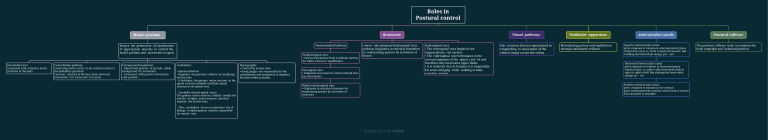
Roles in Postural control Brainstem Motor systems Ventromedial Pathway Ensure the generation of coordination of appropriate muscles to control the body’s position and movement in space Pyramidal tracts: concerned with voluntary motor activities of the body. Corticobulbar pathway: connecting motor cortex in the cerebral cortex to the medullary pyramids Function: muscles of the face, head and neck. Innervates: v,vii, motor part of x,xi,xii. Extrapyramidal pathway: - Adjust body posture to provide stable background for movement. - Concerned with grosser movements and posture. Vestibulospinal tract: ▪ Carries information from vestibular nucleus for reflex control of equilibrium . Cerebellum: ▪ Spinocerebellum : - Regulates the postural reflexes by modifying muscle tone. - It facilitates the gamma motor neurons in the spinal cord via cerebello-vestibulo-spinal neurons in the spinal cord. - Cerebello-reticulo-spinal tracts : The gamma motor neurons reflexly modify the activity of alpha motor neurons and thus regulate the muscle tone. - Thus, cerebellum forms an important site of linkage of alpha-gamma systems responsible for muscle tone Basal ganglia: ▪ Control the muscle tone. ▪ Basal ganglia are responsible for the coordination and integration of impulses for these reflex activities. Tectospinal tract: ▪ Originates in tectum for control of head and eye movements . Medial reticulospinal tract: ▪ Originates in reticular formation for maintaining posture by activation of extensors. Lateral reticulospinal Rubrospinal tract: pathway Originates in reticular formation for maintaining posture by activation of flexors Visual pathway: Rubrospinal tract: ▪ The rubrospinal tract begins in the magnocellular red nucleus. ▪ The rubrospinal tract terminates in the cervical segments of the spinal cord 24 and therefore only innervates upper limbs. ▪ It is believed that in humans it is responsible for arms swinging while walking or baby crawling motion. Has neurons that are specialized in responding to movement of the retinal image across the retina. Vestibular apparatus: Maintaining posture and equilibrium through statokinetic reflexes. semi-circular canals Superior Semicircular Canal: gives response to rotation in anteroposterior plane (transverse axis), i.e. front to back movements like nodding the head while saying ‘yes – yes’. Horizontal Semicircular Canal: gives response to rotation in horizontal plane (vertical axis), i.e. side to side movements (left to right or right to left) like shaking the head while saying ‘no – no’. Posterior Semicircular Canal: gives response to rotation in the vertical plane (anteroposterior axis) by which head is rotated from shoulder to shoulder. Postural reflexes: The postural reflexes help to maintain the body inupright and balanced position.