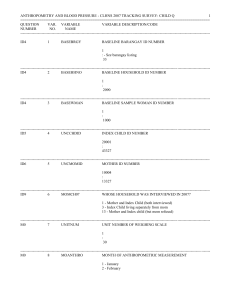
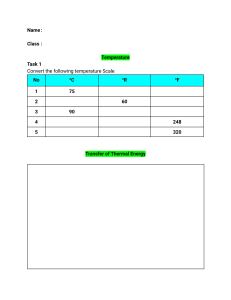
ISEN 330 Human Systems Interaction Review Questions for Exam 2 n Control II: Response Selection & Execution 1. What are the ways to classify controls as response selection and execution? 2. What are the four main principles of response selection? 3. What are response time, reaction time, and movement time? What is their relationship? 4. What affects simple reaction time and choice reaction time? 5. What is the Hick-Hyman Law? 6. What is information content? Can you apply the Hick-Hyman Law to estimate (choice) reaction time? 7. What is the Fitts’ Law? 8. What is index of difficulty? Can you apply the Fitts’ Law to estimate movement time? 9. What is tracking? What system parameters or factors affect tracking performance and how? 10. What are the basic elements of a tracking loop? 11. Do you know the difference between open-loop and closed-loop movements? Can you provide some examples of each? n Engineering Anthropometry 1. What does Engineering Anthropometry as a process or a sub-specialty consist of? 2. What are two types of anthropometric data? Examples? 3. What measurement methods are available for acquiring anthropometric data? 4. Can you name and explain some of the major sources of human anthropometric variability? 5. What does Xth percentile mean? 6. Are you familiar with the statistics involved in an anthropometric analysis? 7. Besides stature and dimensions, what are other anthropometric measures or anthropometrics? 8. What are the anthropometric design principles? 9. What are the general steps in an anthropometry design process? n Physical Work Capacity 1. Which two attributes define an individual’s physical work capacity? Why are they important? 2. What is the standard anatomical posture and how are three orthogonal anatomical planes defined? 3. Can you differentiate flexion vs extension, abduction vs adduction, medial vs lateral bending, pronation vs supination? 4. What are the factors that can affect ROM and what are their effects? 5. What are the different types of strength measurements and how are they conducted? 6. Why and how does posture affect strength? 7. Why and how does motion affect strength? 8. What are the individual (personal) factors that can affect strength? n Biomechanics of Work 1. What is Biomechanics? What is Occupational Biomechanics? 2. What are the main functions of the musculoskeletal system? 3. What are the six component tissues of the musculoskeletal system? Which ones are connective tissues and which ones are soft tissues? 4. Do you know the muscle basic hierarchical structure and contractile mechanism (presented in Work Physiology Topic also)? 5. What are the major forms of muscle contraction (strength)? 6. What is the first condition of equilibrium? What is the second condition of equilibrium? 7. How are reactive forces and moments at joints calculated? 8. Why do low-back discs become highly stressed during a typical lifting task? 9. Can you use a low-back biomechanical model to estimate the low-back muscle force and disc compression? 10. What are the groups of factors that can affect manual materials handling capability and risk of musculoskeletal disorder associated with the performance? 11. What are the four scientific bases (also called criteria) for NIOSH lifting guidelines? 12. Which factors or job variables are considered in the guidelines? 13. What are the differences between the 1981 and 1991 guidelines? 14. Can you apply the 1981 or 1991 NIOSH equation to assess a lifting task? 15. What are some of the caveats of introducing materials handling devices (MHD) into work places? 16. How is sitting fundamentally different from standing? 17. What are the objectives of seating with regard to the spine? 18. How sitting postures and seat design parameters such as backrest inclination angle and lumbar support (dimension) affect low-back disc pressure? 19. What are the methods and measures that can be used to evaluate seat design? 20. What are cumulative trauma disorders (CTDs)? 21. What are some of the common forms of CTDs and their corresponding risk factors or risk activities? 22. What do you know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)? 23. How does the “pulley” hand/wrist biomechanical model relate wrist posture and size to the force acting on the tissue structures? 24. What are the general principles for hand tool design that help in CTD prevention? n Work Physiology 1. What are classic IE approaches and modern engineering or ergonomic approaches to address physically demanding jobs (hard jobs/heavy work)? 2. What are the three different types of muscles? 3. Can you describe the muscle energy metabolic processes and how they may lead to muscle fatigue and oxygen debt? 4. Do you know the respiratory basics for estimating the aerobic metabolism rate of 4.7 kcal/min? 5. Do you know the circulatory basics, healthy range of blood pressure, ranges of HR, and cardiac output (Q) required by work at various levels of physical demand? 6. What is the Cooper Formula and the 40% Rule of Thumb for sustained HR? 7. What are basal, resting, and working metabolisms? 8. How does physical work capacity change as time on the work changes? In other words, how does the long-term maximum physical work capacity (MPWC) change in reference to the short-term MPWC? 9. Can you apply the Murrell Formula to determine the work/rest cycles? 10. What are the ways to objectively or subjectively measure workload? 11. What is the basic premise of the Energy Expenditure Prediction Model? How is it applied to estimation of the workload of a job? n Thermal Stress 1. What is the thermal regulatory mechanism? 2. When do we say that an environment poses thermal stress to a person? 3. What is heat stress and what are the factors influencing the heat stress? 4. What is heat strain? Thermal comfort? 5. What are the physiological responses to thermal (heat or cold) stress? 6. What are the ways of the human body exchanges heat with the environment? 7. Can you describe the heat balance equation and explain the meaning of each term? 8. Can you name and explain some of the heat disorders? 9. What are the basic thermal environment elements? 10. What is WBGT and how is it measured? 11. How do environmental heat (as measured by WBGT) and work activity (as indicated by metabolic heat rate) affect the recommended work-rest schedule? 12. What are the factors that can affect protection against heat stress? 13. What are the basic methods for mitigating heat effects? 14. What variables are included in the windchill index and how do they affect the windchill index?