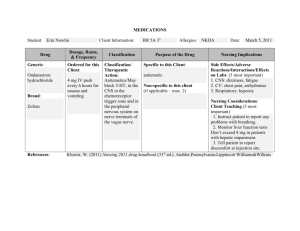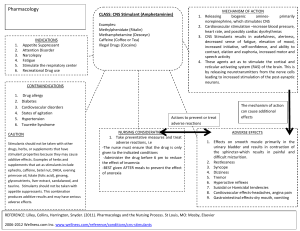
CNS Stimulants By: Angel Mendez, Sujin Ham, Brennette Jaime Classifications ● Analeptics - respiratory stimulation ● Anorexiants - decreased appetite ● Psychomotor Stimulants - stimulate the prefrontal cortex & the frontostriatal circuits of the brain Sub-Classifications ● CNS Stimulants are also classified as controlled substances ● CNS Stimulants = Schedule II drugs Prototype Drug ● Definition = drug that is the most representational of a particular class of drugs ● Similarities: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic effects, side effects, contraindications, drug/food interactions ● CNS Stimulant Prototype Drug = methylphenidate Effects on Body Systems 01 02 Nervous Cardiovascular Dilated pupils, increased motor activity & mental alertness, diminished fatigue Increased blood pressure & heart rate 03 04 Respiratory Gastrointestinal Increased respiratory rate Decreased appetite Therapeutic Action / Uses ❖ Primary Uses ➢ Treatment of narcolepsy ➢ Management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) ❖ Other Uses ➢ Treatment of obesity ➢ Adjuvant treatment of depression ➢ Treatment of respiratory depression & recovery from anesthesia Drug Examples methylphenidate (Ritalin) Usually prescribed for children diagnosed with ADHD dextroamphetamine/ amphetamine combination (Adderall) Prescribed for ADHD & narcolepsy Side Effects/Adverse Reactions CNS CV EENT Anxiety, seizures, psychosis, paranoia Palpitations, chest pain, tachycardia, arrhythmias Dry mouth/throat, blurred vision RESP GI, GU HEME Shortness of breath, cough, dyspnea Abdominal pain, hepatotoxicity, hematuria, priapism ↓ platelet count, leukopenia Drug Interactions Antihypertensives Anticonvulsants Decreased effectiveness of antihypertensives Inhibited metabolism & increased blood level of these drugs MAO inhibitors Possibly increased adverse effects of methylphenidate, possibly severe hypertension SSRIs, tricyclic antidepressants Increased risk of serotonin syndrome Food Interactions ● Caffeine: Increase methylphenidate effects ● Acidic foods (cranberries, dairy products, grains, nuts): Decrease absorption of medication which reduces medication’s effect Toxicities Cocaine & Amphetamines ● S/S of toxicity: Dysrhythmias, lethargy, skin pallor, psychosis Nicotine ● S/S of toxicity: Heart palpitations, tachyarrhythmias, confusion, depression, seizures Nursing Implications Educate patients on the short-term and longterm effects of stimulants While caffeine is a relatively safe stimulant, other stimulants can pose a significant health threat. Monitor and manage patient needs Disturbed sleep pattern -> drug to be given daily in the morning Check vital signs every 6 to 8 hours if tachycardia, hypertension, or palpitations occur. Nursing Assessments Assessment of the patient receiving a CNS stimulant depends on the drug, the patient, and the reason for administration. Nursing Assessments (Cont.) Use general survey techniques such as simply observing the patient to assess for cues of behavior. ● Patient’s mood, hygiene, appearance, or movement. Assess patient’s cardiac history ● Patient history of previous cardiac disease, seizures or palpitations. Physical examination, BP, Pulse, Respiration Rate ● Including a careful cardiac examination Use therapeutic communication to ask questions. ● ● Determine how your patient is feeling emotionally and perceiving the world “Tell me more about how you are feeling today?” Nursing Assessments (Cont.) ADHD Assess attention span, impulse control, and interactions with others in children. Therapy may be interrupted at intervals to determine if symptoms are sufficient to warrant continued therapy. Narcolepsy Observe and document frequency of episodes Nursing Assessments (Cont.) ADHD - amphetamine is prescribed Respiratory Depression - analeptic is used Obesity - anorexiant is used Nursing Interventions Administer medication during the day ● It can allow for undisturbed nighttime sleep. Monitor unexpected weight loss ● It can be imbalance nutrition; related to diminished appetite Monitor CNS stimulants closely due to the potential for abuse ● Patients can become tolerant to the euphoric and appetite suppressant effects of the drug Nursing Interventions (Cont.) Taper the dose gradually when withdrawing patients from CNS stimulants ● Patients may experience depression and severe fatigue if they stop taking the drug abruptly Monitor Vital Signs closely ● ● It may affect patient’s heart and blood pressure. Unexpected or undesired increases in either of these may indicate the need for a lower dosage. Monitor breathing pattern ● It could be related to respiratory depression. Patient Education Take the drug as early in the day as possible, with the last dose no later than 4:00 p.m Report to provider if patients experience anorexia or unexpected weight loss Report to provider cardiovascular effects, such as palpitations or tachycardia. Patients should taper the drug slowly. -> it can develop abstinence syndrome when they quit taking medication abruptly; this results in severe exhaustion, hypersomnia, or excessive slope, mental depression and an overwhelming urge to eat NCLEX Question #1 1. The nurse is developing a plan of care for a patient receiving an anorexiant. Which nursing diagnosis is most appropriate? A. B. C. D. Deficient fluid volume Sleep deprivation Impaired memory Imbalanced nutrition, less than body requirements NCLEX Question #1 1. The nurse is developing a plan of care for a patient receiving an anorexiant. Which nursing diagnosis is most appropriate? A. B. C. D. Deficient fluid volume Sleep deprivation Impaired memory Imbalanced nutrition, less than body requirements NCLEX Question #2 1. The nurse is reviewing medication therapy with the parents of an adolescent with ADHD. Which statement is correct (select all that apply) A. “Be sure to have your child blow his nose before administering the nasal spray” B. “This medication is used only when symptoms of ADHD are severe” C. “The last dose should be taken 4 to 6 hours before bedtime to avoid interference with sleep” D. “Be sure to contact the physician right away if you notice expression of suicidal thoughts” E. “If adverse effects become severe, stop the medication for 3 to 4 days” NCLEX Question #2 1. The nurse is reviewing medication therapy with the parents of an adolescent with ADHD. Which statement is correct (select all that apply) A. “Be sure to have your child blow his nose before administering the nasal spray” B. “This medication is used only when symptoms of ADHD are severe” C. “The last dose should be taken 4 to 6 hours before bedtime to avoid interference with sleep” D. “Be sure to contact the physician right away if you notice expression of suicidal thoughts” E. “If adverse effects become severe, stop the medication for 3 to 4 days” References ● ● ● ● ● Adams, M., Holland, L. N., & Urban, C. Q. (2020). Pharmacology for Nurses: A Pathophysiologic Approach (6th ed.). Pearson. Bartlett, J. L. (2023) Nurse's Drug Handbook. Jones & Bartlett Learning. Central Nervous System Stimulants. Basicmedical Key. (2016, August 14). Retrieved March 26, 2023, from https://basicmedicalkey.com/central-nervous-system-stimulants/ Farzam K., Faizy R. M., & Saadabadi A. (2023) Stimulants. StatPearls Publishing. Vallerand, A. H., & Sanoski, C. A. (2021). Davis's Drug Guide for Nurses (17th ed.). F.A. Davis Company. Thank you! CREDITS: This presentation template was created by Slidesgo, including icons by Flaticon and infographics & images by Freepik