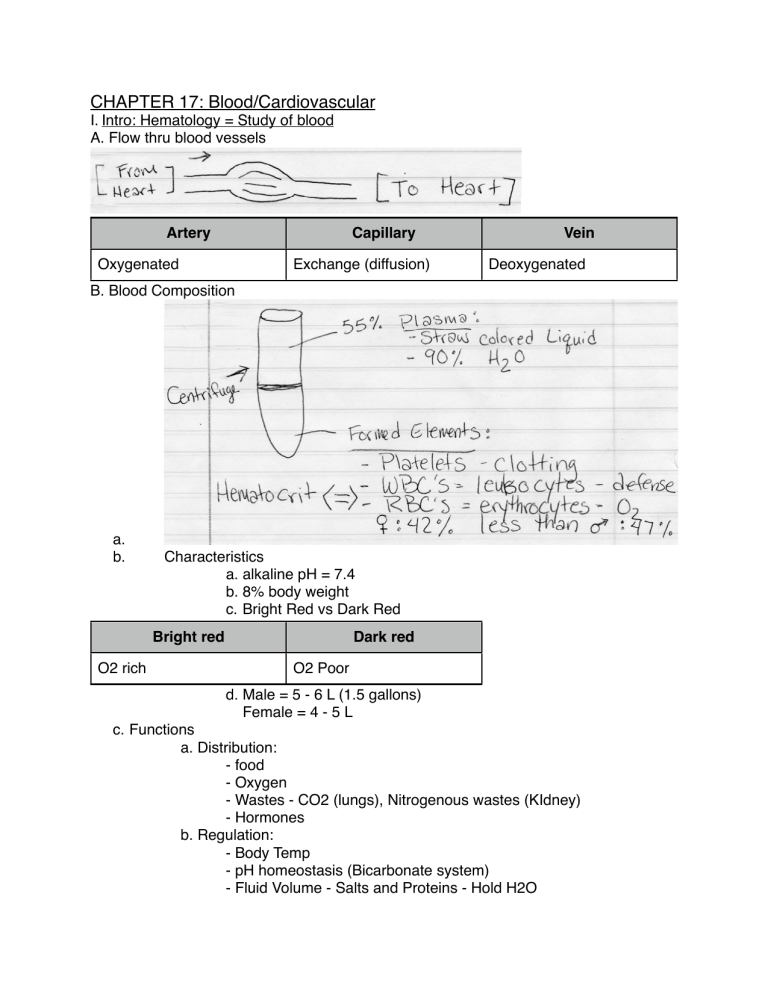
CHAPTER 17: Blood/Cardiovascular I. Intro: Hematology = Study of blood A. Flow thru blood vessels Artery Capillary Oxygenated Exchange (diffusion) Vein Deoxygenated B. Blood Composition a. b. Characteristics a. alkaline pH = 7.4 b. 8% body weight c. Bright Red vs Dark Red Bright red O2 rich Dark red O2 Poor d. Male = 5 - 6 L (1.5 gallons) Female = 4 - 5 L c. Functions a. Distribution: - food - Oxygen - Wastes - CO2 (lungs), Nitrogenous wastes (KIdney) - Hormones b. Regulation: - Body Temp - pH homeostasis (Bicarbonate system) - Fluid Volume - Salts and Proteins - Hold H2O c. Protection: - Antibodies, WBCs, Complement proteins - clotting - prevent excess loss d. Plasma: - 90% H2O - More than 100 dissolved solutes e.g. calcium, wastes (urea) (bilirubin) - Plasma Proteins = maintains osmotic balance (along with Na+) a. Made by liver; not taken up by cells (e.g. Albumin) II. Blood Cells = aka “Formed Elements” - “different” cells 1. most amitotic (marrow made) 2. 2/3 Not true cells 3. Survive only a few days A. Erythrocytes (red blood cells) 1. Most numerous blood cell 2. Anatomy - Biconcave (held by spectrin protein [spectrin help RBC pliability]) - 7.5 micrometers in diameter 3. Hemoglobin - Carries oxygen = made of globin 2 alpha, 2 beta chains bound to ring-like heme group - each holds Fe --> 1 billion O2 molecules 4. Functions: - Hb caries O2 and CO2 (20%) 5. Production - (Hemopoiesis) - made in red bone marrow (e.g. epiphysis of long bone) - erythropoiesis - starts as pleuripotential stem cells - blood needs balance: increase RBCs --> more viscous decrease RBCs --> not enough oxygen [hypoxia] - Depends on Fe, B-vitamins, aminoacids, testosterone (more in males) and EPO (erythropoietin) - EPO is made in kidneys - depends on how much O2 getting to kidney cells 6. Destruction a. lifespan = 100-120 days b. RBCs destroyed in spleen & liver (macrophages) c. Hemoglobin B. Leukocytes (white blood cells) 1. Intro: 4800-10800 WBCs/mm3 - Functions - Defense (viruses, bacteria, tumor cells) - diapedesis = leave capillary bed - granulocytes/agranulocytes - 5 types i. Neutrophils - never Most ii. Lymphocytes - let I iii. Monocytes - monkeys I iv.eosinophils - eat V v. basophils - bananas Least 2. Granulocytes a. Neutrophils (50 - 70% WBCs) - granules take up basic & acidic dye - bacteria slayers; first line of defense - lysosome granules - nuclei: 3-6 lobes (aka polymorpho nuclear leukocytes) - mechanism: respiratory burst - neutrophils produce lots of H2O2 (peroxide) and bleach, defensins (spears), during phagocytosis b. Eosinophils (2 - 4% WBCs) - Nucleus: bilobed - Granules: lysosomes break down parasites (not bacteria) - Lessen allergies by digesting antibody-antigen complexes c. Basophils (.5 - 1.0%) - Largest granules (contain histamines) a. vasodilate b. attract WBCs - Contain heparin - Binds to IgE 3. Agranulocytes a. Lymphocytes (20 - 25%) - large nucleus; makes up most of cell volume - most stored in lymphatic tissues e.g. spleen; lymph nodes T-Cells B-Cells direct attack on enemy plasma cells e.g. cancer cells, viruses antibodies b. Monocyte (3 - 8%) - Largest (18 Micrometers) diameter - phago-cytic - activates lymphocytes - can become wandering * production - red marrow = leukopoiesis - hormonally stimulates by interleukins, CSFs (colony stimulating factors) I I V make & made by T-lymphocytes C. Leukemias 1. Renegade leukocyte from a single clone divides out of control 2. named according to abnormal cell type e.g. lymphocytic leukemia Acute Chronic Quick Advancing Slow Advancing Children/Adolescents Elderly (slowly weakening immune system) D. Infectious Mononucleosis - contagious, viral (epstein-barr) links to leukemia - “foamy” cytoplasm - kissing IV. Clotting A. Platelets - cell fragments of megakaryocytes - granules have clotting factors - no nucleus or organelles - Kept inactive by prostaglandins and NO2 B. Hemostasis: “halting of bleeding” 3 Phases: a. Vascular Spasms: - vasoconstriction - reduces blood loss - due to chemicals releases by platelets + endothelial cells b. Platelet Plug Formation - platelets attach to collagen fibers of wounded vessel - Positive feedback - Thrombin (enzyme) activates platelets when attached: - Platelet granules release: a. seratonin enhances vascular spasms b. adp attracts more platelets - Fibrin threads reinforce c. Coagulation (clotting) = blood made from liquid to gel Intrinsic Pathway Extrinsic Pathway Vessel Endothelium Rupture Tissue Cell Trauma Platelets stick to collagen Tissue factor (TF) - made by dying cells PF3 (made by platelets) Clotting Factors > 200 Prothrombiin activator Prothrombin Thrombin (measu ured time to clot) Fibrin nogen FIbrin (cross-linkages off fibrin polymer = CLOT) C. Hemostatic Disorders a. Thrombus = Clot in an unbroken blood vessel b. Embolus = Floating thrombus c. Embolism = Embolus that blocks (often lungs) * Warfarin - interferes with Vit. K: liver production of procoagulants goes down * Aspirin - 81 mg -----> 50% of decline in heart attacks * Plasmin - natural clot buster * Procoagulants - Vit. K helps liver make clotting factors - broccoli - cabbage - cauliflower * Anticoagulants - Vit E Quinone + O2 - e.g. Grapeseed * TPA = clot busters used in stroke & Heart attack D. Bleeding Disorders a. Liver Malfunctions - liver needed to absorb fat along with vitamin K - Liver malfunction a. more bleeding b. less procoagulants made c. less fat & Vit K absorption b. Hemophilia = genetic Hemophilia A (83%) Factor VIII Hemophilia B Factor IX Sex-linked (X chromosomes) (makes more) Hemophilia C Factor XI Male and Female Prolonged bleeding genetically engineered Facto or VIII c. Abnormal Hemoglobin a. Thalassemias = - faulty/absent globin chain - Hb fragile decrease RBCs [no problem] - greek + Italian b. Sickle Cell Anemia - 1/287 of amino acids malformed in globin chain - beta chains sticky w/ low O2 - RBC jams up in capillaries - recessive - malaria parasite III. Blood Disorders A. Anemia “lacking blood” a. Blood has a low O2 carrying capacity - insufficient RBC levels Hemorrhagic Anemia Cut wound blood loss Hemolytic Anemia Aplastic Anemia RBC ruptures red marrow inhibited e.g. - parsitic attacks - mismatched blood types e.g. Chemotherapy radiation b. Low Hemoglobin Count - e.g. Iron deficiency anemia = RBC level normal but less hemoglobin in them a. nutritional - not enough iron - e.g. Pernicious Anemia = not enough Vitamin B-12 IV. ABO Blood Groups = Based on presence or absence of agglutinogens A or B Blood: A B AB O Agglutinogen A B A&B None Antibodies B A None A&B * Rh factor = Antigen (agg.) on RBC; 85% Rh+; 15% Rh- 2nd pregnancy, placenta ruptures + babys blood gets into mama---> Rh+ made antibodies. Treat: Rhogam V. Diagnostic Blood Tests a. Differential Cell Count a. % WBCs [part of complete blood count] b. Complete Blood count - totals of formed elements - Hematocrit - Clotting factor tests c. SMAC = Blood Chemistry Profile e.g. Ca++ -------> Cancer Bilirubin----> Liver Urea -------> Kidney d. Prothrombin Time = Rate of clotting