5. Two parameters: mean and standard deviation. 6. 68% of the area is one standard deviation above and below the mean. 7. 95% of the area is within two standard deviations above and below the mean. Standard Scores - Raw scores that has been converted from one scale to another scale. - Position of test takers performance relative to other test takers is readily apparent. Z Scores – 1 T Scores – 10 A Scores – 100 IQ Scores – 15 Stanine – Mean: 5, SD: 2 Correlation - Statistical technique that is used to measure and describe the relationship between two variables. Strength of Correlation - Correlation coefficients range from 1.00 to -1.00. - Closer to 1: stronger (regardless of the sign). Types of Correlation: ➢ Positive Correlation – one variable increase or decreases, another variable also increases or decreases. ➢ Negative Correlation – one variable increases, another variable decreases. RELIABILITY, VALIDITY, AND UTILITY RELIABILITY - Consistency in measurement. - Reliability Coefficient: an index of reliability, a proportion that indicates the ratio between the true score variance on a test and the total variance. - Proportion of the total variance attributed to true variance. - Greater proportion of the total variance attributed to true variance: more reliable. Classical Test Theory – score on a test is presumed to reflect not only the test taker’s true score but also error. Error – component of the observed test score that does not have to do with the test taker’s ability. X=T+E Variance – standard deviation squared, statistic useful n describing sources of test score variability. True Variance – variance from true differences. Error Variance – variance from true differences TYPES OF ERROR ➢ Measurement Error – all of the factors associated with the process of measuring some variable, other than the variable being measured. ➢ Random Error – source of error in measuring targeted variable – by unpredictable fluctuations and inconsistencies of other variables. ➢ Systematic Error – typically constant or proportionate to what is presumed to be the true value of the variable being measured. SOURCES OF ERROR VARIANCE ➢ Test Construction ➢ Test Administration ➢ Test Scoring and Interpretation TEST-RETEST RELIABILITY ESTIMATES - Reliability obtained by correlating pairs of scores from the same people on two different administrations of the same test. - Appropriate when evaluating the reliability of a test that purports to measure something that is relatively stable over time. - Interval between administrations increases = correlation between the scores obtained on each testing decreases. - Longer time passes = reliability coefficient will be lower. - Coefficient of Stability – interval between testing is greater than 6 months. Internal Consistency Estimate of Reliability or Inter-Item Consistency - Degree of correlation among all the items on a scale (homogeneity). - Split-half Reliability Estimates – correlating two pairs of scores obtained. SPEARMAN - BROWN FORMULA - To estimate internal consistency reliability from a correlation of two halves of a test. - Specific application of a more general formula to estimate the reliability of a test that is lengthened or shortened by any number of items. General Spearman-Brown Formula: Adjusted/Corrected: Reliability increases = test length increases - Based on consideration of the entire test – tend to be higher than those based on half of a test. - To determine the number of items needed to attain a desired level of reliability – new items must be equivalent in content and difficulty. KUDER-RICHARDSON FORMULA - G. Frederic Kuder and M.W. Richardson - 20th formula developed in a series. - Statistic of choice for determining the inter-item consistency of dichotomous items – items that can be scored right or wrong. - COEFFICIENT ALPHA - Mean of all possible split-half correlations, corrected by the Spearman-Brown formula. - Appropriate for use on tests containing non-dichotomous items. Measures of Inter-Scorer Reliability - Scorer reliability, judge reliability, observer reliability, and interrater reliability. - Degree of agreement or consistency between two or more scorers with regard to a particular measure. - Coding non-verbal behavior. - Coefficient of inter-scorer reliability. • Test-retest – stability of a measure • Alternate Forms – relationship between different forms of a measure. • Internal Consistency – extent to which items on a scale relate to one another. • Inter Scorer – level of agreement between raters on a measure. True Score Model of Measurement and Alternatives - Classical Test Theory (CTT) – each test taker has a true score on a test that would be obtained but for the action of measurement error. - Domain Sampling Theory/Generalizability Theory – to estimate the extent to which specific sources of variation under defined conditions are contributing to the test score. - Item Response Theory (IRT) – item difficulty and item discrimination. • Item Difficulty – attribute of not being easily accomplished, solved, or comprehended. • Item Discrimination – degree to which an item differentiates among people with higher or lower levels of the trait or ability. VALIDITY - Judgement or estimate of how well a test measures what it purports to measure in a particular context. - Appropriateness of inferences drawn from test scores. - Validation/Validation Studies – gathering and evaluating evidence about validity. - Local Validation Studies – when the test user plans to alter in some way the formal, instructions, language, or content of the test. Trinitarian Model of Validity - Content Validity – measure of validity based on an evaluation of the subjects, topics, or content covered by the items in the test. - Test Blueprint – a plan regarding the types of information to be covered by the items. - Criterion-Related Validity – obtained by evaluating the relationship of scores obtained on the test to scores on other tests or measures. o Concurrent Validity – index of the degree to which a test score is related to some criterion measure obtained at the same time. o Predictive Validity – predicts some criterion measure. Base Rate – trait, behavior, characteristic, or attributes exist in the population. - Hit Rate – proportion of people a test accurately identifies as possessing or exhibiting a particular trait, behavior, characteristic, or attribute. - Miss Rate – those who fails to identify as having, or not having, a particular characteristic or attribute, amounts to an inaccurate prediction. - False Positive – a miss wherein the test predicted that the test taker did possess the particular characteristic or attribute being measured when in fact the test taker did not. - False Negative – a miss wherein the test you predicted that the test taker did not possess the particular characteristic or attribute being measured when the test taker actually did. Validity Coefficient - A correlation coefficient that provides a measure of the relationship between test scores and scores on the criterion measure. - Incremental Validity – degree to which an additional predictor explains something about the criterion measure that is not explained by predictors already in use. Trinitarian Model of Validity • Construct Validity – “umbrella validity” • Construct – informed, scientific idea developed or hypothesized to describe or explain behavior. Evidence of Construct Validity • Evidence of Homogeneity – how uniform a test is in measuring a single concept/construct. • Evidence of Changes with Age – if a test score purports to be a measure of a construct that could be expected to change over time, then, the test score too should show the same progressive changes with age to be considered a valid measure of the construct. • Convergent Evidence – from a number of sources. • Discriminant Evidence – showing little relationship between test scores and/or other variables with which scores on the test being construct-validated should not theoretically be correlate. Validation Strategies • Ecological Validity – how well a test measures what it purports to measure at the time and place that the variable being measured is actually emitted. • Face Validity – how relevant test items appear to be, if a test definitely appears to measure what it purports to measure ‘on the face of it’. Factor Analysis - Class of mathematical procedures designed to identify factors or specific variables that are typically attributes, characteristics, or dimensions on which people may differ. o Exploratory Factor Analysis – estimating or extracting factors, deciding how many factors to retain, and rotating factors to an interpretable orientation. o Confirmatory Factor Analysis – testing the degree to which a hypothetical model fits the actual data. o Factor Loading – testing the degree to which a hypothetical model fits the actual data. Test Bias and Rating Errors • Bias – factor inherent in a test that systematically prevents accurate, impartial measurement, bias implies systematic variation. • Rating Error – judgement resulting from the intentional or unintentional misuse of a rating scale. • Leniency/Generosity Error – from the tendency on the part of the rater to be lenient in scoring, marking, and/or grading. • Severity Error - to be overly critic in scoring, marking, and/or grading. • Central Tendency Error – rater exhibits a general and systematic reluctance to giving ratings at either the positive or the negative extreme. • Restriction of Range Rating Errors – central tendency, leniency, and severity errors. • Rankings – requires the rater to measure individuals against one another instead of against an absolute scale, used to overcome restriction of range rating errors. Halo Effect – tendency to give a particular ratee a higher rating than he or she objectively deserves because of the rater’s failure to discriminate among conceptually distinct and potentially independent aspects of a ratee’s behavior. UTILITY - How useful a test is. Practical value of using a test to aid in decision making. Improve efficiency. Factors that Affect a Test’s Utility • Psychometric Soundness – reliability and validity of a test. • Costs – disadvantages, losses, or expenses in both economic and noneconomic terms. • Benefits – profits, gains, or advantages in both economic and noneconomic terms. Utility Analysis - Family of techniques that entail a cost-benefit analysis designed to yield information relevant to a decision about the usefulness - - - and/or practical value of tool of assessment. Expectancy Table or Chart – likelihood that individuals who score within a given range on the predictor will perform successfully on the criterion. Taylor-Russell Tables – increase in base rate of successful performance that is associated with a particular level of criterionrelated validity. Naylor-Shine Tables – likely average increase in criterion performance as a result of using a particular test or intervention, provides a selection ratio needed to achieve a particular increase in criterion performance. Cut Scores - Cutoff Score, reference point derived as a result of a judgement and used to divide a set of data into two or more classifications. Relatively Cut Score/Norm-Referenced Cut Score - Set based on norm-related considerations or with reference to the performance of a group. Fixed Cut Score/Absolute Cut Score - Set with reference to a judgement concerning a minimum level of proficiency required to be included in a particular classification. Multiple Cut Scores - Two or more cut scores with reference to one predictor for the purpose of categorizing test takers. Multiple Hurdles - One collective element of a multistage decision-making process in which the achievement of a particular cut score on one test is necessary in order to advance to the next stage of evaluation in the selection process. Compensatory Model of Selection - Assumption is made that high scores on one attribute can balance out or compensate for low scores on another attribute. Methods of Setting Cut Scores • Angoff Method – by William Angoff, can be applied to personnel selection tasks as well as to questions regarding the presence or absence of a particular trait, attribute, or ability. • The Known Groups Method – collection of data on the predictor of interest from groups known to possess, and not to possess, a trait, attribute, or ability of interest. • IRT-Based Methods – based in item response theory framework. TEST AND TESTING ASSUMPTION 1 o PSYCHOLOGICAL TRAITS AND STATES EXIST Trait – distinguishable, relatively enduring. State – relatively less enduring. Construct – informed, scientific concept developed of explain behavior. Overt Behavior – observable action or the product of an observable action. ASSUMPTION 2 o PSYCHOLOGICAL TRAITS AND STATES CAN BE MEASURED - Carefully defined traits and states to be measured. - Considering the types of item content. - Appropriate ways to score the test and interpreting the results. - Cumulative Scoring – higher score: higher amount of trait. ASSUMPTION 3 o TEST-RELATED BEHAVIOR PREDICTS NON-TEST RELATED BEHAVIORS - Obtained sample of behavior is used to make predictions about future behavior. - Postdict – aid in the understanding of behavior that has already taken place. ASSUMPTION 4 o TESTS AND OTHER MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES HAVE STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES ASSUMPTION 5 o VARIOUS SOURCES OF ERROR ARE PART OF THE ASSESSMENT PROCESS - Error – long standing assumption that factors other than what a test attempts to measure will influence performance on the test. Error Variance – component of a test score attributable to sources other than the trait or ability measured. - Classical Test Theory (CTT) – true score theory. ASSUMPTION 6 o TESTING AND ASSESSMENT CAN BE CONDUCTED IN A FAIR AND UNBIASED MANNER ASSUMPTION 7 o TESTING AND ASSESSMENT BENEFIT SOCIETY - Reliable – consistency, yields the same numerical measurement every time it measures the same thing under the same conditions. Valid – measure what it purports to measure. Norms - Behavior that is usual, average, normal, standard, expected, or typical. - Test performance data of a particular group of test takers that are designed for use as a reference when evaluating or interpreting individual test scores. - Norm-Referenced Testing and Assessment – comparing to scores of a group of test takers. - Criterion-Referenced Testing and Assessment – with reference to a set of standard or criterion. - Normative Sample – group of people whose performance on a - - particular test is analyzed for reference in evaluating the performance of individual test takers. Norming – deriving norms. Race Norming – controversial practice of norming on the basis of race or ethnic background. User Norms/Program Norms – descriptive statistics based on a group of test takers in a given period of time rather than norms obtained by formal sampling methods. Sampling to Develop Norms • Test Standardization – process of administering a test to a representative sample of test takers for the purpose of establishing norms. • Sampling – selecting the portion of the universe deemed to be representative of the whole population – sample. • Random Sampling – every member of the population had the same chance of being included in the sample. Sampling Techniques • Probability Sampling – random selection, equal chances of being selected. - Simple Random Sampling - Systematic Sampling - Stratified Sampling - Cluster Sampling - Multi-Stage Random Sampling • Non-Probability Sampling – selecting samples on the basis of accessibility or personal judgement of researcher. - Convenience/Haphazard/Inciden tal Sampling - Purposive or Judgmental Sampling - Snowball Sampling Types of Norms • Percentile Norms – expression of the percentage of people whose score on a test or measure falls below a particular raw score. • Percentage Correct – distribution of raw scores. • Age Equivalent Scores/Age Norms – average performance of different samples of test takers who were at various ages at the time the test was administered. • Grade Norms • National Norms TEST DEVELOPMENT 1. Test Conceptualization - Conceptualizing the idea or construct of the test. - Through RRL. - Emerging social phenomenon or pattern of behavior. 2. Test Construction - Scaling – setting rules for assigning numbers in measurement. - Age Based Scale – function of age Grade Based Scale – function of grade - Stanine Scale – all raw scores on the test are to be transformed into scores that can range from 1 to 9. Scaling Methods • Rating Scales – group of words, statements, or symbols. • Summative Scale – obtained by summing the ratings across all the items – e.g., Likert scale. • Method of Paired Comparisons – pairs of stimuli. • Comparative Scaling – judgments of a stimulus in comparison with every other stimulus on the scale. • Categorical Scaling – stimuli are placed into one of two or more alternative categories that differ quantitatively with respect to some continuum. • Guttman Scale – has weak and strong statements. Item Format - Form, plan, structure, arrangement, and layout of individual test items. - Selected-Response Format – set of alternative responses – e.g., multiple choices. - Constructed-Response Format – to supply or to create the correct answer. Writing Items • Item Bank – collection of test questions. - • Computerized Adaptive Testing (CAT) – interactive, computer administered test-taking process. • Item Branching – ability of the computer to tailor the content and order of presentation of test items on the basis of responses to previous items. • Floor Effect – low end of the ability. • Ceiling Effect – high end of the ability. Scoring Items • Cumulative Model – higher score: higher test taker is on the ability, trait, or other characteristic that the test purports to measure. • Class Scoring/Category Scoring – test taker responses earn credit toward placement in a particular class or category with other test takers whose pattern of responses is presumably similar in some way. • Ipsative Scoring – comparing test taker’s score. 3. Test Tryout - Informal rule of thumb: there should be no fewer than 5 subjects and preferably as many as 10 for each item on the test. - More subjects the better. 4. Test Analysis - Item-Difficulty Index – achievement tests - Item-Endorsement Index – personality tests - Lower italic ‘P’ is used to denote item difficulty and a subscript refers to the item number. Larger item-difficulty index: easier the item. - Item-Reliability Index – indication of the internal consistency of a test. - Item-Validity Index – provides an indication of the degree to which a test is measuring what it purports to measure. - Needs: Item-Score Standard Deviation and Correlation between the Item Score and the Criterion Score. - Item-Discrimination Index – indicates how adequately an item separates or discriminates between high scorers and low scorers on an entire test – highest possible value: 1.00, lowest: -1.00 - Item Characteristic Curve – graphic representation of item difficulty and discrimination. Qualitative Item Analysis - Nonstatistical procedures to explore how individual test items work. 5. Test Revision - Cross Validation – revalidation of test on a sample of test takers other than those on whom test performance was originally found to be a valid predictor of some criterion. - Validity Shrinkage – decrease in item validities that inevitably occurs after cross-validation of findings. - - Co-Validation – conducted on two or more tests using the same sample of test takers. (conorming)