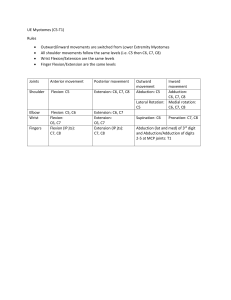
Complete MSK Study Bundle Subjective assessment cheat sheet Objective assessment cheat sheets Origins & Insertions cheat sheets Exercise prescription cheat sheet 7 topics to know before placement Worth $28 www.learningphysiotherapy.com Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd.© 2021. Built For Students Progressively overload each of these exercises by adding resistance, repetitions, sets, decreasing rest time etc. You can also increase difficulty by adding unstable surfaces, dual tasking, increasing ROM, increasing eccentric or concentric contraction time etc. Also remember the importance of specificity! Use sets/reps appropriate for training goals i.e. strength, power, endurance. Hip/Glutes o PROM -> AROM -> Resisted Movements (+theraband): flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, ER, IR o Isometric contractions with 5+ sec hold o Bridges: double leg (DL) -> DL + theraband -> single leg (SL) -> SL + theraband -> + weight o Clamshells in supine -> in side-lying -> side-lying + theraband o Sit to stand -> STS no hands -> STS lower height o SL STS o Straight leg raise o Squats o Goblet squats o Sumo squats o SL squats o Deadlift o Trap bar deadlift o SL deadlift o Romanian deadlifts o Sumo deadlift o Crab walk o Banded lateral side steps o Lunge/reverse lunge o Front foot elevated lunge o Step down/up o Jump squats o Box jumps o Lateral lunge o Lateral step up o Lateral bounds surface o Good mornings o Donkey kickbacks www.learningphysiotherapy.com o o o o o o Supermans Feet-on-ball hip thrust Wall sits Glute ham raise Reverse back extensions Kettlebell swings Quads o PROM -> AROM -> Resisted Movements (+theraband): knee extension, hip flexion o Isometric contractions with 5+ sec hold o Inner range activation o Leg extension machine o Sit to stand -> STS no hands -> STS lower height o SL STS o Squats o Bulgarian split squat o Sissy quats o Goblet squats o Sumo squats o SL squats o Deadlift o Trap bar deadlift o Leg press machine o Lunge/reverse lunge o Front foot elevated lunge o Step down/up o Jump squats o Box jumps o Kettlebell swings o Wall sits Hamstrings o PROM -> AROM -> Resisted Movements (+theraband): knee flexion, hip extension o Isometric contractions with 5+ sec hold o Bridges: double leg (DL) -> DL + theraband -> single leg (SL) -> SL + theraband -> + weight o Straight leg raise o Squats o SL squats o Deadlift o Trap bar deadlift o SL deadlift o Romanian deadlifts o SL Romanian deadlifts o Seated/lying leg curl machine o Nordic curls o Glute ham raise o Reverse back extensions o Kettlebell swings o Exercise ball hamstring curls o Good mornings Calf Muscles o PROM -> AROM -> Resisted Movements (+theraband): plantarflexion o Isometric contractions with 5+ sec hold o Standing calf raise o Standing single leg calf raise o Seated DL/SL calf raise o DL/SL calf raise off step o Leg press machine DL/SL calf raise o Lunges o Jump squats o Skipping variations o Bounds/lateral bounds o Hopping Ankle Rehab o PROM -> AROM -> Resisted Movements (+theraband): dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, eversion, inversion o Ankle alphabet o Towel scrunches o Any of the above calf raise exercises o SL balance: 30+ sec o DL/SL balance with eyes closed o Balance on unstable surfaces o Wobble board -> + SL -> squatting -> throwing/catching o SL stance with other foot tapping in front, side, back o SL stance throwing ball against wall/with partner o SL stance with external perturbations o DL/SL hopping, skipping, bounding Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd.© 2021. Built For Students Neck o PROM -> AROM -> Resisted Movements (+theraband): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation, retraction o Chin tucks in supine -> + overpressure o Chin tucks in prone -> + overpressure o Chin tucks in sitting -> + overpressure o Isometric contractions o Cat/cow o Cobra extensions o SNAGs o Foam rolling upper traps o Bird-dog o Thoracic extensions over chair o Sustained stretches Shoulder o PROM (use broomstick)-> AROM -> Resisted Movements (+theraband): flexion, extension, IR, ER, abduction, adduction o Scapular retraction/protraction exercises o Sleeper stretch o Doorframe pec stretch o Pendulum swings o Table slides o Dumbbell lateral/front raises o Internal/external rotation in sidelying/standing o Tabletops o Broomstick extensions o Overhead press o Pallof press o Row exercises o Wall pushups o Horizontal prone scaption Y’s o Turkish get-up o Arm pedals/cycling o Boxing o Nerve sliders/gliders www.learningphysiotherapy.com Biceps o PROM -> AROM -> Resisted Movements (+theraband): elbow flexion, supination, pronation, shoulder flexion o Curls o Hammer curls o Isolation curls o Reverse grip curls o Incline curls o Pull ups o Dumbbell supination/pronation o Grip strength exercises o Shoulder front raises o Any of the rotator cuff exercises in the shoulder section o Scapular stabilisation exercises Triceps o PROM -> AROM -> Resisted Movements (+theraband): elbow extension, shoulder extension o Tricep kickbacks o Overhead tricep extensions o Skull crushers o Dips o Pushdowns o Shoulder/scapular exercises o Eccentric bicep exercises Elbow/Forearm/Wrist o PROM -> AROM -> Resisted Movements (+theraband): elbow extension/flexion, supination, pronation, wrist flexion/extension, radial/ulnar deviation o Towel squeeze isometrics o Weighted supination/pronation o Dumbbell wrist flexion/extension o Theraputty/ball squeezes o Towel wringing o Tabletops +/- rocking forwards/backwards/lateral o Triceps/biceps exercises o Nerve sliders/gliders Thoracic/Lumbar Spine o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o Supine flexion Prone extension Rotational stretches Cobras Cat/cow Foam rolling Thoracic extensions over chair Bridges Supine knee tucks McKenzie repeated movements Bird-dogs Deadbugs Planks Side-planks Supine open book rotations Happy baby Downward dog Core activation exercises Compound movements: squats, deadlifts, pushups, pullups, lunges, hip thrusts Straight leg raise Deep muscle activation exercises Core o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd.© 2021. Sit up/crunch variations Plank variations Side planks Pikes (towel under feet) Bird-dogs Deadbugs Bicycle crunches Weighted standing oblique crunches Farmers carry Suitcase carry Mountain climbers Weighted bridges V-sits Leg raises Dragon flags TRX plank movements L-sits Russian twists Any compound movement Flutter kicks Pushups Supine toe touches Pallof press Built For Students www.learningphysiotherapy.com Date: Name: DOB: ©Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd 2021 Built for Students. Age: History of Presenting Condition Current symptoms: VAS Score: Date pain started: Pain a result of: specific event/insidious onset Aggravations: Eases: 24 Hour Pattern: Treatment to date: Condition is: improving/stable/worsening Cross areas of pain Tick areas that are cleared Past Medical History: Red Flags Is patient experiencing symptoms of any of the following conditions? Tick or cross each one. - Cauda Equina Syndrome or spinal cord compression - Fracture - Infection and/or inflammatory condition - Malignancy - Night pain - 5Ds’: dizziness, dysarthria, dysphagia, diplopia and drop attacks - Urinary/bowel incontinence/retention - DVT - Marked weakness or sensory changes Current Medications: Social History Occupation: Leisure activities: Home environment: Family/support: Personal ADLs – needs assistance? yes/no Community ADLs – needs assistance? yes/no Domestic ADLs – needs assistance? yes/no Smoke/ETOH/IV drug use: Pain is stopping them from: Previous exercise tolerance: Current exercise tolerance: Patient Goals: Patient would like to return to: By this date: Why is this important for them? www.learningphysiotherapy.com Yellow Flags Is patient experiencing any of the following? Tick or cross each one. (Consider your approach when asking about the following potentially sensitive topics) - A negative attitude towards their pain - Fear avoidance behaviour - Reduced activity because of excess caution - A PMHx of depression, anxiety, low morale and/or social withdrawal - Social and/or family problems - Financial and/or compensation problems - Work problems - An expectation that there is a “quick fix” - Has seen multiple different healthcare practitioners Goals of Treatment Session: Patient wants to know: Patient wants to leave feeling: . ©Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd 2021. Built for Students. Muscular Origins, Insertions, Actions & Innervation: Full Body www.learningphysiotherapy.com Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Study less. Retain more. Muscular Origins, Insertions, Actions & Innervations Muscle Brow Corrugator supercilii Origin Insertion Action Innervation Frontal bone Underneath the eyebrow Facial nerve Occipito-frontalis (occipital belly) Occipito-frontalis (frontal belly) Occipital bone, mastoid process Epicraneal aponeurosis Epicraneal aponeurosis Underneath the skin of the forehead The action of frowning, eyebrows move medially and downward Unfurrowing brow Furring the brow Facial nerve Maxilla Nasal bone Flares nostrils Facial nerve Mandible Underneath chin Facial nerve Maxilla, mandible, sphenoid bone Mandible Orbicularis oris Mandible Underneath lower lip Orbicularis oris, corners of mouth Corners of mouth Protrusion and elevation of lower lip and skin of chin Lateral cheek movement Opens mouth, sliding lower jaw laterally Pulls lower lip downwards Elevation of upper lip Movement of lips Corners of mouth Draws angle of mouth laterally Facial nerve Corners of mouth, orbicularis oris Mandible Action of smiling Facial nerve Closes mouth, chewing Mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve Mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve Medial division of the trigeminal nerve Motor branches of the mandibular nerve Nose Nasalis Mouth Mentalis Buccinator Depressor angulus oris Depressor labii inferioris Levator labii superioris Orbicularis oris Risorius Zygomaticus major Masseter Maxilla Tissue surrounding lips Fascia of the parotid salivary gland Zygomatic bone Maxilla arch, zygomatic arch Corners of mouth Lateral pterygoid Pterygoid process on sphenoid bone Mandible Opens mouth Medial pterygoid Sphenoid bone, maxilla TMJ, mandible Closes mouth Temporalis Temporal bone Mandible Closes mouth Muscle Muscles of the suboccipital region Rectus capitus posterior major www.learningphysiotherapy.com Origin Insertion Spinous process of the C2 vertebrae Action Lateral portion of Extend and rotate the inferior nuchal the head line of the occipital bone Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Facial nerve Facial nerve Facial nerve Facial nerve Facial nerve Facial nerve Innervation Suboccipital nerve Study less. Retain more. Rectus capitus posterior minor Posterior tubercle of the C1 vertebrae Obliquus capitus superior Obliquus capitus inferior Muscles that move the neck Sternocleidomastoid Transverse process of C1 Spinous process of C2 Sternum, clavicle Temporal bone’s mastoid process, occipital bone Longissimus capitis Transverse and articular processes of c/spine and t/spine vertebrae Spinous processes of cervical and thoracic vertebrae Temporal bone’s mastoid process Spinous processes of cervical and thoracic vertebrae Temporal bone’s mastoid process Spinous processes of T3-T6 Transverse processes of C1C3 Spinous process Splenius capitis Muscles that move the back Superficial Layer Splenius capitis Splenius cervicis Intermediate layer Spinalis Longissimus Transverse and articular processes of c/spine and t/spine vertebrae Iliocostalis Between the transverse processes of the corresponding vertebrae Deep Layer Rotatores (brevis and longus) Multifidus www.learningphysiotherapy.com Connect the transverse processes of the thoracic vertebrae Articular, transverse and mammillary processes Medial portion of the inferior nuchal line of the occipital bone Occipital bone Extend and rotate the head Suboccipital nerve Rotation of the head contralaterally, bilateral flexion Lateral flexion and rotation of the head, bilateral extension Lateral flexion and rotation of the head, bilateral extension Accessory nerve CNXI Lateral flexion and rotation of the head, bilateral extension Posterior rami of cervical spinal nerves Between the spinous processes of the corresponding vertebrae Between the transverse processes of the corresponding vertebrae Extend and laterally flex spine Posterior rami of spinal nerves With the spinous processes of the vertebrae one level above Spinous processes 2-5 vertebrae levels above Extend, rotate and laterally flex the spine and head Posterior rami of spinal nerves Transverse process of C1 Temporal bone’s mastoid process Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Anterior rami of C1-C6 Posterior rami of the middle cervical nerves Study less. Retain more. Semispinalis Interspinales Intertransversarii Levatores costarum Muscle Muscles of the thoracic wall Intercostal muscles External intercostals Internal intercostal Innermost intercostal Scalene muscles Anterior scalene Transverse and articular processes of c/spine and t/spine vertebrae Spinous process Transverse process Transverse process of C7-T11 Spinous processes the regional vertebrae Origin Insertion Spinous process Transverse process Superior surfaces of the ribs immediately below Lower margin of the rib to the upper margin of the next lower rib Lower margin of the rib to the upper margin of the next lower rib, From costal angle to sternum Extend, rotate and laterally flex the spine and head Posterior rami of spinal nerves Assists in elevation of the thoracic rib cage Dorsal rami C8T11 Action Innervation Raise the ribs during inspiration 1st to 11th intercostal nerve Lowers the ribs during expiration Intercostal nerves, ventral rami of thoracic spinal nerves Raise the upper ribs during inspiration Raise the upper ribs during inspiration C3-C6 Lower the ribs during inspiration Adjacent lower intercostal nerve C3-C6 transverse processes and anterior tubercles C3-C7 transverse processes and anterior tubercles C5-C7 transverse processes and anterior tubercles Lower margin of the lower ribs to the inner surface of the ribs 2-3 below Sternum and xiphoid process 1st rib (anterior scalene tubercles) 2nd-6th ribs Weakly lower the ribs during expiration 2nd-6th intercostal nerve Muscle Muscles of the abdominal wall External oblique Origin Insertion Action Innervation 5th to the 12th ribs Linea alba, anterior iliac crest, pubic tubercle Intercostal nerve T7-T12 Internal oblique Thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest 10th-12th ribs, linea alba Lateral flexion ipsilaterally, contralateral rotation, pelvic stabilisation Lateral flexion ipsilaterally, contralateral rotation, pelvic stabilisation Middle scalene Posterior scalene Subcostal muscles Transversus thoracis www.learningphysiotherapy.com 1st rib (posterior to groove for scalene artery) 2nd rib Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 C3-C6 Intercostal nerve T7-T12 Study less. Retain more. 7th to 12th costal cartilages, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest Medial head: crest of pubis to pubic tubercle Lateral head: crest of pubis to pubic tubercle Linea alba, pubic crest T12-L5 vertebral bodies (superficial layer) or costal processes (deep layer) T12-L1 vertebrae and intervertebral disks Iliac fossa Iliac crest and iliolumbar ligament Lesser trochanter 12th rib, L1-L4 transverse processes Ipsilateral trunk lateral flexion, expiration Superior pubic ramus Anococcygeal ligament Pelvic diaphragm, supports pelvic viscera Sacral plexus S4 and inferior anal nerve Pubococcygeus Pubis Iliococcygeus Coccygeus Internal obturator fascia of levator ani Sacrum Anococcygeal ligament, coccyx Anococcygeal ligament, coccyx Pelvic diaphragm, supports pelvic viscera Supports pelvic viscera, flexes coccyx Sacral plexus S4 and inferior anal nerve Sacral plexus S4S5 Piriformis Sacrum Greater trochanter Sacral plexus S1S2 Obturator internus Obturator membrane Medial surface of the greater trochanter Hip external rotation, stabilisation and abduction of flexed hip Hip external rotation and abduction of flexed hip Muscle Muscles of the deep perineal space External urethral sphincter Compressor urethrae (females) Urethrovaginal sphincter (females) Origin Insertion Action Innervation Encircles urethra Compresses urethra Pudendal nerve S2-S4 Transversus abdominis Rectus abdominis Muscles of the posterior abdominal wall Psoas major Psoas minor Iliacus Quadratus lumborum Muscles of the pelvic floor Levator Ani Puborectalis www.learningphysiotherapy.com Ischiopubic ramus Anterior urethra 5th – 7th rib cartilage, xiphoid process Rotates trunk to same side, compresses abdomen Flexes trunk, compresses abdomen, stabilises pelvis Intercostal nerve T7-T12 Flexion and external rotation of the hip, trunk lateral flexion Lumbar plexus Intercostal nerve T5-T12 Pecten pubis, iliopubic ramus, iliac fascia Ischial spine External urethral sphincter Interdigitates with opposite side Femoral nerve T12-L4 spinal nerve Sacral plexus L5S1 Compresses urethra and vagina Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Study less. Retain more. Deep transverse perineal Muscles of the superficial perineal space Bulbospongiosus Ischiocavernosus Superficial transverse perineal Quadratus lumborum Muscles of the anal triangle External anal sphincter Inferior pubic ramus, ischial raums Runs anteriorly from perineal body to clitoris (female) or penile raphe (male) Ischial ramus posterior to vagina Wall of vagina or prostate and perineal body Crus of clitoris or penis Perineal body Iliac crest and iliolumbar ligament 12th rib, L1-L4 transverse processes Encircles anus running posteriorly from perineal body to anococcygeal ligament Supports the prostate Pudendal nerve S2-S4 Females: compresses greater vestibular gland, males: assists in erection Maintains erection by assisting in blood flow Stabilises perineal body Ipsilateral trunk lateral flexion, expiration Pudendal nerve S2-S4 Closes the anus Pudendal nerve T12-L4 spinal nerve Muscle Muscles of the pectoral girdle Subclavius Origin Insertion Action Innervation 1st rib Inferior surface of the clavicle Nerve to subclavius C5-C6 Pectoralis minor 3rd – 5th ribs Coracoid process Stabilises the clavicle in the sternoclavicular joint Moves scapular downwards, rotates glenoid inferiorly, assists in respiration Serratus Anterior Superior portion 1st – 9th ribs Medial border of the scapula Lowers raised arms Laterally moves scapula forwards, elevates ribs Lateral rotation of scapula Long thoracic nerve C5-C7 Spinous processes T5-T12 Scapula spine Accessory nerve CN X, C3-C4 Aponeurosis at T1-T4 spinous processes Acromion Moves scapula inferiorly and medially Moves scapula medially Intermediate portion Inferior portion Trapezius Ascending portion Transverse portion www.learningphysiotherapy.com Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Medial and lateral pectoral nerve C6T1 Study less. Retain more. Descending portion Occipital bone, spinous processes C1-C7 Clavicle Upwards rotation of scapula, superior rotation of glenoid cavity Accessory nerve CN X, C3-C4 Levator scapulae Transverse processes of C1C4 Superior angle of scapula Dorsal scapular nerve Rhomboid minor Spinous process of C1-C4 Medial border of scapula Draws scapula medially upward, inclines neck ipsilaterally Steadies scapula, draws scapula medially upward Rhomboid major Spinous process of T1-T4 vertebrae Adduction, internal rotation, assist in respiration Adduction, internal rotation, extension, “cough muscle” assists with respiration Adduction, internal rotation, extension Medial and lateral pectoral nerve C5T1 Flexion, internal rotation, adduction Abduction Adduction, extension, external rotation Axillary nerve C5C6 Abduction Suprascapular nerve C4-C6 Muscles of the shoulder Pectoralis major Clavicle, sternum and costal cartilages 1-6 Greater tubercle crest of humerus Latissimus dorsi Spinous processes T7-T12, scapula, iliac crest Lesser tubercle crest of humerus Teres major Inferior angle of the scapula Lesser tubercle crest of humerus Lateral on third of the clavicle Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus Deltoid Anterior portion Lateral portion Rear portion Rotator Cuff Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor Subscapularis Muscle Muscles of the upper limb Biceps brachii Long head Short head www.learningphysiotherapy.com Acromion Scapular spine Suprascapular fossa Infraspinous fossa of scapula Lateral border of the scapula Subscapular fossa of scapula Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus Greater tubercle of the humerus Dorsal scapular nerve Thoracodorsal nerve C6-C8 Lower subscapular nerve Axillary nerve C5C6 External rotation Lesser tubercle of the humerus External rotation, adduction Internal rotation Axillary nerve Subscapular nerve Origin Insertion Action Innervation Supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula Coracoid process of the scapula Radial tuberosity and bicipital aponeurosis Flexion & supination of the elbow Flexion of the shoulder, stabilisation of the humeral head, Musculocutaneou s nerve C5-C6 Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Study less. Retain more. abduction and internal rotation Brachialis Humerus Coracobrachialis Coracoid process of the scapula Triceps brachii Medial head Lateral head Long head Anconeus Muscle Muscles of the anterior forearm Superficial layer Pronator teres Flexor carpi radialis Ulnar tuberosity and bicipital aponeurosis Humerus Flexion of the elbow Posterior humerus just distal to the radial groove Posterior humerus just proximal to the radial groove Infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula Olecranon of the ulna Extension and adduction of shoulder joint Lateral epicondyle of humerus Olecranon of the ulna Intermediate layer Flexor digitorum superficialis Deep layer Flexor digitorum profundus Flexor pollicis longus Pronator quadratus Muscles of the posterior forearm Superficial layer Extensor digitorum www.learningphysiotherapy.com Radial nerve C6C8 Extension of the elbow Extends the elbow and stabilises the joint Radial nerve C6C8 Origin Insertion Action Innervation Medial epicondyle, coronoid process Medial epicondyle Lateral radius Pronation, mild flexion of wrist Wrist flexion, radial deviation/abduction Mild wrist flexion, tightening of aponeurosis Wrist flexion, ulnar deviation/abduction Median nerve C6-C7 Palmaris longus Flexor carpi ulnaris Flexion, adduction, internal rotation of the humerus Musculocutaneou s nerve C5-C6 & radial nerve C7 Musculocutaneou s nerve C5-C6 Base of 2nd-3rd metacarpal Palmar apneurosis Median nerve C7-C8 Medial epicondyle, olecranon Pisiform, base of 5th metacarpal, hook of hamate Medial epicondyle, anterior border of humerus Sides of the middle phalanges 2-5 Mild wrist flexion, MCP and PIP joint flexion Median nerve C8-T1 Ulnar and interosseous membrane Radius and interosseous membrane Palmar surface of the distal phalanges Distal phalanx of the thumb Median nerve C8-T1 and Ulnar nerve C8-T1 Median nerve C7-C8 Distal ¼ of anterior surface of the ulna Distal radius Mild wrist flexion, MCP, PIP and DIP joint flexion Wrist flexion, radial deviation/abduction, flexion of MCP and IP of thumb Pronation of the hand, stabilisation of the distal radioulnar joint Lateral epicondyle of the humerus Dorsal digital Wrist extension, expansion of 2nd MCP, PIP and DIP – 5th digits extension and Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Ulnar nerve C7T1 Radial nerve C7C8 Study less. Retain more. Extensor digiti minimi Lateral epicondyle of the humerus Dorsal digital expansion of 5th digit Extensor carpi ulnaris Ulnar head of the lateral epicondyle Base of the 5th metacarpal Olecranon, lateral epicondyle of the humerus Radius (between radial tuberosity and insertion of pronator teres) Base of 1st metacarpal Deep layer Supinator abduction 2nd – 5th digits Wrist extension, MCP, PIP and DIP extension and abduction of 5th digit, ulnar deviation of hand Wrist extension, ulnar deviation of the hand Radial nerve C7C8 Radial nerve C7C8 Supination Radial nerve C6C7 Abduction of the hand (radial deviation) and thumb Abduction of the hand (radial deviation), extension of the thumb Abduction of the hand (radial deviation), extension and adduction of the thumb Wrist extension, MCP, PIP and DIP extension of 2nd digit Radial nerve C7C8 Abductor pollicis longus Radius and ulna (interosseous membrane) Extensor pollicis brevis Posterior surface of the radius Base of proximal phalanx of thumb Extensor pollicis longus Posterior surface of the ulna Base of distal phalanx of thumb Extensor indicis Posterior surface of the ulna Posterior digital extension of 2nd digit Distal humerus in the lateral intermuscular septum Lateral epicondyle Styloid process of the radius Elbow flexion and semipronation of the forearm Radial nerve C5C6 Base of the 3rd metacarpal Mild flexion of the elbow, wrist extension and abduction Radial nerve C7C8 Extensor carpi radialis longus Lateral supracondylar ridge of the distal humerus Base of the 2nd metacarpal Muscle Thenar muscles Adductor pollicis Origin Insertion Action Innervation Transverse head of the 3rd metacarpal Scaphoid and trapezium bones, flexor retinaculum Adduction of the CMC joint of the thumb, flexion of the MCP joint of the thumb Abduction of the CMC joint of the thumb Ulnar nerve C8-T1 Abductor pollicis brevis Base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb via the ulnar sesamoid Base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb via Radialis group Brachioradialis Extensor carpi radialis brevis www.learningphysiotherapy.com Radial nerve C6C7 Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Median nerve C8T1 Study less. Retain more. Flexor pollicis brevis Flexor retinaculum, capitate and trapezium bones Opponens pollicis Trapezium Hypothenar muscles Opponens digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi brevis the radial sesamoid Base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb via the radial sesamoid Radial border of the 1st metacarpal Hook of hamate, flexor retinaculum Ulna border of the 5th metacarpal Base of the 5th proximal phalanx Abductor digiti minimi Pisiform Ulnar base of the 5th proximal phalanx Palmaris brevis Ulnar border of the palmar aponeurosis Skin of the hypothenar eminence 1st and 2nd metacarpals Dorsal digital expansion of the 2nd digit, 2nd proximal phalanx 2nd 2nd and 3rd metacarpals 3rd 3rd and 4th metacarpals 4th 4th and 5th metacarpals Dorsal digital expansion of the 3rd digit, radial side of 3rd proximal phalanx Dorsal digital expansion of the 3rd digit, ulnar side of 3rd proximal phalanx Dorsal digital expansion of the 4th digit, ulnar side of 4th proximal phalanx Metacarpal muscles Dorsal interossei 1st Palmar interossei 1st Ulnar side of the 2nd metacarpal Dorsal digital expansion of the 2nd digit, 2nd proximal phalanx 2nd Radial side of the 4th metacarpal 3rd Radial side of the 5th metacarpal Dorsal digital expansion of the 4th digit, 4th proximal phalanx Dorsal digital expansion of the www.learningphysiotherapy.com Flexion of the CMC joint of the thumb Median nerve C8T1, Ulnar nerve C8-T1 Opposition of the CMC joint of the thumb Median nerve C8T1 Opposition of metacarpal Flexion of the MCP joint of the little finger Flexion and abduction of the MCP joint of the little finger, extension of the PIP and DIP joints of the little finger Stabilisation and tightening of the palmar aponeurosis Ulnar nerve C8-T1 2nd to 4th digits perform MCP joint flexion and extension/abduction of DIP joints Ulnar nerve C8-T1 2nd to 4th digits perform MCP joint flexion and extension/abduction of DIP joints Ulnar nerve C8-T1 2nd , 4th and 5th digits perform MCP joint flexion and extension/abduction of DIP joints Ulnar nerve C8-T1 Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Study less. Retain more. 5th digit, 5th proximal phalanx Lumbricals 1st Tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus on the radial side 2nd 3rd 4th Tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus Tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus 2nd digit dorsal digital expansion 2nd - 5th digits perform MCP joint flexion and extension of DIP joints 3rd digit dorsal digital expansion 4th digit dorsal digital expansion Median nerve C8T1 Ulnar nerve C8-T1 5th digit dorsal digital expansion 2nd - 5th digits perform MCP joint flexion and extension of DIP joints Ulnar nerve C8-T1 Muscle Muscles of the gluteal region Gluteus maximus Origin Insertion Action Innervation Sacrum, ilium, thoracolumbar fascia Iliotibial tract, gluteal tuberosity Inferior gluteal nerve L5-S2 Gluteus medius Gluteal surface of the ilium below the iliac crest Lateral surface of the greater trochanter Extension and external rotation of the hip, upper fibres assist in abduction, lower fibres assist in adduction Abduction of the hip, mild extension and external rotation Gluteus minimus Gluteal surface of the ilium below the gluteus medius Pelvic surface of the sacrum Anterolateral surface of the greater trochanter Sacral plexus S1S2 Gemelli Ischial spine/ischial tuberosity Medial surface of the greater trochanter External rotation, abduction and extension of the hip External rotation, abduction and extension of the hip Obturator internus Obturator membrane Quadratus femoris Lateral ischial tuberosity Medial surface of the greater trochanter Intertrochanteric crest of the femur Tensor fasciae latae Anterior superior iliac spine Iliotibial tract Muscle Origin Insertion Piriformis www.learningphysiotherapy.com Greater trochanter apex External rotation and adduction of the hip Abduction, flexion and internal rotation of the hip Action Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Superior gluteal nerve L4-S1 Sacral plexus L5S1 Superior gluteal nerve L4-S1 Innervation Study less. Retain more. Muscles of the anterior thigh Quadriceps femoris Rectus femoris Vastus medialis Vastus intermedius Vastus lateralis Sartorius Anterior inferior iliac spine Tibial tuberosity via the patellar ligament Linea aspera medially Anterior femoral shaft Linea aspera laterally Hip flexion, knee extension Femoral nerve L2L4 Knee extension Anterior superior iliac spine Medial to the tibial tuberosity Hip flexion, abduction and external rotation, knee flexion and internal rotation Femoral nerve L2L3 Inferior pubic ramus Medial border of the tibial tuberosity Obturator nerve L2-L3 Pectineus Pecten pubis Pectineal line of the femur Adductor longus Superior pubic ramus Linea aspera of the femur Adduction and flexion of the hip, flexion and internal rotation of the knee Adduction and external rotation of the hip, assists in stabilising the pelvis Adduction and flexion of the hip, assists in stabilising the pelvis Adductor brevis Inferior pubic ramus Medial compartment of the thigh Superficial layer Gracilis Deep layer Adductor magnus Medial lip of the linea spine, adductor tubercle of the femur Obturator externus Obturator membrane Trochanteric fossa of the femur Muscle Muscles of the posterior thigh Biceps femoris Short head Origin Lateral lip of the linea aspera Ischial tuberosity, sacrotuberous ligament www.learningphysiotherapy.com Obturator nerve L2-L4 Obturator nerve L2-L3 Inferior pubic ramus, ischial tuberosity Long head Femoral nerve and Obturator nerve L2-L3 Adduction and extension of the hip, assists in stabilising the pelvis Adduction and external rotation of the hip, assists in stabilising the pelvis Obturator nerve L2-L4 and tibial nerve L4 Insertion Action Innervation Head of the fibula Knee flexion and external rotation Extension of the hip, flexion and Common fibular nerve L5-S2 Tibial nerve L5-S2 Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Obturator nerve L3-L4 Study less. Retain more. external rotation of the knee Semimembranosus Ischial tuberosity Medial tibial condyle Extension of the hip, flexion and internal rotation of the knee Tibial nerve L5-S2 Semitendinosus Ischial tuberosity and sacrotuberous ligament Pes anserinus medial tibial condyle Muscle Muscles of the anterior lower leg Tibialis anterior Origin Insertion Action Innervation Tibia, interosseous membrane Medial cuneiform and first metatarsal Dorsal aponeurosis of the 1st toe Dorsiflexion and supination of the ankle Dorsiflexion and supination/ pronation of the ankle, extension of the big toe Dorsiflexion and pronation of the ankle, extension of toes 2-5 Dorsiflexion and eversion of the ankle Deep fibular nerve L4-L5 Extensor hallucis longus Fibula Extensor digitorum longus Fibula and tibia, interosseous membrane Dorsal aponeurosis of the 2nd to 5th toes Fibularis tertius Distal fibula Base of the 5th metatarsal Medial and lateral epicondyles of the femur Fibula and tibia Calcaneal tuberosity at the Achilles tendon Plantarflexion of the ankle, flexion of the knee Plantarflexion of the ankle May prevent compression of posterior leg muscles during knee flexion Tibial nerve S1-S2 Interosseous membrane Navicular tuberosity and cuneiforms 2-4 Tibial nerve L4-L5 Flexor digitorum longus Posterior surface of the tibia Bases of 2nd – 5th distal phalanges Flexor hallucis longus Posterior surface of the fibula Base of 1st distal phalanx Plantarflexion and inversion of the ankle, assists in supporting the arches of the feet Plantarflexion and inversion of the ankle, plantarflexion of MTP and IP joints 2-5 Plantarflexion and inversion of the ankle, plantarflexion of Muscles of the posterior lower leg Triceps surae Gastrocnemius Soleus Plantaris Deep muscles of the posterior compartment Tibialis posterior www.learningphysiotherapy.com Lateral epicondyle of the femur Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Deep fibular nerve L5 Deep fibular nerve L5-S1 Tibial nerve L5-S2 Study less. Retain more. MTP and IP joints 2-5, supports longitudinal arch Flexion and internal rotation of the knee Popliteus Lateral femoral condyle Posterior tibial surface Muscle Intrinsic muscles of the foot Extensor hallucis brevis Origin Insertion Action Innervation Dorsal surface of the calcaneus Dorsal surface of the calcaneus Extension of MTP and PIP joints of the 2nd – 4th toes Extension of MTP joints of the 1st toe Deep fibular nerve L5-S1 Extensor digitorum brevis Dorsal aponeurosis of 2nd – 4th toes Dorsal aponeurosis of 1st toe Calcaneal tuberosity, plantar aponeurosis Base of 5th metatarsal Lateral plantar nerve S1-S3 Abductor hallucis Medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity Base of the 1st toe Flexor digitorum brevis Calcaneal tuberosity, plantar aponeurosis Sides of middle phalanges for the 2nd – 5th toes Flexion and abduction of the MTP joint of the 5th toe, supports longitudinal arch Flexion and abduction of the MTP joint of the 1st toe, supports longitudinal arch Flexion and abduction of the MTP and PIP joints of the 2nd – 5th toe, supports longitudinal arch 3rd – 5th metatarsal Medial base of proximal phalanx of the 3rd – 5th toes Lateral plantar nerve S2-S3 Dorsal interossei 1st – 5th metatarsals 1st – 4th proximal phalanges Quadratus plantae Medial border of the calcaneal tuberosity Flexor digitorum longus tendon Lumbricals Flexor digitorum longus tendons Dorsal aponeurosis of 2nd-5th toes Flexion of MTP joints 3-5, extension of IP joints 3-5, adduction of 3-5 toes Flexion of MTP joints 2-4, extension of IP joints 2-4, adduction of 2-4 toes Assists in redirecting the pull of flexor digitorum longus Flexion of MTP joints 2-5, extension of IP joints 2-5, adduction of 2-5 toes Superficial Layer Abductor digiti minimi Deep intrinsic muscles of the sole of the foot Plantar interossei www.learningphysiotherapy.com Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Tibial nerve L4-L5 Deep fibular nerve L5-S1 Medial plantar nerve S1-S2 Lateral plantar nerve S2-S3 Lateral plantar nerve S1-S3 Lateral plantar nerve S2-S3 and Medial plantar nerve S2-S3 Study less. Retain more. Flexor hallucis brevis Lateral cuneiforms, cuboid Base of proximal phalanx of 1st toe Flexion and adduction of MTP joint of big toe Adductor hallucis Bases of 2-5th metatarsals 1st proximal phalanx Flexor digiti minimi brevis Opponens digit minimi Base of 5th metatarsal Long plantar ligament Base of proximal phalanx of 5th toe 5th metatarsal Flexion and adduction of MTP joint of big toe, supports transverse and longitudinal arches Flexion of MTP joint of 5th toe Pulls 5th metatarsal medially www.learningphysiotherapy.com Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Lateral plantar nerve S1-S2 and Medial plantar nerve S1-S2 Lateral plantar nerve S2-S3 Study less. Retain more. Shoulder Normal ROM Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial rotation Lateral rotation 160-180° 50-60° 170-180° 50-75° 70-90° 80-100° Myotomes: C4 Shoulder elevation C5 Shoulder abduction C6 Elbow flexion, wrist extension C7 Elbow extension, wrist flexion C8 Thumb abduction & extension T1 Finger abduction Dermatomes: C4 Clavicle to AC joint C5 Lateral deltoid C6 Anterior arm, radial side of hand to thumb & index finger C7 Lateral arm & forearm to index, middle and ring fingers C8 Medial arm and forearm to middle, ring and little fingers Reflexes: C5 nerve root C6 nerve root C7 nerve root Pathological Pathological Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Triceps Hoffman’s reflex Inverted supinator reflex Muscles and their movements: Flexion Deltoid, pec major, coracobrachialis, biceps brachii Extension Deltoid, latissimus dorsi, teres major, triceps brachii Abduction Deltoid, supraspinatus Adduction Deltoid, pec major, lat dorsi, teres major Internal rotation Deltoid, pec major, lat dorsi, teres major, subscapularis External rotation Deltoid, infraspinatus, teres minor Special Tests: Testing Positive Sensitivity for: result: Rotator cuff pathology Full Can Weakness and pain Lift-Off Weakness: (Gerber) ?subscapularis tear ER lag sign Weakness: ?infraspinatus tear Impingement Cluster Test of: Pain Jobe + Hawkins + reproduced www.learningphysiotherapy.com Specificity 59-89 50 54-82 88 36 95 75 74 Painful arc + Neer + in at least resisted ER 3/5 tests Posterior Pain felt impingement: posteriorly apprehension position Instability Relocation Relief of apprehension Apprehension Apprehensive feeling Load and shift Increased translation of humeral head anteriorly Release Sudden apprehension Sulcus Increased translation of humeral head inferiorly Posterior Increased subluxation test translation of humeral head posteriorly SLAP and biceps related injury Speed’s Pain: ?long-head of bicep tear O’Brien Pain: ?SLAP tear Biceps load test Pain: ?SLAP tear Cluster Test of: Pain Speed’s + Apprehension + O’Brien Passive Pain: ?SLAP tear compression test Scapular Dyskinesis Scapular Decreased pain assistance test Scapular Increased resistance test strength or decreased pain 75.5 85 96.7 78 98.3 71.6 71.7 89.9 91.7 83.5 28-72 86-97 50-91 85-100 54 81 61 29 25 84 78 92 82 86 21-24 71-21 26100 33-70 Causes of Referred Pain & Red Flags: Somatic referred pain: Visceral referred pain: cervical/thoracic spine, diaphragm, heart, spleen, myofascial structures gall bladder, apex of lungs Tumours Acute compartment syndrome Fractures Infection Nerve/vascular Myocardial infarct (left compromise shoulder pain commonly reported) Thoracic outlet syndrome Axillary/long thoracic nerve injury Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021. Study Less. Retain More. 7 TOPICS TO KNOW BEFORE YOUR NEXT MUSCULOSKELETAL CLINICAL PLACEMENT REVIEW THESE TOPICS TO FEEL PREPARED 1 WHAT SHOULD YOU REVIEW? We are taught hundreds of different musculoskeletal topics at university. As a result, it can be hard to narrow down which specific topics you should study before starting your placement. Here are 7 topics to review that will have you feeling prepped and ready! LOWER LIMB ANATOMY Many of the patients you will see will have lower limb injuries. It is important for you to know, and understand, the workings of the lower limb. Start with the hip/pelvis and work distally. Revise the bones, joints and soft tissues, as well as their nerve and blood supplies. Common injuries to study include greater trochanteric pain syndrome, quadriceps/hamstring tears, patellofemoral pain, MCL injuries, medial tibial stress syndrome, achilles tendinopathy, lateral ankle sprains and plantar fascia pain. UPPER LIMB ANATOMY Upper limb pathologies are also common in musculoskeletal practice. Start with the shoulder and work distally. Revise the anatomy in full: bones, joints, soft tissue, nervous supply and blood supply. Common upper limb injuries include subacromial pain syndrome, rotator cuff tendinopathy, adhesive capsulitis, lateral/medial epicondylalgia, radial head fractures, carpal tunnel syndrome, MCP joint sprains. SPINAL ANATOMY It is important for you to have a working understanding of the spine, from head to tail. Neck and back pain are both common presentations in private practice, often being chronic complaints. You should revise the anatomy and biomechanics of the spine, as well as somatic and radicular referral patterns. Common spinal related injuries include chronic neck pain, whiplash associated disorders, acute wry neck, cervical/lumbar radiculopathies, non-specific low back pain, degenerative vertebral changes. 2 NEURODYNAMIC TESTS If suspicious of neural involvement, neurodynamic tests can be great tools to confirm/discount your diagnosis. Not only are they diagnostic, but they can also be used as treatment to mobilise the neural tissue or entrapped nerve. Revise the Upper Limb Tension/Neural Tests (ULNT/ULTT) 1-3, as well as the slump test, prone knee bend and straight leg raise. MCKENZIE REPEATED MOVEMENTS As we mentioned earlier, non-specific low back pain and neck pain are common presentations in MSK physiotherapy. The McKenzie Method of Repeated Movements can be used as a rehabilitative technique to help reduce pain in mechanical injuries. Repeated movements can be utilised on most joints in the body, offering vast clinical applications. PAIN EDUCATION Pain education is growing in popularity amongst MSK physiotherapists. Prior to starting your clinical placement, you should revise the works of Peter O'Sullivan, Lorimer Moseley, David Butler and Adam Meakins. These clinicians are paving the way for physio's by stressing the importance of communication and patient experience. Pain education is vital in a private setting, in particular when dealing with chronic pain and yellow flags. OVER-USE INJURIES Over-use injuries frequently present to MSK physiotherapy settings. Tendinopathies are common, especially in the shoulder, hip, knee and achilles. You should revise the work of Jill Cook, as she is considered to be a tendinopathy/over-use injury 'guru', and has some fantastic research that explores the efficacy of various rehab approaches for these patients. Also consider revising the principles of training load and injury prevention. HAPPY STUDYING! SCROLL TO THE NEXT PAGE FOR A STUDY CHECKLIST 3 CHECKLIST LOWER LIMB ANATOMY UPPER LIMB ANATOMY SPINAL ANATOMY NEURODYNAMIC TESTS MCKENZIE REPEATED MOVEMENTS PAIN EDUCATION OVER-USE INJURIES Use this checklist to tick off the topics once you've revised them. Remember, clinical placement is about learning. Your supervisors do not expect you to know everything - you are there to learn . Don't be hard on yourself if you don't get it straight away; remember you're still a student! Listen to your supervisor, take their feedback on board and enjoy yourself. Remember, every Physiotherapist was once a student in the same position you are now, take a deep breath and go crush it! 4 Shoulder Normal ROM Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial rotation Lateral rotation 160-180° 50-60° 170-180° 50-75° 70-90° 80-100° Myotomes: C4 Shoulder elevation C5 Shoulder abduction C6 Elbow flexion, wrist extension C7 Elbow extension, wrist flexion C8 Thumb abduction & extension T1 Finger abduction Dermatomes: C4 Clavicle to AC joint C5 Lateral deltoid C6 Anterior arm, radial side of hand to thumb & index finger C7 Lateral arm & forearm to index, middle and ring fingers C8 Medial arm and forearm to middle, ring and little fingers Reflexes: C5 nerve root C6 nerve root C7 nerve root Pathological Pathological Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Triceps Hoffman’s reflex Inverted supinator reflex Muscles and their movements: Flexion Deltoid, pec major, coracobrachialis, biceps brachii Extension Deltoid, latissimus dorsi, teres major, triceps brachii Abduction Deltoid, supraspinatus Adduction Deltoid, pec major, lat dorsi, teres major Internal rotation Deltoid, pec major, lat dorsi, teres major, subscapularis External rotation Deltoid, infraspinatus, teres minor Special Tests: Testing Positive Sensitivity for: result: Rotator cuff pathology Full Can Weakness and pain Lift-Off Weakness: (Gerber) ?subscapularis tear ER lag sign Weakness: ?infraspinatus tear Impingement Cluster Test of: Pain Jobe + Hawkins + reproduced www.learningphysiotherapy.com Specificity 59-89 50 54-82 88 36 95 75 74 Painful arc + Neer + in at least resisted ER 3/5 tests Posterior Pain felt impingement: posteriorly apprehension position Instability Relocation Relief of apprehension Apprehension Apprehensive feeling Load and shift Increased translation of humeral head anteriorly Release Sudden apprehension Sulcus Increased translation of humeral head inferiorly Posterior Increased subluxation test translation of humeral head posteriorly SLAP and biceps related injury Speed’s Pain: ?long-head of bicep tear O’Brien Pain: ?SLAP tear Biceps load test Pain: ?SLAP tear Cluster Test of: Pain Speed’s + Apprehension + O’Brien Passive Pain: ?SLAP tear compression test Scapular Dyskinesis Scapular Decreased pain assistance test Scapular Increased resistance test strength or decreased pain 75.5 85 96.7 78 98.3 71.6 71.7 89.9 91.7 83.5 28-72 86-97 50-91 85-100 54 81 61 29 25 84 78 92 82 86 21-24 71-21 26100 33-70 Causes of Referred Pain & Red Flags: Somatic referred pain: Visceral referred pain: cervical/thoracic spine, diaphragm, heart, spleen, myofascial structures gall bladder, apex of lungs Tumours Acute compartment syndrome Fractures Infection Nerve/vascular Myocardial infarct (left compromise shoulder pain commonly reported) Thoracic outlet syndrome Axillary/long thoracic nerve injury Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021. Study Less. Retain More. Wrist and Hand Wrist Normal ROM Flexion Extension Radial deviation Ulnar deviation Supination Pronation Abduction Adduction Opposition 0-80° 0-70° 30° 20° 60° 40° Myotomes: C6 Elbow flexion, wrist extension C7 Elbow extension, wrist flexion C8 Thumb abduction & extension T1 Finger abduction Dermatomes: C6 Anterior arm, radial side of hand to thumb & index finger C7 Lateral arm & forearm to index, middle and ring fingers C8 Medial arm and forearm to middle, ring and little fingers T1 Medial side of forearm to the base of the little finger Wrist Muscles and their movements: Flexion Flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris Extension Extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor carpi ulnaris Radial deviation Flexor carpi radialis, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis Ulnar deviation Flexor carpi ulnaris, extensor carpi ulnaris Finger Muscles and their movements: Flexion at MCP Lumbricals, interossei, flexor digiti minimi Flexion at DIP Lumbricals, flexor digitorum superficialis Flexion at PIP Flexor digitorum profundus Extension at MCP Extensor digitorum, extensor indicis, extensor digiti minimi Extension at DIP Lumbricals, interossei and PIP Abduction at MCP Dorsal interossei, abductor digiti minimi Adduction Palmar interossei Opposition Opponens digiti minimi Thumb Muscles and their movements: Flexion Flexor pollicis longus, flexor pollicis brevis Extension Extensor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis www.learningphysiotherapy.com Abductor pollicis longus, abductor pollicis brevis Adductor pollicis Opponens pollicis Special Tests: Testing for: Positive result: Sensitivity Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Phalen’s Reproduction of 92 symptoms Tinel’s Electric shock 97 sensation or paraesthesia in median nerve distribution Triangular fibrocartilage complex disruption Ulna foveal Tenderness ++ 95.2 sign that replicates pt’s pain Press test Axial ulnar load 100 that reproduces pt’s symptoms Scapholunate Injury Watson’s Reproduction of 69 scaphoid pain +/shift hypermobility Outcome Measures: Measure: Patient Rated Wrist Evaluation DASH & Quick DASH Grip Strength Mayo Wrist Score Michigan Hand Outcomes Questionnaire Specificity 88 91 86.5 NA 66 Assesses: Pain and disability for wrist pathology Physical function, symptoms and quality of life for upper limb disorders Grip strength… Objective and subjective Ax of pain/function/ROM ADLs, pain, aesthetics and satisfaction for hand pathologies Causes of Referred Pain & Red Flags: Carpal dislocation Radial epiphyseal stress reaction (common in gymnastics) Scapholunate/perilunar Kienbock’s disease dislocation Lunotriquetral Carpal instability dissociation Infections Fractures Rheumatoid arthritis Peripheral neuropathy Peripheral vascular Lyme disease disease Tuberculosis Arthritides Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021. Study Less. Retain More. Hip Hip Normal ROM Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Internal rotation External rotation 0-120° 0-30° 0-40° 0-30° 0-45° 0-45° Myotomes: L2 Hip flexion L3 Knee extension S1 Hip extension Dermatomes: L1 Lower back, over trochanter and groin L2 Lower back, front of thigh to knee L3 Lower back, upper buttock, anterior thigh and knee, medial lower leg L4 Medial buttock, lateral thigh, medial leg L5 Buttock, posterior and lateral thigh S1 Buttock, thigh and posterior leg S2 Buttock, thigh and posterior leg Hip Muscles and their movements: Flexion Iliacus, psoas major, rectus femoris, sartorius, pectineus Extension Gluteus maximus, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris Abductors Gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fascia latae, sartorius, piriformis Adductors Adductor magnus, adductor longus, adductor brevis, gracilis, pectineus Internal rotation Gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fascia latae External rotation Gluteus maximus, quadratus femoris, piriformis, obturator externus, obturator internus, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, sartorius Special Tests: Testing for: Positive Sensitivity result: Non-specific Intra-articular Pathology FABER Pain 92 Scour Pain 50 Thomas test Pain and reduced 89 range Labral Tear Painful clicking Clicking 100 in hip www.learningphysiotherapy.com Specificity 88 29 92 FADIR Pain 99 Flexion internal Pain 96 rotation Gluteal Tendinopathy Trendelenburg Drop in the NWB pelvis Resisted internal Weakness and pain rotation Resisted external Pain de-rotation test Resisted hip Weakness and pain abduction Single leg stance for Pain in single leg 30sec stance Hip Osteoarthritis Cluster test of: Lateral >3/5 variables pain on active flexion + present = 68% positive Scour + pain chance of OA with active extension + passive internal 4-5/5 variables present = 91% rotation <25° + chance of OA Squatting aggravates symptoms Outcome Measures: Measure: International Hip Outcome Tool-33 Hip Dysfunction and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score Copenhagen Hip and Groin Outcome Score 6MWT, 10MWT, TUG Harris Hip Score 5 25 61 92 55 69 88 97.3 71 84 100 97.3 NA NA Assesses: Self-administered questionnaire assessing symptoms and function in younger patients Self-administered questionnaire assessing symptoms and function in patients with hip OA or arthroscopy Self-administered questionnaire assessing symptoms and function in patients with hip + groin pain Assessment of function and endurance Assessment of patients post hip surgery Causes of Referred Pain & Red Flags: Avascular necrosis of the Synovial chondromatosis femoral head Slipped capital femoral Perthes disease epiphysis (adolescents) Tumours Fractured NOF Nerve root compression Saddle paraesthesia Night pain Lumps/bumps Infection Inability to weight bear History of trauma Constipation or vomiting 85 Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021. Study Less. Retain More. Knee Knee Normal ROM Flexion Extension Reverse Lachman’s Dermatomes: L1 Lower back, over trochanter and groin L2 Lower back, front of thigh to knee L3 Lower back, upper buttock, anterior thigh and knee, medial lower leg L4 Medial buttock, lateral thigh, medial leg L5 Buttock, posterior and lateral thigh S1 Buttock, thigh and posterior leg S2 Buttock, thigh and posterior leg Knee Muscles and their movements: Flexion Semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris, gastrocnemius, gracilis, sartorius, plantaris, popliteus Extension Rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, vastus medialis, TFL Tibial lateral Biceps femoris rotation Tibial medial Semitendinosus, rotation semimembranosus, gracilis, sartorius, popliteus ACL Injury Lachman’s Test Anterior Drawer Pivot shift Positive result: 63 89 Palpable/audible click or pain Reproduction of patient’s pain Pain 61 84 83 83 61 70 Orally expressed apprehension or decreased quadriceps recruitment 100 89.2 Pain Pain Pain Pain 91 72 72 84 50 43 57 50 Meniscal Tear McMurray’s 0-140° 0-5° Myotomes: L2 Hip flexion L3 Knee extension L5/S1 Knee flexion Special Tests: Testing for: Soft end feel for tibial translation Outcome Measures: Measure: Ottawa Knee Rules Knee Injury and OA Outcome Score (KOOS) Lower Extremity Functional Scale 6MWT, 10MWT, TUG 81 81 Cincinnati Knee Rating System 38 81 28 81 MCL Injury Valgus stress Pain 78 Laxity 91 test at 30° LCL Injury Varus stress test at Pain and/or laxity 30° PCL Injury Posterior sag sign Posterior sagging of tibia Posterior drawer >5mm posterior tibial translation www.learningphysiotherapy.com Patellofemoral Pain Squatting Stair climbing Prolonged sitting Kneeling Specificity Sensitivity Soft end feel for tibial translation >5mm anterior tibial translation Anterior subluxation of tibia Joint line tenderness Apley’s test Patellar Instability Patellar Apprehension Test 67 49 NA NA 46100 22100 100 98 Assesses: Age >55, pain at head of fibula, isolated patella pain, inability to flex >90, inability to WB >4 steps – 2/5 of these positive = imaging required Self-administered questionnaire assessing the pt’s opinion of their knee Self-administered questionnaire assessing symptoms, function, progress and outcome Assessment of function and endurance Assessment of patients post ACL reconstruction Causes of Referred Pain & Red Flags: Tibial plateau fracture Avulsion fracture of the tibial spine Osteochondritis dissecans Complex regional pain (adolescents) syndrome Quadriceps muscle Tumour rupture Nerve root compression, Fracture pins & needles, numbness Referred pain from the Slipped capital femoral hip epiphysis Perthes’ disease Obvious deformity Night pain Lumps/bumps Infection Inability to weight bear History of trauma Constipation or vomiting Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021. Study Less. Retain More. Ankle Ankle Normal ROM Dorsiflexion Plantarflexion Inversion Eversion Impingement ankle sign Pain greater in dorsiflexion than in plantarflexion Achilles Tendon Rupture Thompson’s calf Ankle remains still squeeze test Calf squeeze test Ankle remains still Matles test Neutral or dorsiflexed ankle Palpation of gap in Tendon gap tendon palpable 15-20° 50-60° 30-40° 15-20° Myotomes: L4 Dorsiflexion L5 Big toe extension S1 Plantar flexion, foot eversion S2 Toe flexion Dermatomes: L4 Medial buttock, lateral thigh, medial leg, dorsum of foot and big toe L5 Buttock, posterior and lateral thigh, medial half of sole, 1st – 3rd toes S1 Buttock, thigh and posterior leg S2 Buttock, thigh and posterior leg Reflexes: Pathological Pathological Clonus Babinski/plantar response Ankle Muscles and their movements: Dorsiflexion Tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, peroneus tertius Plantarflexion Gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, peroneus longus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus, peroneus brevis Inversion Tibialis anterior, tibialis posterior Eversion Peroneus longus, peroneus tertius, peroneus brevis Special Tests: Testing for: Positive result: Sensitivity Ligament Injury Anterior Soft end feel +/Drawer (ATFL) anterior translation >4mm Talar tilt (CFL) Excessive inversion translation +/soft end feel Eversion stress Excessive test (deltoid eversion ligament) translation +/soft end feel Syndesmosis Injury Squeeze Test Pain +/- laxity Ankle Impingement www.learningphysiotherapy.com Specificity 3280 80 52 NA 96 84 30 93.5 94.8 88 40 NA 96 88 93 85 73 89 Outcome Measures: Measure: Assesses: Ottawa Ankle Pain at lateral malleolus, pain at Rules medial malleolus, pain at base of 5th metatarsal, pain at navicular, inability to weight bare more than 4 steps 2/5 of these positive = imaging required Foot and Ankle Self-administered questionnaire Ability Measure assessing the pt’s ADLs and sporting activities Lower Extremity Self-administered questionnaire Functional Scale assessing symptoms, function, progress and outcome 6MWT, 10MWT, Assessment of function and TUG endurance Oxford Ankle Self-administered questionnaire Foot assessing disability in children with Questionnaire foot and ankle injuries American Self-administered questionnaire Academy of assessing ankle symptoms and Orthopaedic function Surgeons Foot and Ankle Module Berg Balance Assesses balance Scale 4-Point Balance Assesses balance Scale Causes of Referred Pain & Red Flags: Referred neural pain Sever’s disease (adolescents) Metabolic condition Diabetic neuropathy DVT Tumour Nerve root compression, Fracture pins & needles, numbness CRPS type 1 Greenstick fracture in children Syndesmosis injury Tarsal coalition Night pain Navicular stress fracture Infection Inability to weight bear History of trauma Constipation or vomiting Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021. Study Less. Retain More. Muscular Origins, Insertions, Actions & Innervation: Lower Limb www.learningphysiotherapy.com Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Study less. Retain more. Muscular Origins, Insertions, Actions & Innervations Muscle Muscles of the gluteal region Gluteus maximus Origin Insertion Action Innervation Sacrum, ilium, thoracolumbar fascia Iliotibial tract, gluteal tuberosity Inferior gluteal nerve L5-S2 Gluteus medius Gluteal surface of the ilium below the iliac crest Lateral surface of the greater trochanter Extension and external rotation of the hip, upper fibres assist in abduction, lower fibres assist in adduction Abduction of the hip, mild extension and external rotation Gluteus minimus Gluteal surface of the ilium below the gluteus medius Pelvic surface of the sacrum Anterolateral surface of the greater trochanter Sacral plexus S1S2 Gemelli Ischial spine/ischial tuberosity Medial surface of the greater trochanter External rotation, abduction and extension of the hip External rotation, abduction and extension of the hip Obturator internus Obturator membrane Quadratus femoris Lateral ischial tuberosity Medial surface of the greater trochanter Intertrochanteric crest of the femur Tensor fasciae latae Anterior superior iliac spine Iliotibial tract Muscle Muscles of the anterior thigh Quadriceps femoris Rectus femoris Origin Insertion Action Innervation Anterior inferior iliac spine Tibial tuberosity via the patellar ligament Hip flexion, knee extension Femoral nerve L2L4 Vastus medialis Linea aspera medially Anterior femoral shaft Linea aspera laterally Piriformis Vastus intermedius Vastus lateralis Sartorius www.learningphysiotherapy.com Anterior superior iliac spine Greater trochanter apex External rotation and adduction of the hip Abduction, flexion and internal rotation of the hip Superior gluteal nerve L4-S1 Sacral plexus L5S1 Superior gluteal nerve L4-S1 Knee extension Medial to the tibial tuberosity Hip flexion, abduction and external rotation, Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Femoral nerve L2L3 Study less. Retain more. knee flexion and internal rotation Medial compartment of the thigh Superficial layer Gracilis Inferior pubic ramus Medial border of the tibial tuberosity Pectineus Pecten pubis Pectineal line of the femur Adductor longus Superior pubic ramus Linea aspera of the femur Adductor brevis Inferior pubic ramus Deep layer Adductor magnus Adduction and flexion of the hip, flexion and internal rotation of the knee Adduction and external rotation of the hip, assists in stabilising the pelvis Adduction and flexion of the hip, assists in stabilising the pelvis Obturator nerve L2-L3 Femoral nerve and Obturator nerve L2-L3 Obturator nerve L2-L4 Obturator nerve L2-L3 Inferior pubic ramus, ischial tuberosity Medial lip of the linea spine, adductor tubercle of the femur Adduction and extension of the hip, assists in stabilising the pelvis Adduction and external rotation of the hip, assists in stabilising the pelvis Obturator nerve L2-L4 and tibial nerve L4 Obturator externus Obturator membrane Trochanteric fossa of the femur Muscle Muscles of the posterior thigh Biceps femoris Short head Origin Insertion Action Innervation Head of the fibula Long head Lateral lip of the linea aspera Ischial tuberosity, sacrotuberous ligament Knee flexion and external rotation Extension of the hip, flexion and external rotation of the knee Common fibular nerve L5-S2 Tibial nerve L5-S2 Semimembranosus Ischial tuberosity Medial tibial condyle Extension of the hip, flexion and internal rotation of the knee Tibial nerve L5-S2 Semitendinosus Ischial tuberosity and sacrotuberous ligament Pes anserinus medial tibial condyle Muscle Muscles of the anterior lower leg Origin Insertion Action Innervation www.learningphysiotherapy.com Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Obturator nerve L3-L4 Study less. Retain more. Tibialis anterior Tibia, interosseous membrane Dorsiflexion and supination of the ankle Dorsiflexion and supination/ pronation of the ankle, extension of the big toe Dorsiflexion and pronation of the ankle, extension of toes 2-5 Dorsiflexion and eversion of the ankle Deep fibular nerve L4-L5 Extensor hallucis longus Fibula Extensor digitorum longus Fibula and tibia, interosseous membrane Dorsal aponeurosis of the 2nd to 5th toes Fibularis tertius Distal fibula Base of the 5th metatarsal Medial and lateral epicondyles of the femur Fibula and tibia Calcaneal tuberosity at the Achilles tendon Plantarflexion of the ankle, flexion of the knee Plantarflexion of the ankle May prevent compression of posterior leg muscles during knee flexion Tibial nerve S1-S2 Interosseous membrane Navicular tuberosity and cuneiforms 2-4 Tibial nerve L4-L5 Flexor digitorum longus Posterior surface of the tibia Bases of 2nd – 5th distal phalanges Flexor hallucis longus Posterior surface of the fibula Base of 1st distal phalanx Popliteus Lateral femoral condyle Posterior tibial surface Plantarflexion and inversion of the ankle, assists in supporting the arches of the feet Plantarflexion and inversion of the ankle, plantarflexion of MTP and IP joints 2-5 Plantarflexion and inversion of the ankle, plantarflexion of MTP and IP joints 2-5, supports longitudinal arch Flexion and internal rotation of the knee Muscle Intrinsic muscles of the foot Extensor hallucis brevis Origin Insertion Action Innervation Dorsal surface of the calcaneus Dorsal aponeurosis of 2nd – 4th toes Extension of MTP and PIP joints of the 2nd – 4th toes Deep fibular nerve L5-S1 Muscles of the posterior lower leg Triceps surae Gastrocnemius Soleus Plantaris Deep muscles of the posterior compartment Tibialis posterior www.learningphysiotherapy.com Medial cuneiform and first metatarsal Dorsal aponeurosis of the 1st toe Lateral epicondyle of the femur Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Deep fibular nerve L5 Deep fibular nerve L5-S1 Tibial nerve L5-S2 Tibial nerve L4-L5 Study less. Retain more. Extensor digitorum brevis Dorsal surface of the calcaneus Dorsal aponeurosis of 1st toe Extension of MTP joints of the 1st toe Deep fibular nerve L5-S1 Calcaneal tuberosity, plantar aponeurosis Base of 5th metatarsal Lateral plantar nerve S1-S3 Abductor hallucis Medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity Base of the 1st toe Flexor digitorum brevis Calcaneal tuberosity, plantar aponeurosis Sides of middle phalanges for the 2nd – 5th toes Flexion and abduction of the MTP joint of the 5th toe, supports longitudinal arch Flexion and abduction of the MTP joint of the 1st toe, supports longitudinal arch Flexion and abduction of the MTP and PIP joints of the 2nd – 5th toe, supports longitudinal arch 3rd – 5th metatarsal Medial base of proximal phalanx of the 3rd – 5th toes 1st – 4th proximal phalanges Flexion of MTP joints 3-5, extension of IP joints 3-5, adduction of 3-5 toes Flexion of MTP joints 2-4, extension of IP joints 2-4, adduction of 2-4 toes Assists in redirecting the pull of flexor digitorum longus Flexion of MTP joints 2-5, extension of IP joints 2-5, adduction of 2-5 toes Lateral plantar nerve S2-S3 Superficial Layer Abductor digiti minimi Deep intrinsic muscles of the sole of the foot Plantar interossei Dorsal interossei 1st – 5th metatarsals Quadratus plantae Medial border of the calcaneal tuberosity Flexor digitorum longus tendons Flexor digitorum longus tendon Flexor hallucis brevis Lateral cuneiforms, cuboid Base of proximal phalanx of 1st toe Flexion and adduction of MTP joint of big toe Adductor hallucis Bases of 2-5th metatarsals 1st proximal phalanx Flexor digiti minimi brevis Opponens digit minimi Base of 5th metatarsal Long plantar ligament Base of proximal phalanx of 5th toe 5th metatarsal Flexion and adduction of MTP joint of big toe, supports transverse and longitudinal arches Flexion of MTP joint of 5th toe Pulls 5th metatarsal medially Lumbricals www.learningphysiotherapy.com Dorsal aponeurosis of 2nd-5th toes Ó Learning Physiotherapy Pty Ltd. 2021 Medial plantar nerve S1-S2 Lateral plantar nerve S2-S3 Lateral plantar nerve S1-S3 Lateral plantar nerve S2-S3 and Medial plantar nerve S2-S3 Lateral plantar nerve S1-S2 and Medial plantar nerve S1-S2 Lateral plantar nerve S2-S3 Study less. Retain more.