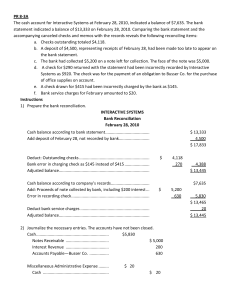
BANK RECONCILIATION MICHAEL G. AUDITOR WHAT IS BANK RECONCILIATION? activity that reconciles an entity’s bank account with its financial records a useful financial internal control tool used to prevent fraud output of bank reconciliation process is a bank reconciliation statement outlines the deposits, withdrawals, and other activities affecting a bank account for a specific period WHY RECONCILE? the account balance as reported by the bank is compared to the general ledger of a business businesses maintain a cash book and the bank too keeps an account for every customer The bank sends the account statement to its customers every month or at regular intervals. Sometimes these balances do not match. The business needs to identify the reasons for the discrepancy and reconcile the differences. This is done to confirm every item is accounted for and the ending balances match. OTHER PURPOSE OF BR? Detecting errors such as double payments, missed payments, calculation errors A check payment of P10,000 was recorded at P100,000 by the company. Tracking and adding bank fees and penalties in the books Bank service charge for the month of February 2022 and checkbook fees are reflected in the bank statement but not yet taken up in the company’s book Spot fraudulent transactions and theft ABC made P100,000 deposit per deposit control book of the treasury department but was not found in the bank statement received. The investigation unveiled that such deposit didn’t really happened and that two employees had collided to commit the fraud Keeping track of accounts payable and receivables of the business The bank statement can reveal the checks encashed by suppliers and amount of cash/check credited to its accounts from customers, creditors, lenders, etc. You receive a bank statement, typically at the end of each month, from the bank. The statement itemizes the cash and other deposits made into the checking account of the business. The statement also includes bank charges such as for account servicing fees. Before the reconciliation process, business should ensure that they have recorded all transactions up to the end of your bank statement. Businesses that use online banking service can download the bank statements for the regular reconciliation process rather than having to manually enter the information. STEP 1 COMPARE THE AMOUNTS Compare the amount of each deposit recorded in the debit side of the bank column of the cashbook with credit side of the bank statement. BOOK DEPOSITS vs BANK CREDITS Compare the amount of each credit side of the bank column with the debit side of the bank statement. BOOK DISBURSEMENTS vs BANK DEBITS DBO BANK ABC, ENTERPRISE Book Debits Feb-01 Feb-02 Feb-05 Feb-10 Feb-13 Feb-15 Feb-18 Feb-20 Feb-23 Feb-27 Feb-28 Total Bank Credits/ Deposits Amount 10,000.00 20,000.00 30,000.00 12,000.00 3,000.00 28,000.00 3,600.00 18,500.00 6,000.00 18,100.00 2,000.00 151,200.00 Feb-04 Feb-05 Feb-11 Feb-13 Feb-16 Feb-18 Feb-21 Feb-23 Feb-26 Feb-28 CM1 Feb-28 CM2 Total Amount 10,000.00 20,000.00 15,000.00 12,000.00 3,000.00 28,000.00 3,600.00 18,500.00 6,000.00 100,000.00 5,000.00 221,100.00 Deposits in transit are amounts that are received and recorded by the business but are not yet recorded by the bank. TREATMENT: They must be added to the bank statement. Outstanding checks are those that have been written and recorded in cash account of the business but have not yet cleared the bank account. This often happens when the checks are written in the last few days of the month. CERTIFIED CHECKS are not considered outstanding. TREATMENT: They need to be deducted from the bank balance. Bank errors are mistakes made by the bank while creating the bank statement. Common errors include entering an incorrect amount or omitting an amount from the bank statement. Compare the cash account’s general ledger to the bank statement to spot the errors. STEP 2. ADJUST THE BANK STATEMENTS Adjust the balance on the bank statements by adding deposits in transit deducting outstanding checks add/deduct bank errors. Book deposits Less Dep. Ackn. By Bank Total Bank Credits Less items not deposited Deposits Acknowledged Deposit in transit 151,200.00 221,100.00 120,000.00 101,100.00 50,100.00 Balance Per Bank Statement Add: Deposit in Transit Add: Effect of bank errors 116,750.00 50,100.00 Book disbursements Less Checks. Ackn. By Bank Total Bank debits 104,350.00 Less items not checks 6,850.00 Deposits Acknowledged Outstanding checks 137,000.00 97,500.00 39,500.00 Balance Per Bank Statement Add: Deposit in Transit Add: Effect of bank errors Less: Outstanding Checks Less: Effect of bank errors 116,750.00 50,100.00 39,500.00 STEP 3. ADJUST THE CASH ACCOUNT Adjust the cash balances in the business account by adding interest or deducting monthly charges and overdraft fees. Bank charges are service charges and fees deducted for the bank’s processing of the business’ checking account activity. This can include monthly charges or charges from overdrawing your account. They must be deducted from your cash account. If you’ve earned any interest on your bank account balance, they must be added to the cash account. An NSF (not sufficient funds) check is a check that has not been honored by the bank due to insufficient funds in the entity’s bank accounts. This means that the check amount has not been deposited in your bank account and hence needs to be deducted from your cash account records. Errors in the cash account result in an incorrect amount being entered or an amount being omitted from the records. The correction of the error will increase or decrease the cash account in the books. DBO BANK ABC, ENTERPRISE Book Debits Feb-01 Feb-02 Feb-05 Feb-10 Feb-13 Feb-15 Feb-18 Feb-20 Feb-23 Feb-27 Feb-28 Total Bank Credits/ Deposits Amount 10,000.00 20,000.00 30,000.00 12,000.00 3,000.00 28,000.00 3,600.00 18,500.00 6,000.00 18,100.00 2,000.00 151,200.00 Feb-04 Feb-05 Feb-11 CM3 Feb-13 Feb-16 Feb-18 Feb-21 Feb-23 Feb-26 Feb-28 CM1 Feb-28 CM2 Total Amount 10,000.00 20,000.00 15,000.00 12,000.00 3,000.00 28,000.00 3,600.00 18,500.00 6,000.00 100,000.00 5,000.00 221,100.00 Book Credits Feb-01 Feb-02 Feb-05 Feb-08 Feb-12 Feb-13 Feb-17 Feb-21 Feb-24 Feb-25 Feb-26 Total Bank Debits/ Disbursements Chk No. 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 010 011 Amount 5,000.00 2,000.00 8,000.00 12,000.00 28,000.00 15,000.00 17,000.00 33,000.00 4,500.00 3,600.00 8,900.00 137,000.00 Feb-06 Feb-08 Feb-09 Feb-17 Feb-18 Feb-21 Feb-26 Feb-28 Feb-28 Total Chk No. 001 003 002 005 007 008 009 DM1 DM2 Amount 5,000.00 8,000.00 2,000.00 28,000.00 17,000.00 33,000.00 4,500.00 850.00 6,000.00 104,350.00 Balance Per Book/ Ledger Add: Credit Memo Items Add: Effect of book errors Less: Debit Memo Items Less: Effect of book errors Adjusted balance per Book 14,200.00 120,000.00 6,850.00 127,350.00 STEP 4. COMPARE THE BALANCES After adjusting the balances as per the bank and as per the books, the adjusted amounts should be the same. If they are still not equal, you will have to repeat the process of reconciliation again. Once the balances are equal, businesses need to prepare journal entries for the adjustments to the balance per books. ADJUSTMENTS FOR CMs Check on the nature of the CMs. It could probably be a bank loan automatically credited to account, collections made by the bank, or interest accrued on company’s deposits.) FOR DMs Check on the nature of the DMs. It could probably be a bank service fees/ charges, or NSF checks ABC Enterprise Statement of Bank Reconciliation February 28, 2022 Balance Per Book/ Ledger Add: Credit Memo Items Add: Effect of book errors Less: Debit Memo Items Less: Effect of book errors Adjusted balance per Book 14,200.00 Balance Per Bank Statement 120,000.00 Add: Deposit in Transit Add: Effect of bank errors 6,850.00 Less: Outstanding Checks Less: Effect of bank errors 127,350.00 Adjusted balance per DBO CIB A/R 15,000.00 CIB LP 100,000.00 15,000.00 100,000.00 CIB A/R 5,000.00 BSC CIB 850.00 Checking fee CIB 5,000.00 850.00 6,000.00 6,000.00 116,750.00 50,100.00 39,500.00 127,350.00 HOW OFTEN SHOULD YOU RECONCILE YOUR BANK ACCOUNT? Reconcile your bank account each time you receive a statement from your bank. This is often done at the end of every month, weekly and even at the end of each day by businesses that have a large number of transactions. INTEGRATE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM Bank reconciliation done through accounting software is easier and error-free. The bank transactions are imported automatically allowing you to match and categorize a large number of transactions at the click of a button. This makes the bank reconciliation process efficient and controllable. READ AND LEARN MORE What is DAUD DAIF NSF Certified checks Window dressing Kiting Imprest Cash System Internal Control System for Cash Stale check Post-dated check Overdraft IOUs